多种类杂环化合物的药理和毒理活性系数构效关系
朱志臣 王 强 贾青竹 夏淑倩 马沛生
(1天津城建大学理学院,天津300384;2天津科技大学材料科学与化学工程学院,天津300457;3天津科技大学海洋科学与工程学院,天津300457;4天津大学化工学院,天津300072)
1 Introduction
Heterocyclic compounds are important as drugs.According to Hammond,1the most important objective of synthesis is not production of new compounds,but production of properties.And for the drug discovery process,the aim is at bringing to market new drugs with desirable pharmaco-dynamicity,and favorable ADMET(Absorption,Distribution,Metabolism,Elimination,and Toxicity)properties.2-5Therefore,drug designers and toxicologists pay much attention to the beneficial and deleterious effects of heterocyclic moieties in molecules.
In view of the fact that most potential therapeutic agents and the majority of known drugs do not have experimental data available for their evaluation,theoretical calculations are very useful in the initial screening of compound libraries.Previous studies have demonstrated that quantitative structure-activity/property relationships(QSAR/QSPR)approach is successful in predicting activities,properties,and toxicities including mutagenicity(described as lnR)of aromatic and hetero-aromatic amines.6-12For example,the aryl hydrocarbon receptor binding affinity(described as pEC50)is well documented in the field of toxicology for organics.13-15Basak et al.16proposed a hierarchical quantitative structure-activity relationship(HiQSAR)approach for the pEC50prediction.According to their investigation,the topostructural(TS)and topochemical(TC)descriptors could provide a good model for the pEC50prediction with a r2value of 0.852.And with Basak et al.′smethod,the r2value is of 0.748 for lnR prediction.17In order to explore the binding mode and interaction mechanism between hydroxylated polychlorinated biphenyls and aryl hydrocarbon receptor,Cao et al.18proposed some comparative molecular similarity index analysis models by using molecular dynamics simulations.And their optimum 3D-QSAR model could show good predictive ability(r2=0.913)and good mechanism interpretability.
Recently,a universal positional distributive contribution theory for the prediction of various properties of organic compounds was developed.19-21In this theory,the specific position of a group in the molecule was considered as the position factor.Here,the position factor was used to take into account longer distance interactions,which could distinguish the overall isomer including cis-and trans-or Z-and E-structures of organic compounds for their thermodynamics properties.Moreover,our previous works suggest that it is possible to use a totally same universal framework to predict the critical properties and the thermodynamics properties of organic compounds containing various functionalities.
Very recently,a topological index was proposed based on atom characters(e.g.,atom radius and atom electronegativity etc.)by our research group,which has been successfully used for predicting the critical micelle concentration(CMC)of various surfactants,22the decomposition temperature,23toxicity of ionic liquids,24and the aquatic toxicity for various narcotic pollutants.25And,it is logical to see if this topological index could be used for prediction of pharmacological and toxicological activities of drugs.
In this work,based on this topological index and through data mining,a universal model has been developed for prediction of the two different properties.The major objectives of this study are:(i)to propose a set of norm indexes,(ii)to establish a more general QSPR model for prediction of pharmacological and toxicological activities of heterocyclic compounds,and(iii)to compare the performance of our model with other methods.
2 Methodology
2.1 Pharmacological and toxicological activity data
2.1.1 Aryl hydrocarbon(AH)receptor data
In this work,a set of 32 dibenzofurans compounds(structure shown as in Fig.1)with AH receptor binding potency values obtained from the literature26were used for QSAR model development,and the experimental data are listed in Table S1(shown as Supporting Information).
2.1.2 Mutagenicity of aromatic and heteroaromatic amines
The set of 95 aromatic and heteroaromatic amines used to study mutagenic potency(described as lnR)was obtained from Debnath et al.,27and their experimental mutation rates are listed in Table S2(shown as Supporting Information).
2.2 Proposed method
In our previous work,22the extended adjacency matrix MA,the extended interval matrix MB,the extended interval jump matrix MC,and extended distance matrix MDare defined,respectively.

The constituents of the distance matrix Mdand the extended matrix,Me,are described as follows.

Md=(aij),distance matrix aij=n
(if the path length between the atoms i and j is n)

Fig.1 Structure for the dibenzofuran data set provided in Table S1

Here,as for MA,MB,MC,and MD,a set of norm indexes have been proposed as follows.

where norm(MA,1)means the largest column sum of matrix MA,norm(MA,2)means the largest singular value of matrix MA,norm(MA,fro)is the frobenius-norm of matrix MA,and norm(MA,inf)is the infinite-norm of matrix MA.
