Influences of Surface Drip Irrigation on the Growth,Yield and Quality of Several New Species of Guitang Sugarcane
Shuning XU,Sheng TANG,Weian XU,Yingzhi CHEN,Yijie LI,Jinlan XIE,Lihang QIU, Weizan WANG*
1.Sugarcane Research Institute,Guangxi Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Nanning 530007,China;
2.Nanning Longan Guangxi County Land Technical Service Station,Longan Guangxi 532799,China
Influences of Surface Drip Irrigation on the Growth,Yield and Quality of Several New Species of Guitang Sugarcane
Shuning XU1,Sheng TANG1,Weian XU2,Yingzhi CHEN1,Yijie LI1,Jinlan XIE1,Lihang QIU1, Weizan WANG1*
1.Sugarcane Research Institute,Guangxi Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Nanning 530007,China;
2.Nanning Longan Guangxi County Land Technical Service Station,Longan Guangxi 532799,China
[Objective]This paper discussed the influences of surface drip irrigation on the growth,yield and quality of several new species of Guitang,in order to provide references for the promotion of new species and high-yield cultivation.[Method]One species is planted in each region,and there were two controls dripping technology or no-dripping technology in each region.[Results]The average yield of dripping-processed land was 115.91 t/hm2,which was 19.73 t/hm2higher than the control.The maximum output was GT31,followed by GT34.The output of all Guitang new species was higher than the control ROC22.The average sucrose of dripped sugarcane was 14.68%,which was 0.19%less than the control of 14.83%.The dripping technology was economically beneficial,rising by 15.2% compared with the control.The highestdripping efficiencywasGT31,while the lowestone was ROC22.The increasing ratios of drip irrigation efficiency of the tested new Guitang species were higher than ROC22. [Conclusions]Under the drip irrigation condition, the sugarcane yield was extremely higher than the control of non-dripping irrigation, and the economic efficiency was significant.However,the sugar in the sugarcane declined slightly.The sensitivity of several new Guitang species to water was higher than the control ROC22.
Sugarcane;Drip irrigation;Different species;Yield;Sucrose
S ugarcane is an essential economic pillar industry in Guangxi,and above 90%sugarcane grows in the arid hillside field. The drought from autumn to spring makes it difficult for the seedlings to grow,which exerts considerable influences on the sugarcane yield.Therefore,it is of great significance to adopt advanced sugarcane cultivation tech nologies[1-2].Drip irrigation is based on the water absorbing capacity of plants, and reduced the wastes of water to the maximum extent.This increases the moisture use efficiency,and is one of the most advanced water conservation irrigation technology in the world[3-4]. Drip irrigation is a new efficient water irrigation technology based on the increasingly perfection of drip irrigation technology[5-6].Compared with ground drip irrigation,underground drip irrigation can reduce the water evaporation in the soil,elongate the use of dripping tube,and cut down labor and management costs.
In the end of 1990s,N etafim from Israel introduced drip irrigation technology into China,and demonstrated such technology at first on the cotton and grapes in Xinjiang,and then on the sugarcane in Guangxi from the year of 2003[8].In recent years,researchers like Xu Lin et al.[10]have carried out more studies on applying drip irrigation technology on the sugar-cane.Chen Guifen et al.[11]have studied different drip fertilizing technologies.Li Yijie et al.[2]have studied the different irrigation amounts.At present, studies on the application ofdrip technology mainly focus on the influences of fertilizing technology,irrigation method and irrigation amount on the sugarcane,and there are few studies about the high yield of various sugarcane species.We tested the six new species of Guitang,and New Taitang No.22 as the control.This paper discussed the influences of underground drip on the growth,output and quality of new species in order to provide references for the promotion of new species.
Materials and Methods
Test materials
The experiment is carried out in GuangxiSugarcane Institute.The tested speciesareGuitangNo.29 (GT29),Guitang No.30(GT30),Guitang No.31 (GT31),Guitang No.32 (GT33),Guitang No.33(GT33),Guitang No.34(GT34),New Taitang No. 22(ROC22,the control).We need one PVC-U tube of 75 mm,one tube of 16 mm in diameter,0.8 mm of thickness, 40 mm of drip hole distance and 1-2 L/h of flow.The fertilizer used 25% compound fertilizer in which the contentofnitrogen,phosphorus and potassium was 13%,5%,and 7%.
