滇西澜沧江构造带中段新生代多期构造变形特征及时代约束*
吉风宝 戚学祥** 常裕林 张超 赵宇浩 韦诚
JI FengBao1,QI XueXiang1**,CHANG YuLin2,ZHANG Chao1,ZHAO YuHao3 and WEI Cheng1
1. 大陆构造与动力学国家重点实验室,中国地质科学院地质研究所,北京 100037
2. 中国冶金地质总局山东正元地质勘察院,济南 250101
3. 中国地质调查局南京地质调查中心,南京 210016
1. State Key Laboratory of Continental Tectonics and Dynamics,Institute of Geology,Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences,Beijing 100037,China
2. Shandong Zhengyuan Geological Exploration Institute,China Metallurgical Geology Bureau,Jinan 250101,China
3. Nanjing Institutes of Geology and Mineral Resources,China Geological Survey,Nanjing 210016,China
2015-05-05 收稿,2015-09-26 改回.
1 引言
青藏高原东南缘三江构造带是冈瓦纳古陆东北缘块体相继于中晚泥盆世、二叠世和三叠世裂离、向北运移,块体之间的古特提斯洋(澜沧江洋、哀牢山-金沙江洋)、中特提斯洋(班公湖-怒江洋)和新特提斯洋(雅鲁藏布-密支那洋)相继俯冲(Metcalfe,2011,2013),印支(兰坪-思茅)地块、Sibumasu(保山-羌塘)地块和腾冲-缅西地块分别于印支期和燕山晚期相互拼合(Şengör,1984;Dewey et al.,1988;Şengör et al.,1993;从柏林等,1993;莫宣学等,1993;钟大赉,1998;Yin and Harrison,2000;李兴振等,2002;戚学祥等,2010a,b,2012)形成的由多个地块(如腾冲-缅西、Sibumasu/保山-羌塘和印支)以及块体之间残余缝合带(如高黎贡缝合带、澜沧江缝合带和哀牢山-金沙江缝合带)组成的复杂构造带(Mitchell,1993;Mitchell et al.,2004;Morley,2004;Metcalfe,2006;Acharyya,2007;Heppe et al.,2007;杨经绥等,2012)。在喜山运动期间,印度板块向北俯冲碰撞导致青藏高原东南缘块体发生大规模旋转和逃逸(Tapponnier and Molnar,1976;Tapponnier et al.,1982,1990),块体沿古缝合带发生大规模走滑(丁林,1991;钟大赉等,1991;Leloup et al.,1993,1995;钟大赉,1998;刘俊来等,2006,2007,2011;罗照华等,2006;Morkey,2007;Searle et al.,2007;王二七等,2006;Cao et al.,2010)形成由总体走向近南北,向北收敛、向南撒开的三条大型构造带和三个地块组成的构造格局(图1a)。前人对东部哀牢山-金沙江构造带和西部高黎贡构造带中的大规模类型走滑剪切作用进行了广泛的研究,认为前者为左行大型韧性走滑剪切带,主要形成于35 ~21Ma(Schärer et al. ,1990,1994;Harrison et al. ,1992,1996;Leloup et al. ,1993,1995,2001;Zhang and Schärer,1999;Gilley et al. ,2003;Searle et al. ,2010;Li et al. ,2014),后者为大型右行韧性走滑剪切带,形成于38 ~10Ma(钟大赉等,1991;季建清等,2000;Lee et al.,2003;Wang et al.,2006;Lin et al. ,2009;李再会等,2012;Zhang et al. ,2012b;王丹丹等,2013)。但对分隔保山-羌塘地块和兰坪-思茅地块的边界性澜沧江构造带的研究相对薄弱,且主要集中于北段的碧罗雪山至崇山一带,认为碧罗雪山以北以右行走滑为主,碧罗雪山-崇山段以左行走滑为特征,其走滑时限为37 ~21Ma (陈新跃等,2006;Wang et al. ,2006;Akciz et al.,2008;张波,2008;张波等,2009,2011;Zhang et al.,2010,2012a;唐渊等,2013),澜沧江构造带中段(崇山-临沧岩体段)是澜沧江构造带转折段,兰坪-思茅盆地在此段紧缩呈“蜂腰”状,其构造变形特征、形成时限及其与块体的挤出关系仍未查明。近年来,笔者对中段韧性变形特征进行了野外调研,发现该段同时存在典型的左行和右行走滑剪切标志及两组拉伸线理交切的现象。为此,在野外调研的基础上,通过显微构造学、岩石学和同位素年代学等方法,对该段韧性变形特征,左行和右行走滑作用的时空关系及其形成时代进行研究,并结合前人研究成果,揭示澜沧江构造带韧性变形的形成机制及其与块体旋转挤出的关系,为进一步探讨三江构造带的形成演化提供依据。