Using these norm indexes,two QSPR models for pEC50and lnR prediction are expressed as Eq.(1)and Eq.(2).The modeling work is performed with ordinary least squares regression.
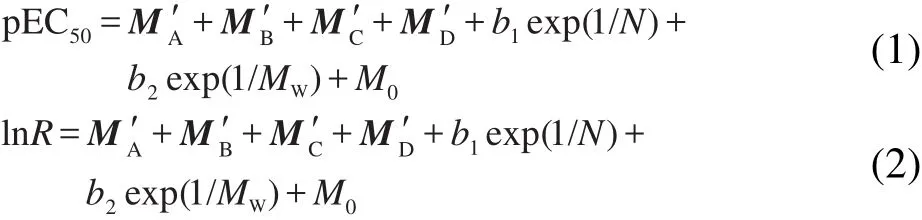
Here,N for total number of atoms,MWis molecular weight,M0is the constant added.As for parameters a,b1,b2,and M0,the regression results for prediction of pEC50and lnR are summarized in Table 1.
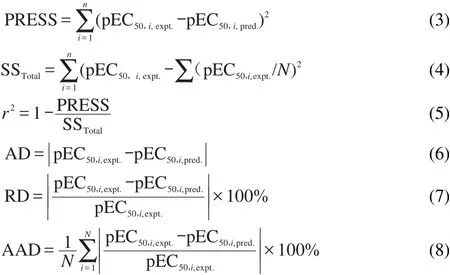
Some statistical metrics for our predictive models are as follows.PRESS stands for the predicted sum of squared error,AD stands for the absolute difference,RD means relative deviation,andAAD is the average absolute difference.

Table 1 Parameters for prediction of pEC50and lnR
3 Results and discussions
3.1 pEC50prediction results
The pEC50prediction results are provided in Table S1(shown as Supporting Information),along with the differences between the experimental and predicted values.The calculated by model Eq.(1)vs experimental pEC50scatter plot for this regression is presented in Fig.2(a).And statistical metrics for the predictive model are listed in Table 2.The results in Fig.2(a)indicate that the predicted pEC50agree well with the“experimental results”.The AAD for pEC50prediction of 32 dibenzofurans compounds is 0.403.Also,our high-quality prediction model is evidenced by a r2value of 0.876 and a PRESS value of 7.734.
3.2 lnR prediction results
The lnR prediction results are provided in Table S2,Table 2,and Fig.2(b).Results indicate that our new model Eq.(2)for predicting lnR has good overall accuracy.The AAD for lnR prediction of 95 aromatic and heteroaromatic amines is 0.702,the r2value is 0.779,and the PRESS value is 80.3.
3.3 Comparison with the HiQSAR approach
The pEC50prediction results with the HiQSAR approach proposed by Basak et al.16had been used for comparison,and the comparison results are also provided in Table S1 and Table 2.According to Basak et al.,16the topostructural(TS)and topochemical(TC)descriptors could provide a good model for the pEC50prediction with a r2value of 0.852.Using their method,the AAD for pEC50prediction is 0.452,and the PRESS value is 9.270.In addition,with the method of Basak et al.,17the AAD for lnR prediction is 0.747,the r2value is of 0.748,and the PRESS value is 87.6.Comparison results therefore indicate that obvious improvement could be obtained with our method.
In Basak et al.′sresearch,prediction for pEC50and lnR of organic compounds was based on about 72 or even more optimal descriptors which had been selected from 300 descriptors.Moreover,in their work,the number of descriptors is large with respect to the number of chemical compounds in the data set,so the ordinary least-square regression is inappropriate.
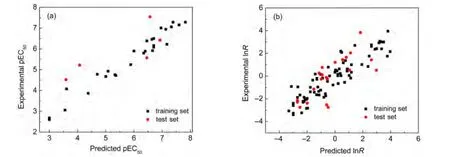
Fig.2 Scatter plot showing the correlation between predicted by our models and experimental pEC50(a)and lnR(b)
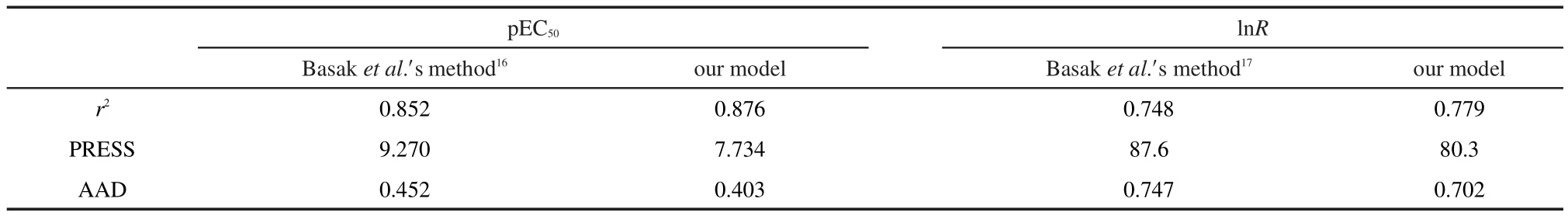
Table 2 Regression results for prediction of pEC50and lnR based on our models and Basak et al.′smethod
While,in our work,based on the extended distance matrix,a set of norm indexes have been proposed.By using these norm indexes,the structure and the composition of molecules could be determined stably,accurately,and completely,and also,the isomers could be distinguished well.Moreover,it should be strongly stated that firstly,only 17 indices are considered for property prediction of chemical compounds,among which 14 indices are deduced from these norm indexes.Secondly and more importantly,a totally same mathematical model is developed for predicting pEC50and lnR of organic compounds containing various functionalities with better prediction performance.
