Quantitative Study on the Relationship between Water Disaster and Grain Production of Hubei Province in the 1990s
Xianyou REN,Tao LI
1.Institute of Geodesy and Geophysics,CAS,Wuhan 430077,China;
2.Hubei Academy of Environmental Sciences,Wuhan 430072,China
Responsible editor:Xiaoxue WANG Responsible proofreader:Xiaoyan WU
H umanity’s most fundamental relationship is with what we eat.Crop is a special strategic commodity and an important part of national safety strategy,laying foundation for national economic development.China is always a country dominated by agriculture.Therefore,drought or flood will cause a great loss of agricultural products,reducing agricultural yields and paralyzing re-production of agriculture in disasterstricken area[1].As a large agricultural province,Hubei is always a key commercial grain production base in China,and the role is increasingly reinforced with weakening of the same role played by Pearl River Delta and Yangtze River Delta.
Hubei has a subtropical monsoon climate and natural disasters occur frequently,in particular water-related disasters.What’s more,disaster varieties tend to be volatile and severe.For example,floods,droughts and waterlogging are expected to occur in varying degrees[2].In the 9thFive-year Plan,for instance,flooding and drought alternate has caused a great loss of agriculture,deteriorated by disease and insect damages,posing threats to crop security in Hubei[3].On basis of the important role of Hubei in national crop safety and high frequency of water-related disasters in Hubei,the research performed quantitative research on the change trends of influential factors and analyzed the effects of water-related disasters on crop safety in Hubei[4],which is of great significance for improving treatment standards of water-related disasters and guaranteeing crop safety provincially or nationally.
Introduction of Crop Production in Hubei Province
Hubei is located in middle part of China (29°5′-33°20′N,108°21′-116°7′E),with an area of 185 900 km2.It has many rivers and lakes,and flat regions are extension.Therefore,crops are suitable to be grown and Hubei becomes an important grain production base in China.For example,grain sowing area accounts for 55% of total area of crops and grain yield represents 4.5%nationwide.
Interannual yield variability tends to be high under influence of natural disasters,investments and social and economic factors,represented by coefficient of variation.The higher the coefficient,the lower grain safety,as follows:
Vi=(Yt-)/,where Virepresents variation coefficient of gross grain yield(positive or negative); Ytrepresents practical yield on the tthyear;y^tis yield developments on the tthyear,indicating growing or declining of gross grain yield upon time;is computed by exponential smoothing.The higher Vi,it means the poorer grain stability or the lower grain safety.In general,the coefficient of variation (Vi) should be controlled equal to or below 2%.
As shown in Fig.1,it can be analyzed that variation coefficient of gross grain yield averaged ±1.37% in Hubei,and there were three years when the coefficient exceeded 2%during 1990-2004.Besides,the highest yield variation reached 2.334 million tons,and variation coefficient was 2.71%,which was higher compared with global level(±2.2%).Except of few years,grains kept higher and more stable in Hubei.
Research Methods and Procedures
Research method
Grey relational analysis is an important method of grey theory.On basis of complexity of geographical phenomena and problems,as well as people’s perception,relationships among many factors are described as being grey and hardly to be precisely measured by coefficients[5-6].Therefore,a grey system proposed grey relational analysis meaning the measurements of correlation of factors’changes in two systems upon time and objects.In development process of the systems,if the factors’ changes coincide,it means correlation keeps higher,or lower.Grey relational analysis provides a quantification method on a system evolvement,which is suitable for dynamic analysis[7-9].For example,water-related disaster shows grey relation with grain production,and it is feasible to perform quantitative research on the relationship in Hubei by grey relational analysis.
Research procedures
Considering the factors affecting productivity are many,the research selected factors of water-related disaster,including effective irrigated areas,growing structure,disaster rate,the maximal rainstorm amount,the amount of chemical fertilizer,total power of agricultural machinery,the purchasing price of agricultural products in the first half of the year as analysis factors to explore the correlation of grain production and water-related disasters and investigate the influential factors of water-related disasters on grain production(Fig.2).
The first step is to compute sequence.The research provides original sequence,reference sequence and comparative sequence.For example,the effective irrigated area,disaster rate,the maximal rainstorm amount,growing structure and grain purchasing price during 1994-2000 were taken as comparative sequences and grain yield was reference sequence(Table1),as follows:
Comparative sequence:
xm(k)={xm1(1),xm1(2),…,xm1(n)},where m represented sequence number and was given 1,2,3,…,7.
equence:
x0(k)={x1(1),x1(2),…,x1(n)},where n was the year(=7).
The 2ndstep is to perform dimensionless treatment on original data,namely,to remove every number from the sequence to form initialized sequence,as follows:
Assuming x0(k)={x0(1),x0(2),…,x0(n)}as an original sequence,ω={ω(1),ω(2),…,ω(n)},∀ω(k)∈ω⇒k∈K(1,2,…,n),it can be concluded that INIT is INIT:x(k)=ω(k)/ω(1)∀k∈K.
Given x as an initialized sequence,the following can be concluded,
The 3rdstep is to compute difference sequence between reference sequence and comparative sequence.