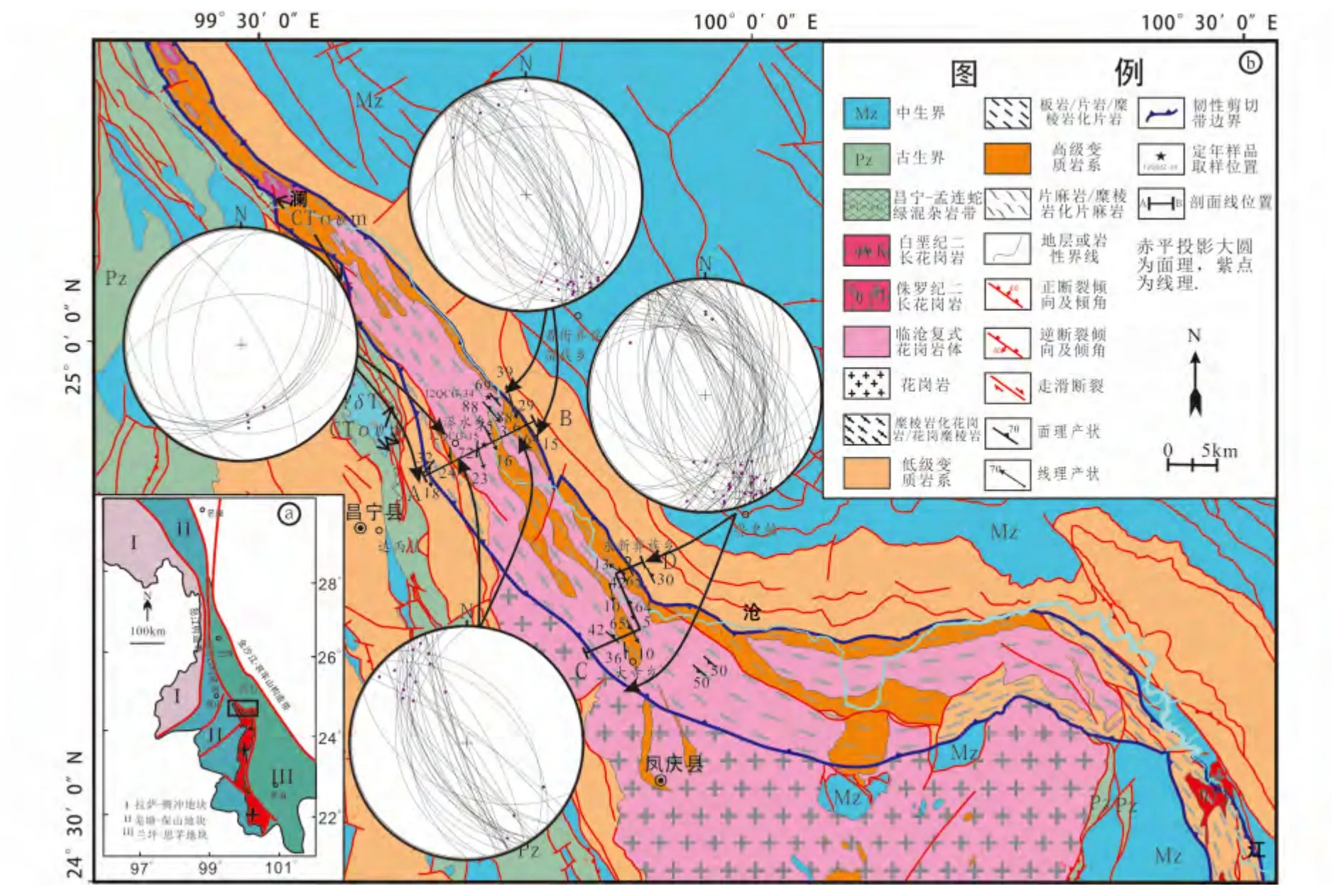
图1 澜沧江构造带中段地质简图(a,据Wang and Burchfiel,1997 修编;b,云南省地质调查院,2011①云南省地质调查院.2011. 1∶250000 凤庆幅地质图修编)Fig.1 Simplified geological map of the middle segment of the Lancang tectonic zone (a,modified after Wang and Burchfiel,1997)
2 区域地质概况
澜沧江构造带位于青藏高原东南缘,北与高黎贡和金沙江构造带平行展布,沿碧罗雪山和崇山山脉向南延入临沧岩体,沿临沧岩体东侧直至进入泰国境内,长约1300km(图1a)。宽3 ~20km,东部以澜沧江逆冲断层带与兰坪-思茅地块为界,西部以昌宁-凤庆逆冲断裂带分隔于保山地块。澜沧江构造带云南境内总体可分为三部分:北段为碧罗雪山以北向南延伸至崇山山脉,南段自以临沧岩体经景洪向南进入泰国,南北两段之间崇山南部至临沧岩体北部构成构造带的中段,即构造带从近南北走向转向南东东走向后又转向近南北向的过渡地段(图1)。北段长约350km,宽3 ~20km,走向近南北,由西侧角闪岩相条带状片麻岩、糜棱岩化片麻岩、花岗质糜棱岩和东侧绿片岩相云母片岩、千枚岩和板岩组成。角闪岩相变质岩糜棱岩化变形明显,糜棱面理和拉伸线理发育,面理总体走向近南北向,倾向、倾角变化较大(倾角一般>60°),两侧倾向相反,呈正花状,线理向南倾伏,倾角较小(<30°,一般<20°)。指向构造发育,碧罗雪山以北以右旋为主,以南以左旋为主(Akciz et al.,2008;张波,2008;张波等,2009,2011;Zhang et al.,2010,2012;唐渊等,2013)。南段由西部的高压蓝片岩带、中部临沧岩体和东部的韧性走滑剪切带构成。其中,东部韧性走滑剪切带宽度变化较大,不同地段糜棱岩化程度不同,多由糜棱岩或初糜棱岩组成。中段长约100km,宽度3 ~20km,整体走向NW-SE,于昌宁-凤庆-云县一带转为近E-W 走向(图1b),主体由高绿片岩相-角闪岩相片麻岩、混合岩和石榴云母片岩组成。带内岩石糜棱岩化明显,糜棱面理和拉伸线理发育,产状变化较大,总体倾向南西,指向构造揭示其存在典型的右行和左行两种走滑运动性质。澜沧江构造带东侧的兰坪-思茅地块内出露的地层为侏罗系-白垩系陆相沉积(红层),内部褶皱、逆冲推覆构造发育。构造带西侧保山-羌塘地块内出露的地层为古生界被动陆缘沉积地层和零星分布的中生界沉积地层,大型北东向左行走滑断裂带南汀河断裂带和畹町断裂带将地块内部分为三部分(图1a),南汀河断裂带北起云县茂兰、向南汇入实皆断裂,未切穿澜沧江构造带(朱玉新等,1994;王晋南等,2006);畹町断裂带向北至湾甸汇入柯街断裂,向南汇入实皆断裂(常祖峰等,2012;Morley,2007)。
3 测试方法
3.1 EBSD 组构
EBSD 组构分析由中国地质科学院地质研究所大陆构造与动力学国家重点实验室完成。定向样品沿垂直面理并平行于线理方向切制光薄片,薄片抛光、喷碳后进行EBSD 测量,测试仪器为日本电子公司(JEOL)制造的JSM-56101V 型扫描电镜和丹麦HKL 公司制造的CHANNEL5 型号EBSD 仪器。加速电压为20kV,工作距离为20mm,将衍射点数进行等面积下半球赤平投影,得到反映晶体CPO 的各主要晶轴空间分布的极密图。组构图解的坐标轴设置为X 轴平行于拉伸线理的方向,XY 为面理方向,Z 轴为垂直面理的方向,晶格优选方位极密图统计由Channel 5 软件完成,详细实验流程参考文献(许志琴等,2009)。
3.2 40Ar/39Ar 年代学
黑云母40Ar/39Ar 定年由中国地质科学院地质研究所同位素热年代学实验室完成。样品破碎后经重液浮选和磁选,选出黑云母初级样品,然后在双目镜下经手工仔细挑选,样品纯度在99%以上。选纯的黑云母单矿物(纯度>99%)用超声波清洗。清洗后的样品被封进石英瓶中送核反应堆中接受中子照射。照射工作是在中国原子能科学研究院的“游泳池堆”中进行的,使用B4 孔道,中子流密度约为2.65 ×1013n·cm-2S-1。照射总时间为1444min,积分中子通量为2.30 ×1018n·cm-2;同期接受中子照射的还有用做监控样的标准样:ZBH-25 黑云母标样,其标准年龄为132.7 ±1.2Ma,K 含量为7.6%。
样品的阶段升温加热使用石墨炉,每一个阶段加热30min,净化30min。质谱分析是在多接收稀有气体质谱仪Helix MC 上进行的,每个峰值均采集20 组数据。所有的数据在回归到时间零点值后再进行质量歧视校正、大气氩校正、空白校正和干扰元素同位素校正。中子照射过程中所产生的干扰同位素校正系数通过分析照射过的K2SO4和CaF2来获得,其值为:(36Ar/37Aro)Ca=0.0002389,(40Ar/39Ar)K=0.004782,(39Ar/37Aro)Ca=0.000806。37Ar 经过放射性衰变校正;40K 衰变常数λ =5.543 ×10-10y-1(Steiger and Jager,1977);用ISOPLOT 程序计算坪年龄及正、反等时线(Ludwig,2001)。坪年龄误差以2σ 给出。详细实验流程参考文献(陈文等,2006;张彦等,2006)。