Experiment methods
Based on the comparison method,each species was planted in each region.The line length was 7 m and the line spacing was 1.2 m.Eight lines were considered as one region, and was about 67.2 m2.Each species includes irrigation and non-irrigation. The sugarcane seedlings were cut into two parts and sowed from March 22 to 23 in 2012.The base fertilizer was 750 kg/hm2.75 kg/hm2of pesticides were sowed after sowing.Then soils were covered over the plants,and drips were laid before spraying pesticides and covering film.Films were peeled in the mid-April,and 750 kg/hm2compound fertilizer was applied on May 29.Besides,1500 kg/hm2compound fertilizer was applied on July 18.Then, we collected ripe sugarcane on January 24,2013.
Drip irrigation
420 m3/hm2of water was used for drip irrigation was conducted for once all over the experimental area five days after sowing.From May to October,drip irrigation was conducted once each month,and the control was not irrigated.Firstly,420 m3/hm2of water was used for 10 hours on May 8. Then,390 m3/hm2of water was used for 14 hours on June 5.Thirdly,150 m3/hm2of water was used for 12 hours on July 15.Fourthly,420 m3/hm2of water was used for 12 hours on August 18.Fifthly,450 m3/hm2of water was used for 12 hours on September 22.Sixthly,405 m3/hm2of water was used for 10 hours on October 20.In total,2 235 m3/hm2of water was used for drip irrigation.
Investigation projects
We recorded the seedling rate and tiller rate in the early stage of the sugarcane growth,the strain growth velocity in the middle period,and the content of sugar cane in the final stage.We learned the yield.
Data statistics analysis
Excel 2003 was applied for data treatment,and DPS7.55 for variance analysis.
Results and Analyses
Influences of different treatments on the seedling and tiller of sugarcanes
According to Table 1,the average seedling rate of the drip irrigated one and the control was similar,mainly because the moisture management of both treatments was the same during the germination period.No matter it is drip irrigation process or the control, the seedling rates ofallGuitang species were less than that of the control ROC22.Since May,water was only used in drip irrigation treatment, rather than being used in the control. Right now the sugarcane was in the tiller period,so the drip irrigation exerted great influences on the tiller of sugarcane (Table 1).According to the three times of tiller from the early tiller period (May 15)to the end of tiller (June 5),there are three tiller periods, as the tiller rate of irrigation processes, and the litter rate of all species were higher than the control.The highest tiller rate was 158.0% in average, which was 39.9%higher than the control that was 118.1%.The tiller rate of two treatments of each species was GT33>GT30>GT31>GT29>GT34>ROC22>GT32.The tiller rate of each irrigated species reached the highest value on May 25,while only GT31, GT32,GT33 and ROC22 of the control group amounted to the highest value on the same day.And the other three species amounted to the highest value until June 5,which suggested that the tiller began early and ended early.
Influences of different treatments on the strain height of sugarcane
As is shown in Table 2,in the ear-ly period of sugarcane(strain height at the end of June),the drip irrigation of all species was obviously higher than the control,and the average strain height was 4.5%higher than the control.The variance was extremely significant.The growth rate of strain height of GT32,GT29,GT34 was much higher than the control ROC22. In the middle period,the growth of irrigated strain heightwasextremely higher than the control.The growth rate of GT29 was the largest one,far more than ROC22,and the values of other species were less than ROC22. The growth of strain height from October to December was the same as the value in the early and middle periods. The GT30 strain growth rate was the largest one,while the control ROC22 was the smallest one.As for the total growth of strain height from August to December,the irrigate treatment was significantly higher than the control, and the growth rate was GT29>GT30>GT 34>GT32>GT22>GT31>GT33,which suggested that the irrigation promoted the sugarcane growth.

