沉默Notch4基因对乳腺癌细胞系MDA-MB-231增殖和迁移侵袭能力的影响
任宗娜
(天津医科大学肿瘤医院肿瘤研究所,国家肿瘤临床医学研究中心,天津市“肿瘤防治”重点实验室,天津300060)
论著
沉默Notch4基因对乳腺癌细胞系MDA-MB-231增殖和迁移侵袭能力的影响
任宗娜
(天津医科大学肿瘤医院肿瘤研究所,国家肿瘤临床医学研究中心,天津市“肿瘤防治”重点实验室,天津300060)
目的:探讨Notch4基因对乳腺癌细胞系MDA-MB-231增殖、迁移侵袭能力的影响。方法:脂质体法用Notch4 siRNA转染乳腺癌细胞系MDA-MB-231,RT-PCR和Western blot检测Notch4基因的表达,通过MTT实验评价MDA-MB-231细胞增殖活性的改变;流式细胞术检测细胞周期,通过Transwell实验评价肿瘤细胞迁移和侵袭能力的改变;RT-PCR方法检测Notch信号通路相关基因的变化。结果:Notch4 siRNA有效地转入细胞并抑制了Notch4基因的表达。转染Notch4 siRNA细胞的增殖活性及体外迁移侵袭能力均显著下降(P<0.05)。细胞周期阻滞在G0/G1,Hes1、Hey1、c-Myc、cyclinD1、MMP9 mRNA水平明显低于对照组(P<0.05)。结论:Notch4 siRNA可明显抑制乳腺癌细胞系MDA-MB-231增殖、迁移和侵袭能力。Notch4基因可做为三阴性乳腺癌基因治疗的靶基因。
Notch4基因;乳腺癌;RNA干扰;增殖;迁移;侵袭
三阴乳腺癌(triple-negativebreastcancer,TNBC)是以雌激素受体α(estrogen receptorα,ERα)、孕酮受体2(progesterone receptor 2,PR)和人表皮生长因子受体(human epidermal growth factor receptor,HER-2)均不表达为特点的乳腺癌细胞[1],占所有乳腺癌细胞的10%~15%[2-4],由于缺乏针对这些受体的有效治疗靶点,无法采用内分泌治疗和曲妥单抗治疗,导致预后较差[5]。化疗存在疗效不稳定、副作用大以及多药耐药等问题,因此,急需找到针对TNBC的有效的分子治疗靶点。Notch信号通路广泛存在于脊椎动物和非脊椎动物,在进化上高度保守,通过相邻细胞之间的相互作用调控胚胎发育、血管发生、程序性细胞死亡和细胞增殖等多种生理过程[6-9],在肿瘤的侵袭、转移、凋亡、增殖和血管生成等病理过程中也发挥着关键作用[10-11]。目前在脊椎动物中共发现 4个同源体 Notch1、Notch2、Notch3、Notch4[12]。Speiser等[13]研究发现Notch4是三阴性乳腺癌的一个生物学标志物。本研究利用RNAi技术沉默乳腺癌细胞系MDA-MB-231的Notch4基因,观察其对乳腺癌细胞系MDA-MB-231的增殖、迁移和侵袭能力的影响。
1 材料与方法
1.1 细胞培养 乳腺癌细胞系MDA-MB-231具有间质特性和高转移能力,来源于美国标准生物品收藏中心(American Type Culture Collection,ATCC)。MDA-MB-231细胞培养于含10%胎牛血清(Fetal bovine serum,FBS;GIBCO公司,美国)的RPMI-1640培养基(GIBCO公司,美国)中。将对数生长期细胞用0.25%胰蛋白酶消化,制成单细胞悬液,用于体外和体内实验。
1.2 siRNA细胞转染 采用Lipofectamine 2000脂质体转染,方法按照说明书。接种1×105个细胞/孔于6孔板,以含血清无抗生素的培养基培养,细胞为30%~50%饱和度时用于转染(表1)。将5 μL(100 pmol)的stealth RNAi加入含有250 μL的Opti-MEM(GIBCO公司,美国)的EP管中,轻轻混匀;将5 μL的 Lipofectamine 2000加入含有 250 μL的Opti-MEM的EP管中,轻轻混匀;室温静置孵育5 min;将上述液体混合,室温静置孵育20 min;将上述混合液缓慢滴入含有1.5 mL OPTI-DMEM无血清培养基的细胞中,4~6 h后换成含10%FBS的培养液。转染48 h后裂解细胞提取总RNA及免疫荧光检测。实验分组:实验组(Notch4 siRNA组);阴性对照组(NC siRNA组);空白对照组(Mock siRNA组)。

表1 siRNA干扰序列Tab 1 The sequences of siRNA oligonucleotides