图2 澜沧江构造带中段昌宁-耈街剖面构造剖面图Fig.2 Changning-Goujie structural section in the middle segment of the Lancang tectonic zone
4 构造变形特征
4.1 韧性剪切变形
韧性剪切带内的岩石都发生不同程度的韧性变形,其中的石英具有明显的波状消光、亚颗粒和动态重结晶现象,长石多发育机械双晶、核幔结构和应力出溶作用(应力蠕英结构、应力条纹结构)、不对称旋转碎斑、多米诺构造,以及长英质条带定向排列构成糜棱面理和拉伸线理,局部形成S-C 组构等。构造带内的岩石都发生不同程度的糜棱岩化,形成超糜棱岩、糜棱岩和初糜棱岩,其中,糜棱岩构成剪切带的主体,超糜棱岩主要分布于剪切带西南部,初糜棱岩不均匀分布。矿物组合主要有:石榴石+黑云母+斜长石+石英、角闪石+黑云母+长石、黑云母/白云母+斜长石+钾长石+石英。糜棱面理产状变化较大,但整体上具有西部倾向南东东,倾角30°左右,中部走向近南北,近直立,东部则变为倾向西,倾角25°左右的变化趋势,且在局部存在“背形”或“向形”式的变化(图2、图3)。拉伸线理相对稳定,向南南东倾伏,倾伏角10° ~25°。局部同一面理上发育两组斜交的线理(120° ~157°∠6° ~15°和308° ~337°∠29° ~39°),且倾伏角较大的线理被近水平线理切割(图4a),反映两期走滑剪切变形特征。
韧性剪切带内指向构造发育。露头尺度上和显微尺度下,在平行拉伸线理和垂直面理的XZ 面上,长英质条带被拉断旋转形成的不对称旋转透镜体和眼球状旋转碎斑、长石及石英团块构成的“δ”或“σ”旋转碎斑(图4)、云母鱼、石英被拉长斜列与云母等片状矿物一起构成S-C 组构、以及长石沿解理面发生滑动形成的“多米诺”构造(图5)显示出明显的走滑性质。其中,这些构造指向标志出构造带中-西部以左行走滑为主,东部以右行走滑为主的特点(图4)。
4.2 脆韧性变形
该阶段构造变形继承了早期糜棱面理,局部存在糜棱面理被拉断、错开,并被同构造石英充填形成的翼状构造(Passchier,2001;Mukherjee,2014)(图4f),长英质脉体被错断而形成的“书斜”构造(图4e)和S-C 组构,以及标志右行剪切作用的云母鱼和钾长石被后期左行剪切作用错开(图5e)等脆韧性变形特征,并在整个剪切带中都展示出左行剪切的运动机制,反映其形成于韧性剪切带隆升到中上部构造层次后发生的构造变形。
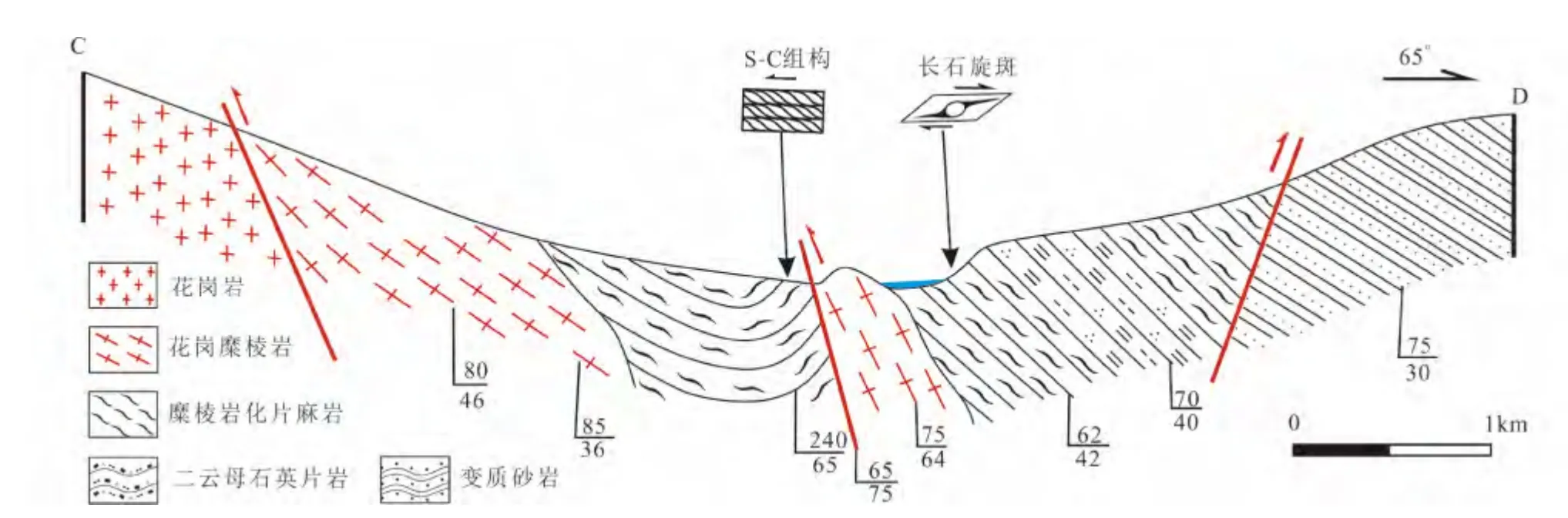
图3 澜沧江构造带中段凤庆-鲁史剖面构造剖面图Fig.3 Fengqing-Lushi structural section in the middle segment of the Lancang tectonic zone
总体来看,澜沧江构造带中段韧性剪切带整体上具有正花状构造特征,即糜棱面理在西部呈低角度倾向北东东,东部低角度倾向南西西,中部面理近直立。韧性剪切带早期以右行韧性走滑剪切变形,后期以左行脆韧性变形走滑剪切变形为特征。
5 石英组构特征
石英晶格优选方位是查明韧性剪切变形走滑方向和变形条件的重要方法。为此,笔者分别对剪切带北部的昌宁-耈街剖面和南部的凤庆-鲁史剖面中的糜棱岩样品进行EBSD 石英C 轴组构分析。其中12QMZ-1-1、13QCG-13和13QCG-25 分别采自昌宁-耈街剖面西翼、中部和东翼的长英质糜棱岩;样品12QFL-8、12QFL-36 和12QFL-53分别采自凤庆-鲁史剖面西南翼的花岗质糜棱岩、中部的长英质糜棱岩和东北翼的长英质糜棱岩。测试结果如图6 所示。
从图6 可以看出,所有样品石英C 轴晶格优选方位极密均存在平行于Y 轴和分布于Z 轴附近的2 个极密,前者为柱面<a >滑移系,反映形成于中温(450 ~600℃)的变形环境(Schmid and Casey,1986),后者为叠加于前期的中低温菱面<a >滑移系和低温底面<a >滑移系的单斜单环带组构类型,变形温度约300 ~550℃(Takeshita,1996)。昌宁-耈街剖面中、东部和凤庆-鲁史剖面样品石英C 轴晶格优选方位图中温变形显示右行剪切指向,后期中低温变形显示左行特征,昌宁-耈街剖面西翼则显示两期左行特征,与剖面整体呈向形构造相符。样品石英C 轴晶格优选方位图结果与野外露头和镜下观察剪切标志相符。
6 年代学研究
6.1 样品描述