Table 1 Comparison of seedling rate and tiller rate of sugarcanes %

Table 2 The sugarcane strain height cm
Influences of different treatments on the sugarcane yield and sugarcane stalk
Table 3 suggested that there were differences in the sugarcane yield and the sugarcane stalk yield.In terms of the stalk length,the irrigated treatment generally was 8.5%higher than the control,and the growth rate of GT29, GT34,and GT32 was higher than the control ROC22,while the value of GT31 and GT32 was less than ROC22.With regard to the stalk diameter,the irrigated treatment rose by 1.6%than the control,with significant difference.The largest rising rate was GT33.All Guitang species were higher than ROC22,except GT29.The effective stalk of irrigated plants rose by 8.4%,significantly higher than the control.The highest growth rate was GT31,andthelowestvaluewas ROC22.As for the sugarcane stalk yield,the irrigated treatmentwas 20.5%higher than the control,and the highest growth rate of the irrigated species was GT31,while the lowest one was ROC22.The sequence was GT31>GT33>GT32>GT34>GT29>GT30>ROC22,which indicated that the growth rate of all irrigated Guitang species was higher than ROC22.
Influences of different treatments on the sucrose in the sugarcane
Samples were delivered to the Center for Inspection and Testing for Quality and Safety of Sugarcane,Ministry of Agriculture (Nanning)in themiddle ten days of December and January.Three species were collected for both the irrigated group and the control.According to Table 4,the average sucrose in the sugarcane was 14.67% in December,which was 0.29%less than the control.The average sucrose in the irrigated sugarcane in January was 14.70%,which was 0.09%less than the control group.The average sucrose of the irrigated group of two tests was 14.68%,0.19%less than the control,which suggested that the average sugarcane sucrose was in decline.

Table 3 Comparison of sugarcane yield and sugarcane stalk yield
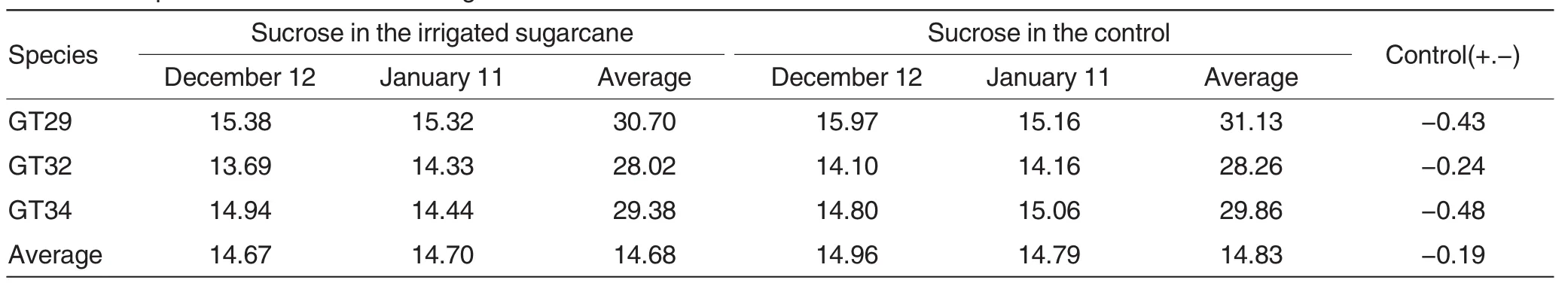
Table 4 Comparison of sucrose in the sugarcane %
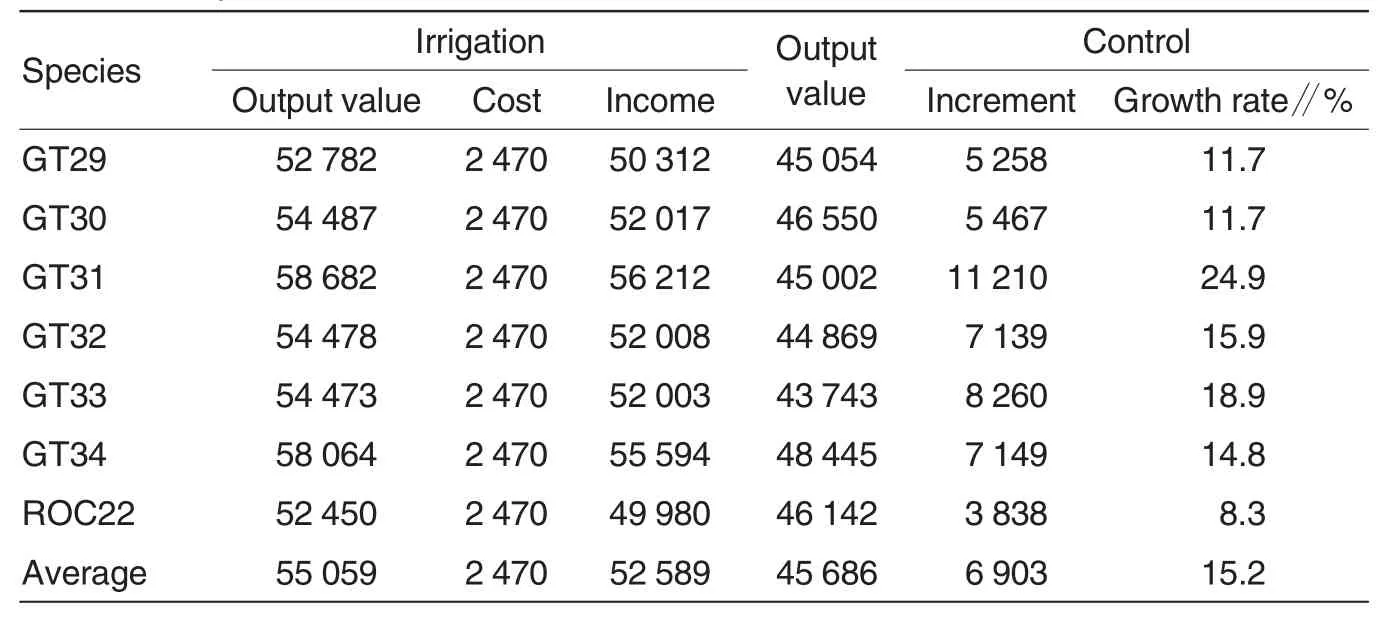
Table 5 Comparison of the economic benefit Yuan/hm2
The economic benefit of sugarcanes
(1)The price of raw materials:the originalsugarcane price was 475 yuan/t.