1.3 MTT 细胞胰酶消化对数期细胞,终止后离心收集,制成细胞悬液。细胞悬液接种于96孔板,细胞计数调整其浓度至3 000个细胞/孔,边缘孔用无菌PBS填充,5%CO2,37℃孵育。设置6个复孔,分别处理1、2、3、4 d后,每孔加入10 μL MTT溶液(5 mg/mL,即0.5%MTT),继续培养4 h。若药物与MTT能够反应,可先离心后弃去培养液,小心用PBS冲2~3遍后,再加入含MTT的培养液。终止培养,小心吸去孔内培养液。每孔加入150 μL二甲基亚砜,置摇床上低速振荡10 min,使结晶物充分溶解。在酶联免疫检测仪OD570nm处测量各孔的吸光值。
1.4 QTR-PCR 提取细胞总RNA,cDNA的合成,QPCR反应。每个样本中每个基因的检测均重复3次。CT值为荧光信号达到设定阈值时所经过的循环数,ΔCT值为各样本中目的基因的CT值与管家基因GAPDH的CT值之差,2-△Ct则为该样本中目的基因相对于GAPDH mRNA的表达量。管家基因GAPDH和目的基因的引物序列均采用Oligo6.0软件设计,引物及探针均由上海生工生物工程公司合成(表2)。

表2 引物序列Tab 2 Primer sequence
1.5 流式细胞仪检测细胞周期 收集转染后72 h各组细胞,乙醇固定过夜,RNA酶水浴加热消化后加入碘化丙啶(PI,50 μg/mL),4℃放置15 min后流式细胞仪检测。
1.6 细胞侵袭和迁移实验 将悬浮于500 μL无血清培养基的5×104个231-siNotch4、231-siControl细胞接种于含Metrigel和不含Metrigel的transwell上室,下层加入750 μL含10%FBS的细胞培养液,培养8 h。取出transwell小室,用棉签拭去上层未穿过的细胞,通过3步染色试剂盒(Thermo Scientific公司,美国)固定、染色,自来水漂洗3次,室温风干,中性树胶固定,于镜下观察穿孔细胞数目,随机选取5个视野计数并取其平均值。
1.7 Western blot检测 使用细胞裂解液裂解细胞,提取总蛋白,在10%聚丙烯酰胺凝胶中电泳。将蛋白膜转至PVDF膜上,5%脱脂奶粉封闭后,加入鼠一抗Notch4(1∶1 000),4℃转动过夜。第2天取出膜,TBST漂洗后,加入羊抗鼠二抗反应,室温孵育1 h,TBST漂洗。化学发光法(ECL)显影,暗室曝光。
1.8 统计学方法 体外细胞学实验均设每组3个复孔细胞,实验数据用±s表示,多组间均数比较采用单因素方差进行分析,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。统计学分析采用SPSS 13.0软件进行处理。
2 结果
2.1 倒置荧光显微镜下观察实验细胞 绝大多数细胞都荧光着色,与背景反差明显,荧光着色细胞有明显的细胞轮廓(图1)。

图1 转染48 h后倒置荧光显微镜下观察转染后实验细胞(x100)Fig 1 MDA-MB-231 cells under fluoroscope at 48 h after transfection(x100)
2.2 RT-PCR和Westernblot检测Notch4的表达 肿瘤细胞体外运动能力的变化RT-PCR和Western blot结果显示,与阴性对照组和空白对照组相比,实验组Notch4的表达明显降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)(图2)。
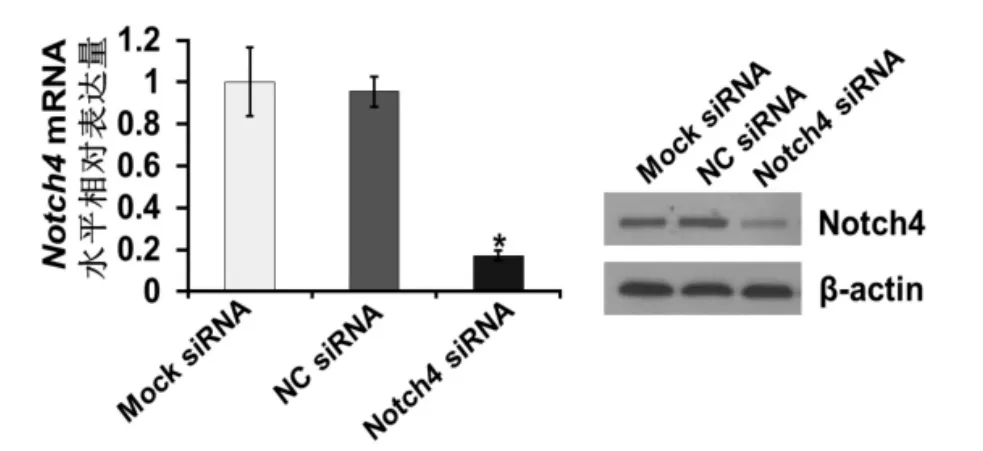
图2 Notch4 siRNA对乳腺癌细胞系MDA-MB-231 Notch4 mRNA和蛋白水平表达的影响(*P<0.05)Fig 2 Effect of siRNA on Notch4 mRNA and protein expression in MDA-MB-231 cells(*P<0.05)
2.3 MTT法检测各组细胞的增殖活性 转染Notch4 siRNA后第1、2天,各实验组增殖活性无明显差异,48 h的OD值,Notch4 siRNA组:0.48±0.07,NC siRNA组:0.51±0.12,Mock siRNA组:0.54±0.17,无明显统计差异(P>0.05)。Notch4 siRNA组较其他两组在第3~5天出现差异,第4天差异最明显,此时Notch4 siRNA组OD值:0.93±0.08,NC siRNA组OD值:1.26±0.29,Mock siRNA组OD值:1.3±0.08,比较有统计学差异(P<0.05)。以时间为横轴、OD值为纵轴绘制生长曲线(图3)。
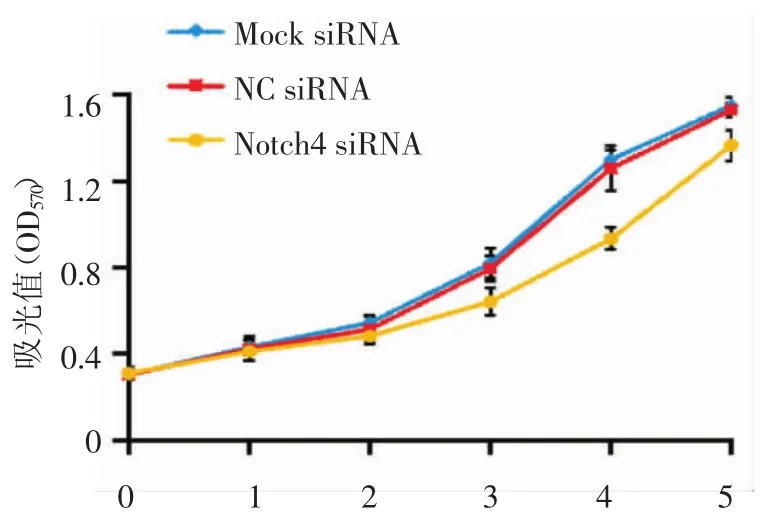
图3 转染Notch4 siRNA对乳腺癌细胞系MDA-MB-231增殖的影响Fig 3 The growth curve by the MTT assay in different groups of MDA-MB-231 after transfection with Notch4 siRNA