黑云母40Ar-39Ar 定年样品采自于的昌宁-耈街剖面中黑云母片岩(12QMZ-15,24°54'12″N,99°43'38″E)和花岗糜棱岩(12QMZ-34,24°56'53″N,99°43'58″E)(图1b)。12QMZ-15黑云母片岩主要矿物组成为黑云母(45%),白云母(5%)、石英(40%)、长石(10%)。其中黑云母呈他形片状定向分布,未发生任何蚀变,石英呈条带状,间隔分布于云母富集带间,定向排列的黑云母、多晶条带状石英构成面理,含少量保留斑晶形态的细粒化长石,其边部零星见蠕英结构,反映岩石经历过韧性变形和动态重结晶作用。12QMZ-34 花岗质糜棱岩主要矿物组成为长石(55%)、石英(35%)、黑云母(9%),副矿物主要有锆石、磷灰石、榍石及磁铁矿等不透明矿物(1%),长石残斑粒度变化较大,约1 ×3mm ~3 ×5mm,长石机械双晶、细粒化作用显著,局部发育蠕英结构。云母呈残缕状,未发生任何蚀变,与细粒化的长石、动态重结晶石英颗粒组成基质。
6.2 定年结果
2 个样品40Ar-39Ar 年龄分析的数据见表1,坪年龄和等时线年龄见图7。12QMZ-15 样品中黑云母840 ~1060℃的7个加热步给出了近一致的表观年龄,对应的坪年龄为17.8 ±0.2Ma(MSWD=0.83),析出39Ar 量占总量的66.5%;等时线年龄为17.7 ±0.3Ma(MSWD=1.4)。12QMZ-34 样品中黑云母840 ~1170℃的10 个加热步给出了近一致的表观年龄,对应的坪年龄15.0 ±0.2Ma(MSWD =0.59),析出39Ar 量占总量的85.3%;等时线年龄为14.7 ±0.4Ma(MSWD =1.04),两样品初始40Ar/36Ar 值分别为296.7 ±5.5 和300.4 ±7.8,与现今大气氩的标准值(295.5 ±5)误差范围内一致,反映样品受污染的程度较小,且等时线年龄与坪年龄在误差范围内一致,年龄真实可信。
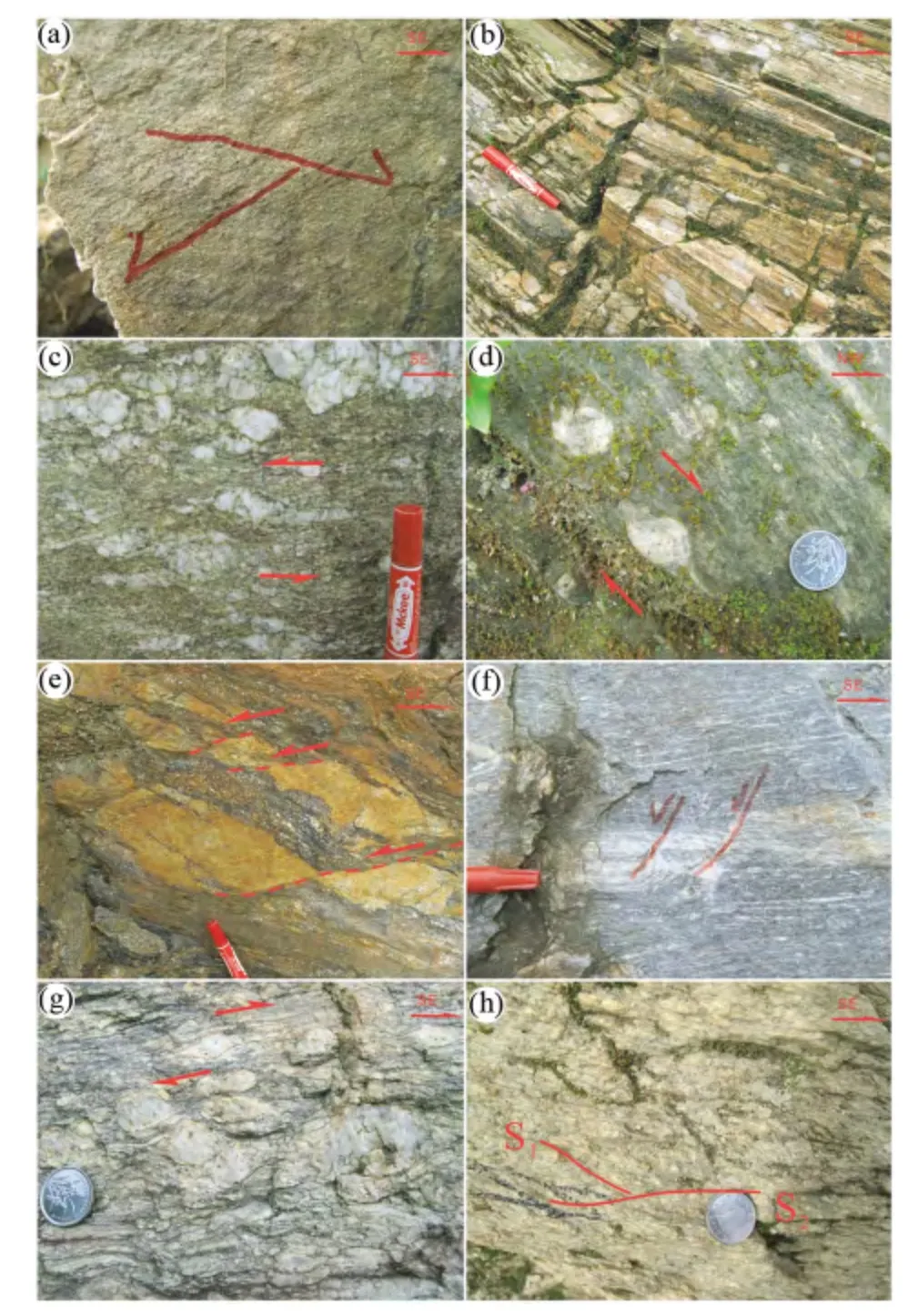
图4 澜沧江构造带中段韧性变形特征(I)昌宁-耈街剖面:(a)剪切带东翼花岗质糜棱岩面理面上发育的两期线理;(b)剪切带西翼超糜棱岩及糜棱线理;(c)剪切带西翼花岗质糜棱岩发育σ 型旋斑,指示左行(XZ 面);(d)剪切带东翼花岗质糜棱岩发育σ 型旋斑,σ 型旋斑指示右行(XZ面);(e)剪切带西翼云母片岩中的浅色花岗岩脉被剪切错开,指示后期脆韧性左行剪切(XZ 面);(f)剪切带东翼长英质糜棱岩发育的翼状构造指示左行脆韧性变形(XZ 面). (Ⅱ)凤庆-鲁史剖面:(g)剪切带东翼花岗质糜棱岩发育σ 型旋斑,σ 型旋斑指示右行(XZ 面);(h)剪切带东翼花岗质糜棱岩发育两期面理(XZ 面)Fig.4 Ductile deformation characterization for the middle segment of the Lancang tectonic zone(I) Changning-Goujie section: (a) two generation mineral stretching lineations on the foliation in granitic mylonite,the east side of the shear zone;(b)ultramylonite in the west side of the shear zone; (c) σ-type porphyroblast in granitic mylonite,indicating sinistral shearing (XZ),west side of the shear zone;(d)σ-type porphyroblast in granitic mylonite,indicating dextral shearing(XZ),east side of the shear zone;(e)dislocation structure in mica schist,indicating brittle-ductile sinistral shearing in later stage(XZ),west side of the shear zone;(f)flanking structures in felsic mylonite,indicating brittle-ductile sinistral shearing(XZ),east side of the shear zone. (Ⅱ)Fengqing-Lushi section:(g)σ-type porphyroblast in granitic mylonite, indicating dextral shearing(XZ),east side of the shear zone;(h)two generation foliations in granitic mylonite (XZ),east side of the shear zone
7 讨论
7.1 走滑作用时代