The drip irrigation input:the dripping tube cost 0.85 yuan per meter, and if the line distance was 1.2 m, there would be 8 400 m/hm2(10 000 m2/1.2 m≈8 400 m),and so the total cost would amount to 7 140.0 yuan/hm2.The PVC-U tube cost 25 yuan for each (4 m),525 yuan/hm2in total.The joint was bought at 0.8 yuan each,and one joint was needed for every 100 meter,67 yuan/hm2.The installation expense was about 60 yuan one day for a temporary worker,and there were three workers in each square meter.The water for irrigation cost 0.22 yuan per square meter,and about 2 235 m3/hm2water was used. Because the drip irrigation can prolong the age of roots,the cost of raw materials for four years were 9 880 yuan/hm2.
(2)Economic benefits:the economic benefit is positively proportional to the yield of sugarcane stalk.The average income of irrigated species was 52 589 yuan/hm2,which was 15.2% higher than the control.The increase rate of drip irrigation was GT31>GT33>GT32>GT34>GT29=GT30>ROC22.That was to say that the economic growth of irrigated new species of Guitang was over ROC22.
Conclusions and Discussions
(1)Besides of the inherent reasons of species,the soil moisture, aeration and soil temperature of the external surroundings would influence the tiller of sugarcane.Temperature, sunshine,nutrients and moisture are the primary factors affecting the stalk length and diameter.As for the sugarcane in the arid land,moisture is the leading factors thatlimitthe growth of sugarcane[14].Because of the direct supply of water to the crops, drip irrigation technology accelerates the assimilation of moisture and fertilizer to the plants[7-15].Experiment proves that drip irrigation promotes the early development of tiller,and thus increases the yield.The average stalk yield of irrigated sugarcane was 20.5% higher than the control,while the largest increase rate was GT31,and the smallest one was the ROC22,as GT31>GT33>GT32>GT34>GT29>GT30>ROC22.The growth rate of all irrigated Guitang species was higher than that of ROC22,which also suggests that ROC22 is a species that is drought-resistant and has a stable yield.
(2)The sucrose in the sugarcane was lower than the control 0.19%,and showed a declining trend,which may because that the drip irrigation significantly increases the fertilizer rate,and causes decline in the sucrose,which is basically consistent with the studies by Chen Guifen et al.[11]and Wei Changbin et al.[14]Studies by Li Yijie et al.[2]and Wang Weizan[12]have different results from our research.Whether the sucrose in the irrigated sugarcane increases or declines is subjected to different species and surroundings. Therefore,we need further studies regarding this aspect.