2.4 流式检测细胞周期变化 由于细胞的增殖与细胞周期密切相关,在观察到siRNA介导的Notoh4下调能够抑制MDA-MB-231细胞的增殖后,利用流式细胞仪检测了MDA-MB-231细胞在转染siRNA 72 h后的细胞周期分布。结果MDA-MB-231细胞在转染后其典型细胞周期分布为G1:52.3%,G2:17.8%,S:30%;而对照组细胞的周期分布为Gl:71.8%,G2:15.8%,S:12.4%;呈G0/G1阻滞(图4)。

图4 Notch4沉默后对乳腺癌细胞系MDA-MB-231细胞周期的影响Fig 4 The effect of Notch4 siRNA on cell cycle progression ofMDA-MB-231 cells
2.5 沉默Notch4基因对乳腺癌细胞系MDA-MB-231体外迁移侵袭能力的影响 增殖抑制实验表明,Notch4基因沉默后第3天开始出现差异。因此,为了减少细胞增殖对迁移侵袭实验的影响,检测迁移侵袭能力的实验选定在转染后24~48 h进行。结果显示Notch4 siRNA组与其余两组相比,细胞的迁移、侵袭能力显著下调,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)(图5)。
2.6 RT-PCR检测基因表达 RT-PCR检测转染72 h后,Notch4 siRNA组、NC siRNA组、Mock siRNA组的不同基因的表达。结果显示Hes1、Hey1、c-Myc、cyclinD1 mRNA表达均明显低于其他两组(P<0.05)(图6)。

图5 Notch4沉默后对乳腺癌细胞系MDA-MB-231体外运动能力的影响(*P<0.05)Fig 5 The effect of Notch4 siRNA on migration and invasion activity of MDA-MB-231 cells in vitro(*P<0.05)
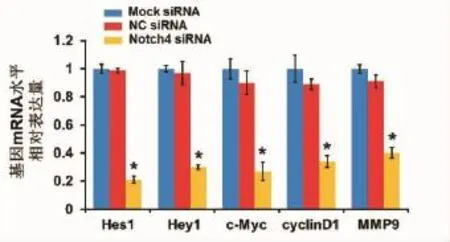
图6 转染后MDA-MB-231细胞的Hes1、Hey1、c-Myc、cyclinD1、MMP9 mRNA表达的差异(*P<0.05)Fig 6 The expression of Hes1,Hey1,c-Myc,cyclinD1 and MMP9 in MDA-MB-231 cells after transfection(*P<0.05)
3 讨论
Naik等[14]研究发现,Notch4异常高表达与乳腺癌的发生和发展密切相关,而且在Basal乳腺癌细胞中高表达。在高表达Notch4的乳腺癌细胞中,Notch4增加细胞的抗凋亡能力,提高对化疗药的耐受性[14]。研究发现,活化的Notch4还可以使正常乳腺上皮细胞在体外发生恶性转化[15]。Lombardo等[16]研究发现,MCF-7细胞高表达Notch4受体,使细胞发生上皮间质转化,增加对内分泌治疗的不敏感性。临床资料显示[17],Notch4高表达的肿瘤患者,其总体生存较短。所以,Notch4基因高表达是乳腺癌患者的不良预后因素。
在细胞周期检测中,沉默Notch4基因后细胞发生了G0/G1阻滞,提示Notch4蛋白是通过促进细胞周期诱导细胞增殖。细胞周期素D1(cyclinD1)属细胞周期素家族成员,可与CDK4结合并激活其活性,调控细胞由G1期至S期的转变。本实验证实抑制Notch4基因的表达能下调cyclinD1,进而阻止人乳腺癌MDAMB-231细胞从G1期进入S期,所以靶向Notch4的药物能缓解乳腺癌细胞的增殖速率。原癌基因c-Myc是决定细胞从G0/G1期进入S期的“开关”,而且在G2/M细胞周期进展中也起着重要作用,与细胞增殖关系密切[18-20]。使用RNA干扰技术沉默c-Myc基因能有效抑制肾癌细胞增殖[21]。张巧琳等[22]发现c-Myc抑制剂能抑制肾癌细胞786-0的增殖并发生G0/G1期细胞周期阻滞。以上研究说明c-Myc基因与细胞的增殖和周期密切相关,同样,我们发现抑制Notch信号通路后乳腺癌细胞增殖受到抑制,而且停留在G0/G1期的细胞比例明显升高。c-Myc与Notch4信号通路在生物学行为上具有相似性,两者可能存在协同性。在本实验中,我们采用小干扰沉默乳腺癌细胞株MDA-MB-231的Notch4蛋白后c-Myc的mRNA水平下调,说明在乳腺癌中c-Myc可能也作为Notch4蛋白的靶基因而发挥作用。本研究发现,在沉默Notch4基因后Hes1和Hey1 mRNA表达水平均明显降低。Notch信号传导是通过信号发出细胞的配体结合信号接收细胞的受体由γ-内分泌酶切除受体胞内段使其激活。胞内段入核后与转录因子CSL形成复合体,调节下游靶基因的表达,可见,Notch信号主要功能取决于下游靶基因的功能。下游靶基因主要是Hes/ Hey家族,转录后主要参与细胞增殖、分化、凋亡等从而决定细胞命运。MMP9是基质金属蛋白酶家族中的成员之一,主要作用就是降解基质中的蛋白,与乳腺癌的侵袭性、转移密切相关[23]。本实验发现,在沉默Notch4基因后MMP9的mRNA表达水平均明显降低,提示在MDA-MB-231细胞中Notch4基因可能通过下调MMP9的水平,抑制细胞的迁移、侵袭能力。