Therefore,it could be demonstrated that our method with these norm indexes could result in significant improvement both in accuracy and generality for predicting pEC50and lnR.Also,owing to the much less variables considered,this algorithm could perform well in the ductility,which is very important and particularly valuable for a prediction method.
3.4 Leave-one-out cross-validation
In this work,the leave-one-out algorithm was used for the validation of the prediction of our QSPR models,and results are also shown in Table 3.Results show that the r2and PRESS are acceptable and they are as good as the results calculated by Eq.(1)and Eq.(2).The calculated values by leave-one-out crossvalidation demonstrate that our QSPR models Eq.(1)and Eq.(2)based on these norm indexes have good predictive stability and reliability for predicting the pEC50and lnR.
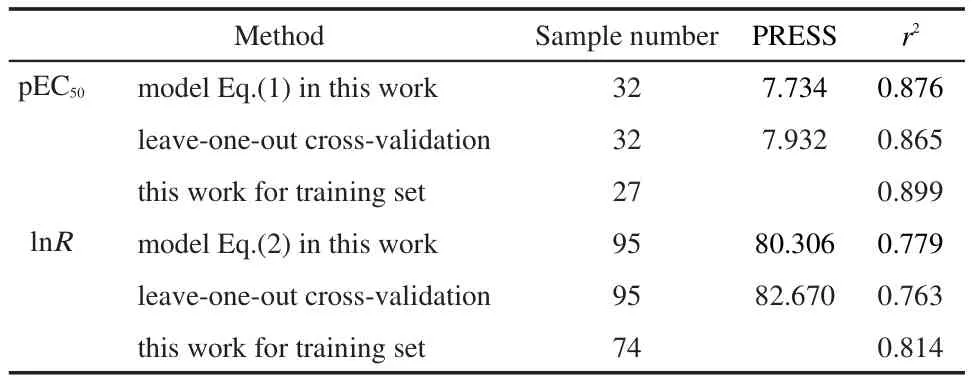
Table 3 Regression results for prediction of pEC50and lnR based on our model and predicting ability test by leave-one-out cross-validation
4 Conclusions
In this work,a set of norm indexes for predicting the AH receptor prediction(pEC50)of 32 dibenzofurans and the mutagenic potency lnR of 95 aromatic and heteroaromatic amines was proposed.Based on these norm index,a totally same mathematical model was developed for predicting pEC50and lnR of organic compounds containing various functionalities.Results indicated that pEC50and lnR were successfully predicted with a significant degree of confidence.With our method,the AAD values for pEC50prediction and lnR prediction are 0.403 and 0.702,r2values are of 0.876 and 0.779,respectively.Also,this research provides better prediction results as compared to the HiQSAR method of Basak et al.,despite the fact that lesser descriptors were considered and used in this research as compared to other models.Moreover,our results demonstrated that it is possible to use a totally same mathematical model for predicting pEC50and lnR of organic compounds containing various functionalities with better prediction performance.
Supporting Information: Experimental and predicted the aryl hydrocarbon(AH)receptor binding affinity(pEC50)of dibenzofurans and the mutagenic potency lnR of aromatic and heteroaromatic amines based on this model and Basak et al.′smethod,and a detailed procedure for the pEC50estimation have been included.This information is available free of charge via the internet at http://www.whxb.pku.edu.cn.
(1)Hammond,G.S.NorrisAward Lecture,1968.