近年来,前人对澜沧江构造带北段(即碧罗雪山-崇山一带)韧性剪切变形特征及其形成时代进行了研究。通过对韧性剪切带中糜棱岩、同构造花岗岩、变形岩脉及未变形岩脉等进行独居石/锆石U-Pb 和黑云母/白云母40Ar-39Ar 同位素年代学测试(Akciz et al.,2008;Zhang et al.,2010,2012a;唐渊等,2013),结果表明同构造花岗岩中独居石/锆石、变形花岗岩脉中锆石变质边U-Pb 年龄为37 ~21Ma,糜棱岩、同构造花岗岩、变形岩脉中黑云母/白云母40Ar-39Ar 分别为13 ~19Ma、14 ~20Ma,说明韧性剪切作用形成于37 ~21Ma。黑云母和白云母封闭温度(350℃和400℃)的特点说明该年龄反映深变质变形带隆升的时代。前人对构造带中段糜棱岩中的黑云母进行了40Ar-39Ar 同位素测试,获得27 ~28Ma(陈新跃等,2006;Wang et al.,2006)和17Ma(李述靖和单业华,1995)两组同位素数据。野外和镜下观察表明构造带中段存在早期韧性和后期左行脆韧性两个阶段的变形,前者形成于中高温条件(450 ~600℃),后者形成于中低温(350 ~550℃)条件,本文获得的黑云母40Ar-39Ar (17 ~15Ma)与前人获得两组年龄数据中的17Ma 年龄数据一致,是对后期左行脆韧性变形期时代上限、韧性剪切变形时代下限的限定,而27 ~28Ma40Ar-39Ar 同位素年龄位于北段与韧性剪切变形有关花岗岩锆石U-Pb 年龄区间,代表韧性剪切变形形成和隆升时代。

图7 澜沧江构造带中段韧性剪切带内黑云母40Ar/39Ar 坪年龄(a、c)和等时线年龄(b、d)Fig.7 40Ar/39Ar plateau age spectra (a,c)and isochron ages (b,d)of biotite from shear zone in middle segment of the Lancang tectonic zone
7.2 构造演化
青藏高原东南缘三江构造域是经历多期次构造运动改造形成的块体拼合、挤出和大规模走滑作用构造变形域,尤其是新生代印度板块向北俯冲碰撞导致青藏高原东南缘块体——印支地块和Sibumasu 地块发生大规模旋转和逃逸(Tapponnier and Molnar,1976;Tapponnier et al.,1982,1990),块体沿古缝合带发生大规模走滑作用(丁林,1991;钟大赉等,1991;钟大赉,1998;Leloup et al.,1993,1995;刘俊来等,2006,2007,2011;罗照华等,2006;Morley,2007;Searle et al.,2007;王二七等,2006;Cao et al.,2010),形成东部以哀牢山-金沙江大规模左行走滑剪切带、西部以高黎贡右行韧性剪切带和中部澜沧江韧性剪切带为界的构造格局(图1a)。澜沧江韧性走滑剪切带的形成时代与前二者一致,反映其形成与兰坪-思茅地块和保山地块之间的相对运动有关。即在挤出过程中,兰坪-思茅地块向南挤出速度快于保山地块时,澜沧江韧性剪切带发生右行走滑剪切作用,形成一系列反映右行走滑剪切的指向构造,反之则形成左行走滑剪切变形。澜沧江构造带中段中部面理糜棱产状近直立,东、西两侧糜棱面理产状和构造指向都截然相反,展示出典型的“花”状构造,以及糜棱面理中保留有早期倾伏角较大的拉伸线理,揭示中下地壳形成的韧性剪切带在斜向挤出隆升过程中,韧性变形岩石以中部近直立糜棱面理糜棱岩为界,分别向东、西两侧斜向逆冲形成的,剪切带两侧边缘部位在中部物质向外挤出、并向东、西两侧逆冲过程中致使糜棱面理(S1)发生弯曲变形,形成两侧分别为倾向相反的两条逆冲断层带控制的的正花状构造的雏形(图8a,b)。在斜向挤出作用下韧性剪切带隆升到上部构造层次后,保山地块内北东走向的畹町和南汀河两条构造带发生左行走滑作用(Erogˇlu et al.,2013),致使南汀河构造带南部的物质(包括临沧岩体)向北东挤压,形成澜沧江构造带中段向北东弯曲的弧形,南段(临沧岩体)直接逆冲于兰坪-思茅盆地之上的构造特征(杨振德,1996;Wang and Burchfiel,1997;段建中,1999;段建中和谭筱红,2000),在此过程中,韧性剪切带东部物质相对向北运移,在韧性剪切带内叠加左行脆韧性变形构造(图8c,d)。
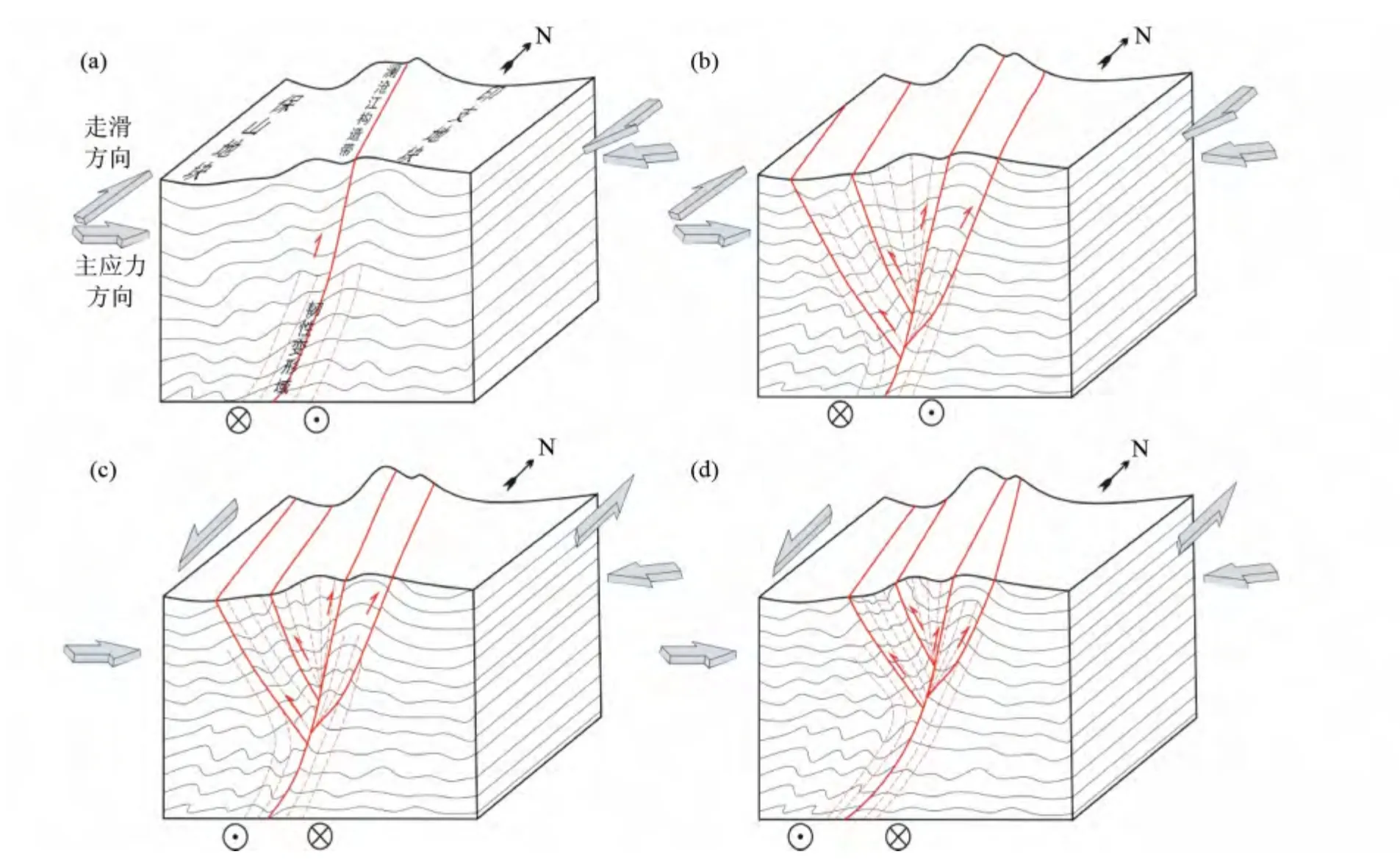
图8 澜沧江构造带中段构造变形过程示意图Fig.8 Structural deformation process evolution in the middle segment of the Lancang tectonic zone
8 结论
(1)澜沧江构造带中段经历了两阶段变形事件:早期南西向北东斜冲右行韧性变形过程形成宏观韧性变形标志东部糜棱面理低角度倾向西、西部低角度倾向东、中部近直立,两侧分别逆冲于未发生变形变质的中生代沉积岩之上的花状构造;后期构造带整体经历近水平左行脆韧性剪切变形作用。
(2)黑云母40Ar-39Ar 定年结果及前人同位素年代学数据表明澜沧江构造带中段早期韧性走滑剪切作用变形作用不晚于28Ma,止于17 ~15Ma,脆韧性变形起始于17 ~15Ma。
致谢 EBSD 测试工作由陈方远副研究员完成,40Ar-39Ar同位素测年在中国地质科学院地质研究所国土资源部同位素地质重点实验室完成,成文过程中李宝龙博士给予了较大帮助,在此一并表示感谢!