综上所述,本实验证实了通过沉默Notch4的表达可明显抑制乳腺癌MDA-MB-231细胞的增殖、迁移、侵袭能力,结合Notch4在增强乳腺癌细胞干性、抗凋亡和耐药性等方面的作用,我们认为靶向Notch4的治疗是可行的,将有可能为三阴性乳腺癌基因治疗的一种新选择。
[1] Sørlie T,Perou C M,Tibshirani R,et al.Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,2001,98(19):10869
[2] Carey L,Winer E,Viale G,et al.Triple-negative breast Cancer:disease entity or title of convenience[J].Nat Rev Clin Oncol,2010,7 (12):683
[3] Dent R,Trudeau M,Pritchard K I,et al.Triple-negative breast cancer:clinical features and patterns of recurrence[J].Clin Cancer Res, 2007,13(15 Pt 1):4429
[4] Rakha E A,El-Sayed M E,Green A R,et al.Prognostic markers in triple-negative breast cancer[J].Cancer,2007,109(1):25
[5] van’t Veer L J,Dai H Y,van de Vijver M J,et al.Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer[J].Nature,2002, 415(6871):530
[6] Fernandez-Valdivia R,Takeuchi H,Samarghandi A,et al.Regulation of mammalian Notch signaling and embryonic development by the protein O-glucosyltransferase Rumi[J].Development,2011,138 (10):1925
[7] Gianni-Barrera R,Trani M,Reginato S,et al.To sprout or to split? VEGF,Notch and vascular morphogenesis[J].Biochem Soc Trans, 2011,39(6):1644
[8] Yalcin-Ozuysal O,Fiche M,Guitierrez M,et al.Antagonistic roles of Notch and p63 in controlling mammary epithelial cell fates[J]. Cell Death Differ,2010,17(10):1600
[9] Monahan P,Rybak S,Raetzman L T.The notch target gene HES1 regulates cell cycle inhibitor expression in the developing pituitary [J].Endocrinology,2009,150(9):4386
[10]Garcia A,Kandel J J.Notch:a key regulator of tumor angiogenesis and metastasis[J].Histol Histopathol,2012,27(2):151
[11]Wang Z,Li Y,Banerjee S,et al.Down-regulation of Notch-1 and Jagged-1 inhibits prostate cancer cell growth,migration and invasion,and induces apoptosis via inactivation of Akt,mTOR,and NF-kappaB signaling pathways[J].J Cell Biochem,2010,109(4):726