(2) Michielan,L.;Moro,S.J.Chem.Inf.Model.2010,50,961.doi:10.1021/ci100072z
(3) Khan,M.T.;Sylte,I.Curr.Drug Discovery Technol.2007,4,141.doi:10.2174/157016307782109706
(4) Mager,D.E.Adv.Drug Delivery Rev.2006,58,1326.doi:10.1016/j.addr.2006.08.002
(5) Zhu,H.;Tropsha,A.;Fourches,D.;Varnek,A.;Papa,E.;Gramatica,P.;Oberg,T.;Dao,P.;Cherkasov,A.;Tetko,I.V.J.Chem.Inf.Model.2008,48,766.doi:10.1021/ci700443v
(6) Basak,S.C.;Mills,D.SAR QSAR Environ.Res.2001,12,481.doi:10.1080/10629360108039830
(7) Gute,B.D.;Balasubramanian,K.;Geiss,K.T.;Basak,S.C.Environ Toxicol Pharmacol,2004,16,121.
(8) Restrepo,G.;Basak,S.C.;Mills,D.Curr.Comput.Aided Drug Des.2011,7,109.doi:10.2174/157340911795677639
(9) Basak,S.C.;Mills,D.R.;Balaban,A.T.;Gute,B.D.J.Chem.Inf.Comput.Sci.2001,41,671.doi:10.1021/ci000126f
(10) Godavarthy,S.S.;Robinson,R.L.,Jr.;Gasem,K.A.M.Fluid Phase Equilib.2008,264,122.doi:10.1016/j.fluid.2007.11.003
(11) Basak,S.C.;Mills,D.;Gute,B.D.;Natarajan,R.Top Heterocycl.Chem.2006,3,39.
(12)Li,X.L.;Ye,L.;Wang,X.X.;Wang,X.Z.;Liu,H.L.;Qian,X.P.;Zhu,Y.L.;Yu,H.X.Sci.Total Environ.2012,441,230.doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.08.072
(13) Doering,J.A.;Wiseman,S.;Beitel,S.C.;Giesy,J.P.;Hecker,M.Aquat.Toxicol.2014,150,27.doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2014.02.009
(14)Gu,C.;Goodarzi,M.;Yang,X.;Bian,Y.;Sun,C.;Jiang,X.Toxicol.Lett.2012,208,269.
(15) Hankinson,O.Arch.Biochem.Biophys.2005,433,379.doi:10.1016/j.abb.2004.09.031
(16)Basak,S.C.;Mills,D.;Mumtaz,M.M.;Balasubramanian,K.Indian J.Chem.2003,42A,1385.
(17) Basak,S.C.;Mills,D.;Gute,B.D.;Hawkins,D.M.Predicting Mutagenicity of Congeneric and DiverseSets of Chemicals Using Computed Molecular Descriptors:a Hierarchical Approach.In Benigni R(ed)Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship(QSAR)Models of Mutagens and Carcinogens;CRC:Boca Raton,FL,2003;pp 207-208.
(18) Cao,F.;Li,X.;Ye,L.;Xie,Y.;Wang,X.;Shi,W.;Qian,X.;Zhu,Y.;Yu,H.Environ.Toxicol.Pharmacol.2013,36,626.doi:10.1016/j.etap.2013.06.004
(19)Wang,Q.;Ma,P.S.;Jia,Q.Z.;Xia,S.Q.J.Chem.Eng.Data 2008,53,1103.doi:10.1021/je700641j
(20)Wang,Q.;Jia,Q.Z.;Ma,P.S.J.Chem.Eng.Data 2012,57,169.doi:10.1021/je200971z
(21) Jia,Q.Z.;Wang,Q.;Ma,P.S.;Xia,S.Q.;Yan,F.Y.;Tang,H.M.J.Chem.Eng.Data 2012,57,3357.doi:10.1021/je301070f
(22)Zhu,Z.C.;Wang,Q.;Jia,Q.Z.;Tang,H.M.;Ma,P.S.Acta Phys.-Chim.Sin.2013,29(1),30.[朱志臣,王 强,贾青竹,汤红梅,马沛生.物理化学学报,2013,29(1),30.]doi:10.3866/PKU.WHXB201210265
(23)Yan,F.;Xia,S.;Wang,Q.;Ma,P.S.J.Chem.Eng.Data 2012,57,805.doi:10.1021/je201023a
(24)Yan,F.;Xia,S.;Wang,Q.;Ma,P.S.J.Chem.Eng.Data 2012,57,2252.doi:10.1021/je3002046
(25)Wang,Q.;Jia,Q.Z.;Yan,L.H.;Ma,P.S.;Xia,S.Q.doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.02.030
(26) So,S.S.;Karplus,M.J.Med.Chem.1997,40,4360.
(27)Debnath,A.K.;Debnath,G.;Shusterman,A.J.;Hansch,C.A.Environ.Mol.Mutagen.1992,19,37.doi:10.1002/em.2850190107