(3)The economic benefit of irrigated treatment was significant,and the control rose by 15.2%.The highest growth rate was GT31,while the lowest one was ROC22,GT31>GT33>GT32>GT34>GT29=GT30>ROC222, which was positively proportional to the sugarcane stalk yield.All the increase rate of new species was higher than ROC22.
[1]DENG YC(邓宇驰),LU GY(陆国盈), WEI H(韦晖),et al.Effects of different rates of water supply and nitrogen fertilizer on mineral nutrients in leaves of sugarcane(不同水肥供应对宿根甘蔗叶片矿质营养的影响)[J].Guangxi Agricultural Sciences(广西农业科学),2009, 40(5):538-542.
[2]LI YJ(李毅杰),WANG WZ(王维赞),HE H(何红),et al.Study on sugarcane drip irrigation water amount based on water surface evaporation(基于蒸发皿水面蒸发量的甘蔗滴灌栽培滴灌量的研究)[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture(南方农业学报),2013,44(7):1130-1134.
[3]HUANG ZR(黄振瑞),PENG DY(彭冬永),YANG JX(杨俊贤),et al.Application prospect of drip irrigation in sugarcane plantation(滴灌技术在甘蔗生产上的应用前景).Sugar Crops of China(中国糖料),2007(3):43-44.
[4]LUO WY(罗文杨),WANG YC(王一承), XI JG(习金根).Movement and transformation of soil moisture under drip-irrigation(滴灌条件下土壤水分运移动态研究)[J].Journal of South China University of Tropical Agriculture(华南热带农业大学学报),2006(3):16-19.
[5]LI DX(李道西),LUO JY(罗金耀).Summary on research and development of subsurface drip irrigation techniques(地下滴灌技术的研究及其进展)[J].China Rural Water and Hydropower(中国农村水利水电),2003(7):15-18.
[6]RAN CW(冉春旺).The development and application of subsurface drip irrigation techniques(地下滴灌技术发展及应用现状)[J].Modern Agricultural Sciences(现代农业科学),2008(7):51-52.
[7]XU L(徐林),LI YR(李杨瑞),HUANG HR (黄海荣),et al.Advance in subsurface drip irrigation (地下滴灌技术的研究进展)[J].Journal of Southern Agriculture(广西农业科学),2008(6):800-804.
[8]HUANG JJ(黄景剑).Application and demonstration of subsurface drip irrigation on the sugarcane(地下滴灌系统在甘蔗种植上的应用研究与示范)[J]. Guangxi Tropical Agriculture(农业研究与应用),2013(1):28-32.
[9]XU L(徐林),HUANG HR(黄海荣), HUANG YY(黄玉溢),et al.Spatial distribution of sugarcane root and soil available nutrients with subsurface drip irrigation in sugarcane field(地下滴灌条件下甘蔗根系和蔗地土壤速效养分分布规律的研究)[J].Guangdong Agricultural Sciences(广东农业科学),2011(1):78-80.
[10]XU L(徐林),HUANG HR(黄海荣), HUANG YY(黄玉溢),et al.Effects of combined application ofnitrogen, phosphorus and potassium on sugarcane yield and its components with subsurface drip irrigation (地下滴灌条件下氮磷钾配施对甘蔗产量及其构成因素的影响).Guangxi Agricultural Sciences (广西农业科学),2010,41(8): 800-803.
[11]CHEN GF(陈桂芬),HUANG YY(黄玉溢),LIU B(刘斌),et al.Effects of subsoil drip irrigation on sugarcane in field conditions(甘蔗地埋式滴灌施肥效应). Guangxi Agricultural Sciences(广西农业科学),2010,41(6):573-576.
[12]WANG WZ(王维赞),FENG LJ(冯礼就),LUO YW(罗亚伟),et al.High yield properties and water use efficiency of different genotypes sugarcane under drip irrigation (地下滴灌条件下不同基因型甘蔗高产性状及水分利用效率)[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences(广东农业科)学,2011(19):29-32.