[12]Ellisen L W,Bird J,West D C,et al.TAN-1,the human homolog of the Drosophila notch gene,is broken by chromosomal translocations in T lymphoblastic neoplasms[J].Cell,1991,66(4):649
[13]Speiser J,Foreman K,Drinka E,et al.Notch-1 and notch-4 biomarker expression in Triple-Negative breast Cancer[J].Int J Surg Pathol,2012,20(2):139
[14]Naik S,Macfarlane M,Sarin A.Notch4 signaling confers susceptibility to TRAIL-Induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells[J].J Cell Biochem,2015,116(7):1371
[15]Girard L,Jolicoeur P.A full-length Notch1 allele is dispensable for transformation associated with a provirally activated truncated Notch1 allele in Moloney MuLV-infected MMTVD/myc transgenic mice[J].Oncogene,1998,16(4):517
[16]Lombardo Y,Faronato M,Filipovic A,et al.Nicastrin and notch4 drive endocrine therapy resistance and epithelial to mesenchymal transition in MCF7 breast cancer cells[J].Breast Cancer Res,2014, 16(3):R62
[17]D’angelo R C,Ouzounova M,Davis A,et al.Notch reporter activity in breast cancer cell lines identifies a subset of cells with stem cell activity[J].Mol Cancer Ther,2015,14(3):779
[18]Eilers M,Picard D,Yamamoto K R,et al.Chimaeras of myc oncoprotein and steroid receptors cause hormone-dependent transformation of cells[J].Nature,1989,340(6228):66
[19]Roussel M F.Key effectors of signal transduction and G1 progression[J].Adv Cancer Res,1998,74:1
[20]Adachi S,Obaya A J,Han Z,et al.c-Myc is necessary for DNA damage-induced apoptosis in the G(2)phase of the cell cycle[J]. Mol Cell Biol,2001,21(15):4929
[21]Tang S W,Chang W H,Su Y C,et al.MYC pathway is activated in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and essential for proliferation of clear cell renal cell carcinoma cells[J].Cancer Lett,2009,273(1):35
[22]张巧琳,徐新,刘琪,等.c-Myc小分子抑制剂10058-F4对肾癌786-0细胞增殖凋亡的影响[J].重庆医学,2010,39(22):3049
[23]Guo J,Xu Y,Ji W,et al.Effects of exposure to benzo[C].2015:201-210