Finally,it should compute grey relational coefficients of grain yield with effective irrigated area,growing structure,disease rate,the amount of chemical fertilizer,total power of agricultural machinery,purchasing price of agricultural products,and the maximal rainstorm amount.
According to spatial mathematics,the coefficients can be concluded as follows:
ξm(k)=where δ represents resolution coefficient(δ∈[0,1])and is usually given 0.5.
Hence,ξm(k)is the grey relational coefficient of comparative sequence and reference sequence in the time of k.
Results and Discussions
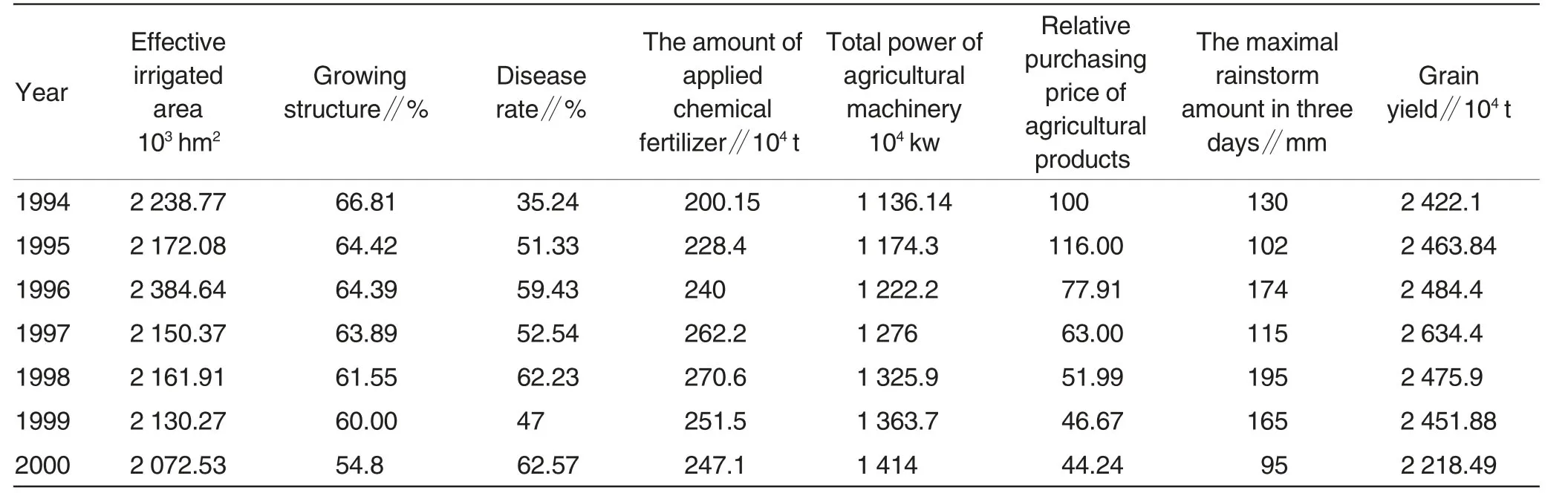
Table1 Statistics factors of grain production capacity in Hubei Province
In accordance with grey relational analysis modeling,the compute program written by Visual Basic was started to obtain grey dynamic relation of grain production with major influential factors in Hubei (Table2).The research mainly explored the correlations of effective irrigated area,growing structure,disease rate and the maximal rainstorm amount with grain production.
Grey relational analysis of disease rate and grain production
Effective irrigated areaThe effective irrigated area refers to farmland or cultivated land with irrigation in normal years,with installed irrigation facilities,water source and relatively leveled land.It is an index concerning grain productions and comprehensively reflecting progresses of water conservancy construction and drought combating.It can be concluded that the effective irrigated area showed high grey relational degree with grain production in Hubei.For example,the relational degree during 1994 -2000 averaged 0.909 8,ranking the 1stamong the factors,which indicated that it is necessary to improve treatment standards of water-related disaster,reinforce agricultural comprehensive development,advance moderate or low-yielding farmland transformation,develop water-saving agriculture,extend effective irrigated area and establish highstandard farmlands.
Growing structureSowing area is a decisive factor in grain production capacity and growing structure incorporates the proportion of grain sowing areas on total sowing area of crops.According to the research made by Yin,grain yield would grow by 0.88%if sowing area increases by 1%.The research investigated that growing structure is if high relation with grain production capacity and the grey relational degree reached 0.845 6,taking the 2ndplace,which indicated that to adjust agricultural growing structure and increasing grain sowing area will enhance grain production capacity and guarantee crop safety.
The maximal rainstorm amount in three daysIt is known that rainstorm seriously affects grain production.On basis of practical rainstorm data in Hubei,the research selected the weighed highest rainstorm amount and conducted grey relational analysis on the amounts with grain production capacity.It is proved that the relational degree averaged 0.570 0,ranking the 6th,which suggested that treatment on water-related disaster reduces loss caused by rainstorms and is of great significance for grain safety.
Disease rateDisease rate is also a factor influencing gain production,and the relational degree with grain production capacity averages 0.426 4.Hubei has subtropical monsoon climate and natural disasters become frequent,so that the disease rate has effects on grain safety.