[13]DENG KZ (邓坤章).Reports on the application of drip irrigation technologies on surgarcane in Beihai(北海市甘蔗滴灌节水技术试验初报)[J].China Agricultural Technology Extension(中国农技推广),2011(1):40-41.
[14]WANG XL(王秀林),YANG XY(杨秀英),HUANG JJ(黄景剑),et al.The effectofcomprehensive application technology drip irrigation system on the growth of sugarcane (滴灌系统综合应用技术对甘蔗生长的影响)[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences (安徽农业科学),2011,39(27):16530-16532.
[15]ZHANG ZC(张智操),JIANG N(姜宁), CHEN HF(陈宏峰).Development of subsurface drip irrigation and effects of technology and environment(地下滴灌技术发展及其技术环境效果)[J]. Water Conservancy Science and Technology and Economy(水利科技与经济),2004(4):215-217
[16]WEI CB(魏长宾),LIU SH(刘胜辉),HE YD(何应对),et al.Primary research of drip irrigation on sugarcane(甘蔗滴灌施肥效果研究初报)[J].Guangdong Agricultural Sciences(广东农业科学), 2008(7):60-61.
Responsible editor:Nana FAN
Responsible proofreader:Xiaoyan WU
地下滴灌对几个桂糖新品种生长及产、质量的影响
许树宁1,唐 胜1,许卫安2,陈引芝1,李毅杰1,谢金兰1,丘立杭1,王维赞1*
(1.广西农业科学院甘蔗研究所/广西甘蔗遗传改良重点实验室,广西南宁 530007;2.广西南宁市隆安县土地技术服务站,广西隆安 532799)
[目的]探讨在地下滴灌的条件下对几个桂糖新品种生长及产、质量的影响,以便为新品种的推广应用及高产栽培提供参考。[方法]每个品种种一个小区,各小区都分为滴灌和不滴灌(对照)两个处理,采用对比法设计,不设重复。[结果]滴灌处理平均产量115.91 T/hm2,比对照96.18 T/hm2增产19.73 T/hm2,增长20.5%,差异极显著;品种间产量最高的是GT31,其次为GT34,所有桂糖新品种均高过对照种ROC22。滴灌平均甘蔗蔗糖分为14.68%,比对照14.83%少0.19%(绝对值),差异显著。滴灌处理的经济效益极显著,较对照增长15.2%;品种间滴灌效益增长率最高的是GT31,最低是低ROC22,所有参试桂糖新品种滴灌效益增长率均高过ROC22。[结论]在滴灌条件下,甘蔗产量极显著地高过非滴灌的对照,经济效益极显著,而甘蔗蔗糖分则略有下降;几个参试桂糖新品种对水分的敏感性超过对照种ROC22。
甘蔗;地下滴灌;不同品种;产量;蔗糖分
国家甘蔗产业技术体系广西创新团阶建设专项(nycytxgxcxtd02);广西科学研究与技术开发计划 (桂科重12118002-1);广西农业科学院基本科研业务专项 (桂农科2012YZ23)。
许树拧(1954-),男,广西崇左人,高级农艺师,主要从事甘蔗栽培及技术推广研究。*通讯作者,E-mail:13077748639@126.com。
2015-06-01
修回日期 2015-07-07
Supported by National Sugarcane Industrial Technology System Guangxi Innovation Team Program (nycytxgx-cxtd-02);Guangxi Scientific Research and Technological Development Program (No.12118002-1);Basic Scientific and Research Program of Guangxi Agricultural Sciences(No.2012YZ23).
*Corresponding author.E-mail:13077748639@126.com
Received:June 1,2015 Accepted:July 7,2015
 Agricultural Science & Technology2015年8期
Agricultural Science & Technology2015年8期
- Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Variations of Frost-free Period and Its Impact on Grain Yields in Henan Province during 1961-2013
- Fuzzy Analysis Method for Orthogonal Test on Seed Propagation of Eurya chinensis
- Establishment of a Method for Determination of Anemoside B4 Content in Pulsatilla Water Extract
- Anther Dehiscence Disturbed by High Temperature and Water Stress Presented in OsDIR Gene Expression in Rice(Oryza sativa L.)
- Study on Honey Stirred Yoghurt
- Interspecific Cross Compatibility of Rhododendron in Changbai Mountain