Acharyya SK. 2007. Collisional emplacement history of the Naga-Andaman ophiolites and the position of the eastern Indian suture.Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,29(2):229 -242
Akciz S,Burchfiel BC,Crowley JL,Yin JJ and Chen LZ. 2008.Geometry,kinematics,and regional significance of the Chong Shan shear zone, Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis, Yunnan, China.Geosphere,4(1):292 -314
Cao SY,Liu JL and Leiss B. 2010. Orientation - related deformation mechanisms of naturally deformed amphibole in amphibolite mylonites from the Diancang Shan,SW Yunnan,China. Journal of Structural Geology,32(5):606 -622
Chang ZF,An XW and Zhang YF. 2012. Study on Late-Quaternary activity and displacement of drainage systems along the Wanding fault. Seismology and Geology,34(2):228 -239 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chen W,Zhang Y,Zhang YQ,Jin GS and Wang QL. 2006. Late Cenozoic episodic uplifting in southeastern part of the Tibetan Plateau:Evidence from Ar-Ar thermochronology. Acta Petrologica Sinica,22(4):867 -872 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chen XY,Wang YJ,Fan WM and Peng TP. 2006. Microstructural characteristics of Chongshan shear zones in Yunnan Province and geochronological constraints. Geotectonica et Metallogenia,30(1):41 -51 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Cong BL,Wu GY,Zhang Q,Zhang RY,Zhai MG,Zhao DS and Zhang WH. 1993. Petrotectonic evolution of Paleo-Tethys in western Yunnan,China. Science in China (Series B),37(8):1016-1024
Ding L. 1991. The characteristics of deformation and tectonic implications in south Gaoligong western Yunnan,China. Master Degree Thesis.Beijing:Institute of Geology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,1 -92(in Chinese)
Duan JZ. 1999. Characteristics of the cenozoic stirke slip (transform)convergent structure in Sanjiang area of western Yunnan Province.Yunnan Geology,18(2):99 -111 (in Chinese)
Duan JZ and Tan XH. 2000. The nature and feature of Cenozoic main strike-slip fauit in the Three-River area of West Yunnan. Yunnan Geology,19(1):8 -23 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Erogˇlu S,Siebel W,Danišík M,Pfänder JA and Chen FK. 2013. Multisystem geochronological and isotopic constraints on age and evolution of the Gaoligongshan metamorphic belt and shear zone system in western Yunnan,China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,73(8):218 -239
Gilley LD,Harrison TM,Leloup PH,Ryerson FJ,Lovera OM and Wang JH. 2003. Direct dating of left-lateral deformation along the Red River shear zone,China and Vietnam. Journal of Geophysical Research-Solid Earth,108(B2):183 -185
Harrison TM,Chen WJ,Leloup PH,Ryerson FJ and Tapponnier P.1992. An early Miocene transition in deformation regime within the Red River fault zone,Yunnan,and its significance for Indo-Asian tectonics. Journal of Geophysical Research,97(B5):7159 -7182
Harrison TM,Leloup PH,Ryerson FJ,Tapponnier P,Lacassin R and Chen WJ. 1996. Diachronous initiation of transtension along the Ailao Shan-Red River Shear zone,Yunnan and Vietnam. In:Yin A and Harrison TM (eds. ). The Tectonic Evolution of Asia. New York:Cambridge University Press,208 -225
Heppe K,Helmcke D and Wemmer K. 2007. The Lancang River Zone of southwestern Yunnan,China:A questionable location for the active continental margin of Paleotethys. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,30(5 -6):706 -720
Ji JQ,Zhong DL and Zhang LS. 2000. Kinematics and dating of Cenozoic strike-slip faults in the Tengchong area,West Yunnan:Implications for the block movement in the southeastern Tibet Plateau. Chinese Journal of Geology,35(3):336 -349 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Lee HY,Chung SL,Wang JR,Wen DJ,Lo CH,Yang TF,Zhang YQ,Xie YW,Lee TY,Wu GY and Ji JQ. 2003. Miocene Jiali faulting and its implications for Tibetan tectonic evolution. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,205(3 -4):185 -194
Leloup PH,Harrison TM,Ryerson FJ,Chen WJ,Li Q,Tapponnier P and Lacassin R. 1993. Structural,petrological and thermal evolution of a Tertiary ductile strike-slip shear zone,Diancang Shan,Yunnan.Journal of Geophysical Research,98(B4):6715 -6743
Leloup PH,Lacassin R,Tapponnier P,Schärer U,Zhong DL,Liu XH,Zhang LS,Ji SC and Trinh PT. 1995. The Ailao Shan-Red River shear zone (Yunnan,China),Tertiary transform boundary of Indochina. Tectonophysics,251(1 -4):3 -10,13 -84
Leloup PH,Arnaud N,Lacassin R,Kienast JR. Harrison TM,Phan Trong TT,Replumaz A and Tapponnier P. 2001. New constraints on the structure,thermochronology and timing of the Ailao Shan-Red River shear zone. Journal of Geophysical Research,106(B4):6683-6732
Li BL,Ji JQ,Wang DD,Gong JF and Ma ZJ. 2014. Determination of Eocene-Oligocene (30 ~40Ma)deformational time by zircon U-Pb SHRIMP dating from leucocratic rocks in the Ailao Shan-Red River shear zone,Southeast Tibet,China. International Geology Review,56(1):74 -87
Li SJ and Shan YH. 1995. Arcuate nappe structure on the northern margin of the Wuliangshan Mountains in western Yunnan. Acta Geologica Sinica,69(4):296 - 305 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li XZ,Jiang XS,Sun ZM,Shen GF and Du DX. 2002. The Collisional Orogenic Processes of the Nujiang-Lancangjiang-Jinshajiang Area,Southwestern China. Beijing:Geological Publishing House,1 -213(in Chinese)
Li ZH,Wang LQ,Lin SL,Cong F,Xie T and Zou GF. 2012. LA-ICPMS zircon U-Pb age of granitic mylonite in the Gaoligong shear zone of western Yunnan Province and its tectonic significance. Geological Bulletin of China,31(8):1287 -1295 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Lin TH,Lo CH,Chung SL,Hsu FJ,Yeh MW,Lee TY,Ji JQ,Wang YZ and Liu DY. 2009.40Ar/39Ar dating of the Jiali and Gaoligong shear zones:Implications for crustal deformation around the Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,34(5):674-685
Liu JL,Song ZJ,Cao SY,Zhai YF,Wang AJ,Gao L,Xiu QY and Cao DH. 2006. The dynamic setting and processes of tectonic and magmatic evolution of the oblique collision zone between Indian and Eurasian plates:Exemplified by the tectonic evolution of the Three River region,eastern Tibet. Acta Petrologica Sinica,22(4):775 -786 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu JL,Cao SY,Zhai YF,Song ZJ,Wang AJ,Xiu QY,Cao DH,Gao L and Guan Y. 2007. Rotation of crustal blocks as an explanation of Oligo-Miocene extension in southeastern Tibet:Evidenced by the Diancangshan and nearby metamorphic core complexes. Earth Science Frontiers,14 (4):40 - 48 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu JL,Tang Y,Song ZJ,Dung TM,Zhai YF,Wu WB and Chen W.2011. The Ailaoshan belt in western Yunnan tectonic framework and tectonic evolution. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),41(5):1285 -1303 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ludwig KR. 2001. Isoplot/Ex,Rev.2.49:A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley Geochronology Center, Special Publication,(1a):55