(2015-05-06收稿)
Inhibition effect of silencing Notch4 gene on the proliferation and migration and invasion activity of breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231
REN Zong-na
(Cancer Institute and Hospital,Tianjin Medical University,National Clinical Research Center of Cancer,Tianjin Key Laboratory of Cancer Prevention and Therapy,Tianjin 300060,China)
Objective:To investigate the effect of Notch4 gene on the proliferation and migration and invasion activity of breast cancer cells.Methods:Lipofectin Reagent was used to transfect Notch4 siRNA into breast cancer cell MDA-MB-231.The mRNA and protein expression level of Notch4 were detected by RT-PCR and Western blot.Cell grow curve was measured by MTT assay.Matrigel-coated Transwell and Transwell inserts were applied to examine cell migration and invasion activity in vitro.The cell cycle distribution was assessed by flow cytomentry.The expression levels of Hes1,Hey1,c-Myc,cyclinD1 and MMP9 were detected by RT-PCR.Results:The Notch4 siRNA was effectively transfected into MDA-MB-231 cells.The mRNA and protein expression level of Notch4 were inhibited.MTT test showed that the proliferation of transfected cells was significantly lower than those of the other two groups(P<0.05).Transwell chamber testshowed thatthe migration and invasion capability of transfected cells was significantly lower than control(P<0.05).Cell cycle of Notch4 siRNA transfected group cells was arrested in G0/G1 phase.The expression levels of Hes1,Hey1,c-Myc,cyclinD1 and MMP9 between Notch4 siRNA transfected group and other two groups were statistically different(P<0.05).Conclusion:Notch4 gene by Notch4 siRNA can remarkably inhibitproliferation and migration and invasion activity of cell lines of MDA-MB-231.Notch4 gene may be used as the target for triple-negative breastcancer gene therapy.
Notch4 gene;breast cancer;RNAi;proliferation;migration;invasion
R737.9
A
1006-8147(2015)06-0469-05
任宗娜(1989-),女,硕士在读,研究方向:生物化学与分子生物学;E-mail:zongnaren@163.com。