The relationship between grain variation coefficient and water-related disaster
It can be concluded from grey relational coefficient that effective irrigated area and growing area are major factors affecting grain yield in Hubei for a long term,and the effects of disease rate and the maximal rainstorm amount in three days are generallylower.However,from grey relational coefficients,the major factors affecting grain yield tend to be changed upon natural factors and national policies.As shown in Fig.3,the coefficients of variation kept higher in 1997,1998 and 2000.Specifically,the coefficient in 1997 exceeded average value in the years,and the coefficient of effective irrigated area was the highest.What’s more,the variations of grey relational coefficient of effective irrigated area coincided with that of grain variation coefficient during 1996-1997.Therefore,it is the increase of effective irrigated that that causes the growth of variation coefficient of grain in 1997.Besides,variation coefficients in 1998 and 2000 were lower compared with average value.In 2000,grey relational coefficient was the highest of effective irrigated area,indicating that the decline of grain yield in the year was under influence of changes of effective irrigated area,causing by floods in 1998.

Table2 The grey relational degrees of influential factors of grain production in Hubei
Conclusions
Hubei is a large grain-producing province as well as a most densely populated province.Nevertheless,frequent water-related disasters have affected grain production,and provincial grain safety and economy development.According to grey relational analysis of factors influencing grain yield,effective irrigated area plays the most significant effects in grain variations in Hubei,and the relational coefficient averaged 0.909 8,followed by growing structure with a coefficient of 0.845 6,the maximal rainstorm amount in three days and disease rate.Hence,it is of significance for improving grain production capacity in Hubei Province to scientifically adjust agricultural growing structure,and enhance treatments on water-related disaster and regional standards of irrigation and drainage.
[1]XIE YG(谢永刚).The economics of water-related disasters(水灾害经济学)[M].Beijing:Economic Science Press (北京:经济科学出版社).2003,13-14.
[2]YUAN J,XU JP,SUN LJ,et al Study on the Future Climate Change and Its Influence on the Growth Stage and Yield of Wheat in Weifang City [J].Asian Agricultural Research 2015,7(3):82-84,98.
[3]HUANG LM(黄 利 民),LIU CW(刘 成 武).The features and reasons of the flood disaster in Hubei Province in modern times (湖北省近代洪涝灾害的特点及其成因分析)[J].Journal of HuaZhong Normal University(Natural Sciences)(华中 师 范 大 学 学 报 ( 自 然 科 学版)),2006,40(1):115-118.
[4]LIU CW(刘成武),HUANG LM(黄利民),WU BX (吴彬祥).Statistical properties analysis of flood and drought calamities in historical period of Hubei province(湖北省历史时期洪、旱灾害统计特征分析)[J].Journal of Natural Disasters(自然灾害学报),2004,13(3),109-115.
[5]DENG JL (邓聚龙),Grey system theory course ( 灰色系统理论教程) [M],Huazhong University of Science &Technology Press (华中科技大学出版社),1990.
[6]FANG SB(房世波),YANG WN(杨武年),PAN JJ(潘剑君),et al.Study on cultivated land reduction in the course of Nanjing’s urbanizations with gray theory(应用灰色理论研究南京市城市化进程对耕地数量的影响)[J].Journal Of Sichuan Normal University (Natural Science)(四川师范大学学报(自然科学版)),2002,25(4):432-434.
[7]FU L (傅立).Theory and application of grey system (灰色系统理论及其应用)[M].Beijing:Scientific and Technical Documentation Press(北京:科学技术文献出版社),1992.
[8]SUN YC(孙 燕 瓷),ZHANG XL(张 学 雷),CHENG XQ(程训强),et al.Gray correlative analysis of the impact from growing urbanization process on pedodiversity in Nanjing area (城市化对南京地区土壤多样性影响的灰色关联分析)[J].地理学报,2006,61(3):311-318.
[9]XU JH(徐建华).Gray correlative analysis of the impact from growing urbanization process on pedodivertsity in Nanjing area (现代地理学的数学方法)[M].Beijing:Higher Education Press(北京:高等教育出版社),1994.197-199.
[10]ZHOU HQ (周惠秋).The overall grain production capacity in Northeast China(东北地区粮食综合生产能力研究)[M].Beijing:China Agriculture Press(北京:中国农业出版社).2005.108-126.
 Agricultural Science & Technology2015年8期
Agricultural Science & Technology2015年8期
- Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- On Genetic Parameter Estimation of Xinjiang Brown Cattle’s Main Economic Characters
- Effect of Flooding and Air-drying on Nutrition Content of Soil in Embankment WLFZ of Chaohu Lake
- Influences of Nitrogen-phosphorus Ratio on the Growth and Competition of Chlorella vulga and Anabaena sp.strain PCC
- Fatty Acid Composition and Seed Quality Traits of the Transgenic Rapeseed W-4(Brassica napus L.)with Down-regulated Expression of fad2 Gene
- Research on the Construction of Remote Plant and Animal Hospital in Omnimedia Era
- Study on Physical Properties and Related Spectral Characteristics of Composited Soil with Different Ratio of Feldspathic Sandstone and Sand