Luo ZH,Mo XX,Hou ZQ,Deng WM,Wang JH,Zhao ZD,Yu XH and Li JP. 2006. An integrated model for the Cenozoic evolution of the Tibetan plateau:Constraints from igneous rocks. Earth Science Frontiers,13(4):196 -211 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Metcalfe I. 2006. Palaeozoic and Mesozoic tectonic evolution and palaeogeography of East Asian crustal fragments:The Korean Peninsula in context. Gondwana Research,9(1 -2):24 -46
Metcalfe I. 2011. Tectonic framework and Phanerozoic evolution of Sundaland. Gondwana Research,19(1):3 -21
Metcalfe I. 2013. Gondwana dispersion and Asian accretion:Tectonic and palaeogeographic evolution of eastern Tethys. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,66:1 -33
Mitchell AHG. 1993. Cretaceous-Cenozoic tectonic events in the western Myanmar (Burma)-Assam region. Journal of the Geological Society,150(6):1089 -1102
Mitchell AHG,Ausa CA,Deiparine L,Hlaing T,Htay N and Khine A.2004. The Modi Taung-Nankwe gold district,Slate belt,central Myanmar:Mesothermal veins in a Mesozoic orogen. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,23(3):321 -341
Mo XX,Lu FX,Shen SY,Zhu QW,Hou ZQ,Yang KH,Deng JF,Liu XP and He CX. 1993. Sanjiang Tethyan Volcanism and Related Mineralization. Beijing:Geological Publishing House,1 -267 (in Chinese)
Molnar P and Tapponnier P. 1975. Cenozoic tectonics of Asia:Effects of continental collision. Science,189(4201):419 -426
Morley CK. 2004. Nested strike-slip duplexes,and other evidence for Late Cretaceous-Palaeogene transpressional tectonics before and during India-Eurasia collision,in Thailand,Myanmar and Malaysia.Journal of the Geological Society,161(5):799 -812
Morley CK. 2007. Variations in Late Cenozoic-Recent strike-slip and oblique-extensional geometries,within Indochina:The influence of pre-existing fabrics. Journal of Structural Geology,29(1):36 -58
Mukherjee S. 2014. Review of flanking structures in meso-and microscales. Geological Magazine,151(6):957 -974
Passchier CW. 2001. Flanking structures. Journal of Structural Geology,23(6 -7):951 -962
Qi XX,Li HQ,Li TF,Cai ZH and Yu CL. 2010a. Zircon SHRIMP UPb dating for garnet rich granite veins in high pressure granulites from the Namche Barwa complex,eastern syntaxis of the Himalayas and the relationship with exhumeation. Acta Petrologica Sinica,26(3):975 -984 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Qi XX,Zhu LH,Li HQ,Hu ZC and Li ZQ. 2010b. Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating for mylonitized granite from the Ailaoshan-Jinshajiang tectonic zone in the eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and its tectonic significance. Acta Geologica Sinica,84(3):357 -369 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Qi XX,Zhao YH,Zhu LH and Li ZQ. 2012. Discovery of high-pressure pelitic granulite in Ailaoshan orogenic belt southeastern Tibet,and its tectonic implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica,28(6):1846 -1856 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Royden LH,Burchfiel BC,Robert D and van der Hilst. 2008. The geological evolution of the Tibetan Plateau. Science,321(5892):1054 -1058
Schärer U,Tapponnier P,Lacassin R,Leloup PH,Zhong DL and Ji SC.1990. Intraplate tectonics in Asia:A precise age for large-scale Miocene movement along the Ailao Shan-Red River shear zone,China. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,97(1 -2):65 -77
Schärer U,Zhang LS and Tapponnier P. 1994. Duration of strike-slip movements in large shear zones:The Red River belt,China. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,126(4):379 -397
Schmid SM and Casey M. 1986. Complete fabric analysis of some commonly observed quartz c-axis patterns. In:Hobbs BE and Heard HC (eds. ). Mineral and Rock Deformation:Laboratory Studies:The Paterson Volume. American Geophysical Union Monograph,36.American Geophysical Union,246 -261
Searle MP,Noble SR,Cottle JM,Waters DJ,Mitchell AHG,Hlaing T and Horstwood MSA. 2007. Tectonic evolution of the Mogok metamorphic belt,Burma (Myanmar)constrained by U-Th-Pb dating of metamorphic and magmatic rocks. Tectonics,26(3),doi:10.1029/2006TC002083
Searle MP,Cottle JM,Streule MJ and Waters DJ. 2010. Crustal melt granites and migmatites along the Himalaya: Melt source,segregation, transport and granite emplacement mechanisms.Geological Society of America Special Papers,472:219 -233
Şengör AMC. 1984. The Cimmeride orogenic system and the tectonics of Eurasia. Geological Society of America Special Papers,195:1 -74
Şengör AMC,Natal’In BA and Burtman VS. 1993. Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Palaeozoic crustal growth in Eurasia.Nature,364(6435):299 -307
Steiger RH and Jager E. 1977. Subcommission on geochronology:Convention on the use of decay constants in geo-and cosmochronology. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,36(3):359-362
Takeshita T. 1996. Estimate of physical conditions for deformation based on c-axis transitions in naturally deformed quartzite. The Journal of the Geological Society of Japan,102(3):211 -222
Tang Y,Yin FG,Wang LQ,Wang DB,Liao SY,Sun ZM and Sun J.2013. Structural characterization of and geochronological constraints on sinistral strike-slip shearing along the southern segment of Chongshan shear zone,western Yunnan. Acta Petrologica Sinica,29(4):1311 -1324 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Tapponnier P and Molnar P. 1976. Slip-line field theory and large-scale continental tectonics. Nature,264(5584):319 -324
Tapponnier P,Peltzer G,Ledain AY,Armijo R and Cobbold PR. 1982.Propagating extrusion tectonics in Asia:New insights from simple experiments with plasticine. Geology,10(12):611 -616
Tapponnier P,Lacassin R,Leloup PH,Schärer U,Zhong DL,Wu HW,Liu XH,Ji SC,Zhang LS and Zhong JY. 1990. The Ailao Shan/Red River metamorphic belt:Tertiary left-lateral shear between Indochina and South China. Nature,343(6257):431 -437
Wang DD,Li BL,Ji JQ,Song SG,Wei CJ and Gong JF. 2013. The thermal evolution and deformational time limit of the Gaoligong metamorphic belt in western Yunnan. Acta Geologica Sinica,87(12):1887 -1900 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang EC and Burchfiel BC. 1997. Interpretation of Cenozoic tectonics in the right-lateral accommodation zone between the Ailao Shan shear zone and the eastern Himalayan syntaxis. International Geology Review,39(3):191 -219
Wang EC,Fan C,Wang G,Shi XH,Chen LZ and Chen ZL. 2006.Deformational and geomorphic processes in the formation of the Ailao Shan-Diancang range,west Yunnan. Quaternary Sciences,26(2):220 -227 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang JN,Wang YL,An XW and Yang XD. 2006. Analysis of latest activity on NE-segment of west branch of Nantinghe fault. Journal of Seismological Research,29 (3):264 - 268 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang YJ,Fan WM,Zhang YH,Peng TP,Chen XY and Xu YG. 2006.Kinematics and40Ar/39Ar geochronology of the Gaoligong and Chongshan shear systems,western Yunnan,China:Implications for early Oligocene tectonic extrusion of SE Asia. Tectonophysics,418(3 -4):235 -254
Xu ZQ,Wang Q,Liang FH,Chen FY and Xu CP. 2009. Electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD)technique and its application to study of continental dynamics. Acta Petrologica Sinica,25(7):1721 -1736 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang JS,Xu ZQ,Duan XD,Li J,Xiong FH,Liu Z,Cai ZH and Li HQ. 2012. Discovery of a Jurassic SSZ ophiolite in the Myitkyina region of Myanmar. Acta Petrologica Sinica,28(6):1710 -1730(in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang ZD. 1996. Thrust-imbricate structure and nappe of Lincang granite.Scientia Geologica Sinica,31(2):130 - 139 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yin A and Harrison TM. 2000. Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogen. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences,28(1):211 -280
Zhang B. 2008. Kinematics and deformational mechanism of the Cenozoic sinistral transpression along the Lancangjiang structural belt,western Yunnan,China. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing:Peking University,1-105 (in Chinese)
Zhang B,Zhang JJ,Zhong DL and Guo L. 2009. Architecture,kinematics and thermochronology analysis in Lancangjiang structural zone,in western Yunnan. Chinese Journal of Geology,44(3):889-909 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang B,Zhang JJ and Zhong DL. 2010. Structure,kinematics and ages of transpression during strain-partitioning in the Chongshan shear zone,western Yunnan,China. Journal of Structural Geology,32(4):445 -463
Zhang B,Zhang JJ,Zhong DL,Wang XX,Qu JF and Guo L. 2011.Structural feature and its significance of the northernmost segment of the Tertiary Biluoxueshan-Chongshan shear zone,east of the Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis. Science China (Earth Sciences),54(7):959-974
Zhang B,Zhang JJ,Chang ZF,Wang XX,Cai FL and Lai QZ. 2012a.The Biluoxueshan transpressive deformation zone monitored by synkinematic plutons,around the Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis.Tectonophysics,574(11):158 -180
Zhang B,Zhang JJ,Zhong DL,Yang LK,Yue YH and Yan SY. 2012b.Polystage deformation of the Gaoligong metamorphic zone:Structures,40Ar/39Ar mica ages,and tectonic implications. Journal of Structural Geology,37:1 -18
Zhang LS and Schärer U. 1999. Age and origin of magmatism along the Cenozoic Red River shear belt,China. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,134(1):67 -85
Zhang Y,Chen W,Chen KL and Liu XY. 2006. Study on the Ar-Ar age spectrum of diagenetic I/S and the mechanism of39Ar recoil loss:Examples from the clay minerals of P-T boundary in Changxing,Zhejiang Province. Geological Review,52(4):556 - 561 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhong DL,Wang Y and Ding L. 1991. The Tertiary Gaoligong intracontinental strike-slip fault and its associated extensional structure in western Yunnan,China. Annual Report 1989-1990 Lab. Lithos. Tecton. Evolution. Inst. Geol. Academia Sinica.Beijing:Science and Technology of China Press,18 - 24 (in Chinese)
Zhong DL. 1998. The Tethyan Orogenic Belt in Western Yunnan.Beijing:Science Press,1 -231 (in Chinese)
Zhu YX,Li P and Ren JW. 1994. Activity of Nandinghe fault zone and its paleoearthquake events. Earthquake Research in China,10(4):347 -356 (in Chinese with English abstract)
附中文参考文献
常祖峰,安晓文,张艳凤. 2012. 畹町断裂晚第四纪活动与水系构造变形. 地震地质,34(2):228 -239
陈文,张彦,张岳桥,金贵善,王清利. 2006. 青藏高原东南缘晚新生代幕式抬升作用的Ar-Ar 热年代学证据. 岩石学报,22(4):867 -872
陈新跃,王岳军,范蔚茗,彭头平. 2006. 云南崇山剪切断裂系显微构造特征及其40Ar-39Ar 年代学约束. 大地构造与成矿学,30(1):41 -51
从柏林,吴根耀,张旗,张儒媛,翟明国,赵大升,张雯华. 1993.中国滇西古特提斯构造带岩石大地构造演化. 中国科学(B辑),23(11):1201 -1207
丁林. 1991. 滇西高黎贡山南体南段构造变形特征及演化历史讨论.硕士学位论文. 北京:中国科学院地质研究所,1 -92
段建中. 1999. 滇西三江地区新生代走滑(转换)会聚构造特征. 云南地质,18(2):99 -111
段建中,谭筱红. 2000. 滇西三江地区新生代主要走滑断裂性质及特征. 云南地质,19(1):8 -23
季建清,钟大赉,张连生. 2000. 滇西南新生代走滑断裂运动学、年代学、及对青藏高原东南部块体运动的意义. 地质科学,35(3):336 -349
李述靖,单业华. 1995. 滇西无量山北缘弧形推覆构造. 地质学报,69(4):296 -305
李兴振,江新胜,孙志明,沈敢富,杜德勋. 2002. 西南三江地区碰撞造山过程. 北京:地质出版社,1 -213
李再会,王立全,林仕良,丛峰,谢韬,邹光富. 2012. 滇西高黎贡剪切带内花岗质糜棱岩LA-ICP-MS 锆石U-Pb 年龄及其构造意义. 地质通报,31(8):1287 -1295
刘俊来,宋志杰,曹淑云,翟云峰,王安建,高兰,修群业,曹殿华.2006. 印度-欧亚侧向碰撞带构造-岩浆演化的动力学背景与过程——以藏东三江地区构造演化为例. 岩石学报,22(4):775-786
刘俊来,曹淑云,翟云峰,宋志杰,王安建,修群业,曹殿华,高兰,管烨. 2007. 用陆块旋转解释藏东南渐新世-中新世伸展作用——来自点苍山及邻区变质核杂岩的证据. 地学前缘,14(4):40 -48
刘俊来,唐渊,宋志杰,Dung TM,翟云峰,吴文彬,陈文. 2011. 滇西哀牢山构造带:结构与演化. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),41(5):1285 -1303
罗照华,莫宣学,侯增谦,邓万明,王江海,赵志丹,喻学惠,李建平. 2006. 青藏高原新生代形成演化的整合模型——来自火成岩的约束. 地学前缘,13(4):196 -211
莫宣学,路凤香,沈上越,朱勤文,侯增谦,杨开辉,邓晋福,刘祥品,何昌祥. 1993. 三江特提斯火山作用与成矿. 北京:地质出版社,1 -267
戚学祥,李化启,李天福,蔡志慧,于春林. 2010a. 东喜马拉雅构造结南迦巴瓦群高压麻粒岩中含石榴石花岗岩脉锆石SHRIMP U-Pb 定年及其与折返作用. 岩石学报,26(3):975 -984
戚学祥,朱路华,李化启,胡兆初,李志群. 2010b. 青藏高原东缘哀牢山-金沙江构造带糜棱状花岗岩的LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 定年及其构造意义. 地质学报,84(3):357 -369
戚学祥,赵宇浩,朱路华,李志群. 2012. 青藏高原东南缘哀牢山构造带泥质高压麻粒岩的发现及其构造意义. 岩石学报,28(6):1846 -1856
唐渊,尹福光,王立全,王冬兵,廖世勇,孙志明,孙洁. 2013. 滇西崇山剪切带南段左行走滑作用的构造特征及时代约束. 岩石学报,29(4):1311 -1324
王丹丹,李宝龙,季建清,宋述光,魏春景,龚俊峰. 2013. 滇西高黎贡变质带热史演化与变形时限研究. 地质学报,87(12):1887 -1900
王二七,樊春,王刚,石许华,陈良忠,陈智樑. 2006. 滇西哀牢山-点苍山形成的构造和地貌过程. 第四纪研究,26(2):220 -227
王晋南,王洋龙,安晓文,杨向东. 2006. 南汀河西支断裂北东段最新活动性分析. 地震研究,29(3):264 -268
许志琴,王勤,梁凤华,陈方远,许翠萍. 2009. 电子背散射衍射(EBSD)技术在大陆动力学研究中的应用. 岩石学报,25(7):1721 -1736
杨经绥,许志琴,段向东,李静,熊发挥,刘钊,蔡志慧,李化启.2012. 缅甸密支那地区发现侏罗纪的SSZ 型蛇绿岩. 岩石学报,28(6):1710 -1730
杨振德. 1996. 云南临沧花岗岩的逆冲断叠瓦构造与推覆构造. 地质科学,31(2):130 -139
张波. 2008. 滇西澜沧江构造带新生代左行挤压走滑(Transpression)的运动学特征和变形机制. 博士学位论文. 北京:北京大学,1-105
张波,张进江,钟大赉,郭磊. 2009. 滇西澜沧江构造带及邻区几何学、运动学和构造年代学分析. 地质科学,44(3):889 -909
张波,张进江,钟大赉,王晓先,曲军峰,郭磊. 2011. 喜马拉雅东构造结东缘碧罗雪山-崇山剪切带北段构造变形特征及构造意义. 中国科学(地球科学),41(7):945 -959
张彦,陈文,陈克龙,刘新宇. 2006. 成岩混层(I/S)Ar-Ar 年龄谱型及39Ar 核反冲丢失机理研究——以浙江长兴地区P-T 界线粘土岩为例. 地质论评,52(4):556 -561
钟大赉,王毅,丁林. 1991. 滇西高黎贡陆内第三纪走滑断裂及其伴生拉张构造. 中国科学院地质研究所岩石圈构造演化开放研究实验室年报. 北京:中国科学技术出版社,18 -24
钟大赉. 1998. 滇川西部古特提斯造山带. 北京:科学出版社,1-231
朱玉新,李玶,任金卫. 1994. 南定河断裂带断层活动特征与古地震事件. 中国地震,10(4):347 -356

