多自由度裂纹转子系统非线性动力学特性分析
于 海, 陈予恕, 曹庆杰
(哈尔滨工业大学 航天学院,哈尔滨 150001)
裂纹是指材料在应力或环境(或两者同时)作用下产生的裂隙。 转子是旋转机械的重要部件,转轴由于材料缺陷、加工缺陷、或者疲劳等原因会出现裂纹,其潜在危害性与一般故障的危害性相比较要严重得多,因此转轴裂纹故障的研究特别引起工程界的重视。自从六十年代末期在汽轮机轴上发现裂纹以来,各国学者纷纷开展裂纹转子振动特性的研究工作。最简单的裂纹转子模型是Jeffcott 裂纹转子,并假设裂纹产生在转盘根部。这种简单的单盘转子模型略去了陀螺效应和支承弹性 ,方便了数学处理,计算所得结论揭示了裂纹转子振动的最基本特征,因而大部分研究者[1-3-8]都采用这一模型。在这基础上,有的研究者开始考虑支承(弹性支承[9],油膜轴承[10-12]) 和多条裂纹[13-14]的影响,试图对更一般的模型进行研究,深入探求裂纹转子的振动特性。另外,一些学者先用有限元法[15-17-19]、传递矩阵法[20-21]以及能量原理结合假定模态法[7,21]对裂纹转子状态空间离散化,然后对时间直接积分,得到裂纹故障系统的动力学响应。朱厚军等[22]分析了刚性支承Jeffcott裂纹转子在转轴涡动时的耦合振动。Seklar[23]研究了刚性支承裂纹转子通过临界转速时的瞬态特征。Tsai[24]在对裂纹转子的文献作了大量调查的基础上, 并用传递矩阵法研究了具有横向裂纹的刚支转子动力学特性。Gasch[25]对具有横向裂纹的单盘转子系统动力学的一些研究成果进行了总结和分析;杨积东等[26]对裂纹扩展过程进行了动力学仿真,发现裂纹引入的非线性因素将对转子动力学行为产生重大影响。褚福磊等[27]对裂纹转子系统中现有的几种刚度模型进行简略的总结后,提出两种新的确定刚度的方法。曾复等[28]研究了单盘刚性支撑转子的分岔现象。何成兵等[29]研究了裂纹转子弯扭耦合振动的非线性特性分析。这些文献对裂纹转子系统的动力特性进行了研究,获得了一些非常有价值的结论,但多采用较简单的支撑(集中于刚性支承或是线性油膜轴承)和单盘转子,且很少对于滑动油膜支撑的多盘非线性含裂纹转子的二分之一亚谐共振进行分析。
POD(Proper Orthogonal Decomposition)方法最早是由Loeve(1945)和Karhunen (1946)处理信号时提出来的,随着计算工具的发展,正交模态分解技术(POD) 已经在各个领域有了广泛的应用[30-31]。近些年来,一些学者将其应用到简单结构的非线性动力系统降维中[32-33],虽然有一定效果,但降维后系统仍保留了较高的自由度数,无法应用现有的分岔理论对之进行理论分析。
本文目的是利用现有分岔理论,通过引入新的降维方法,实现对高维裂纹故障转子的非线性动力学特性的理论分析。利用拉格朗日原理建立了具有26个自由度的含有裂纹故障的高维非线性动力学模型。为实现对其进行分岔理论分析,引进改进的POD方法成功将高维非线性系统降为两自由度等效的非线性系统。数值模拟结果显示降维系统具有与原系统一致的非线性动力学特征;进而利用C-L方法对其进行分岔分析,讨论了系统参数与系统动态行为之间的关系,得到了裂纹转子各种不同分岔模式,得到了裂纹二分之一亚谐共振条件下的非线性动力学特征。该结果对高维转子-轴承系统的裂纹故障诊断及其治理,以及非线性动力学设计有一定指导意义。
1 含裂纹故障系统建模
1.1 裂纹模型

图1 裂纹截面示意图
图1是裂纹截面示意图,a为裂纹深度,β为不平衡量与裂纹法向之间夹角,R为转轴半径。设裂纹法向与x轴初始夹角为0。在考虑重力占优的情况下,裂纹开闭函数f(φ)可描述为转角ωt的函数[34],若k为转轴的裂纹刚度,Δkξ, Δkη分别为裂纹法向和切向刚度变化量,则含裂纹转轴的刚度为:
其中:
1.2 转子系统模型与建模
考虑裂纹转子系统模型,图2为该模型的示意图,假设在如图位置处发生裂纹, 转子两端是由两个相同的滑动轴承支撑,Oi(i=1,…,13)是转盘的几何中心;mi(i=1,…,13)是转盘的等效质量;ci(i=1,…,13)是等效阻尼;ki(i=1,…,13)是转轴的等效刚度。
根据拉格朗日方程的建模方法,得到系统方程和无量纲化后的方程(见式(1)与式(2)),
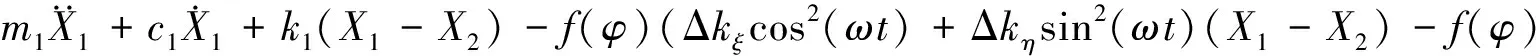
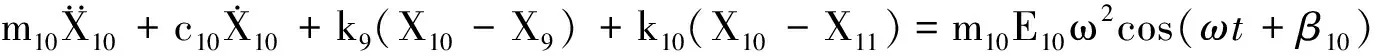
利用:
可得无量纲化后的系统方程:
(2)
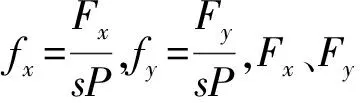
其中在x和y方向的非线性油膜力表达式为:
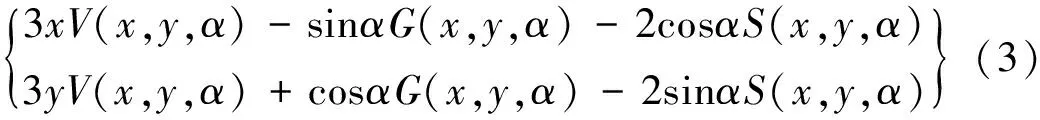
式中
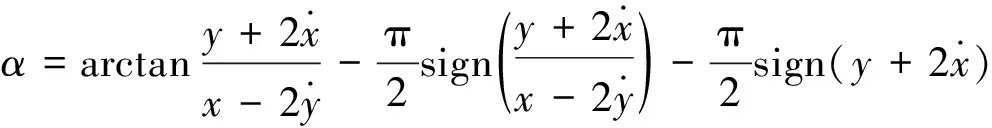
为方便计算讨论,将多自由度非线性系统动力学方程可以写为:
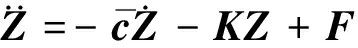
(4)
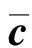
为对(4)式进行数值求解,取系统的参数的计算数值如下:
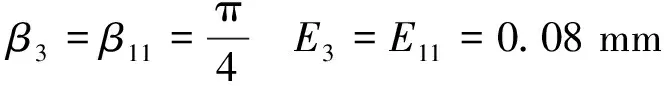
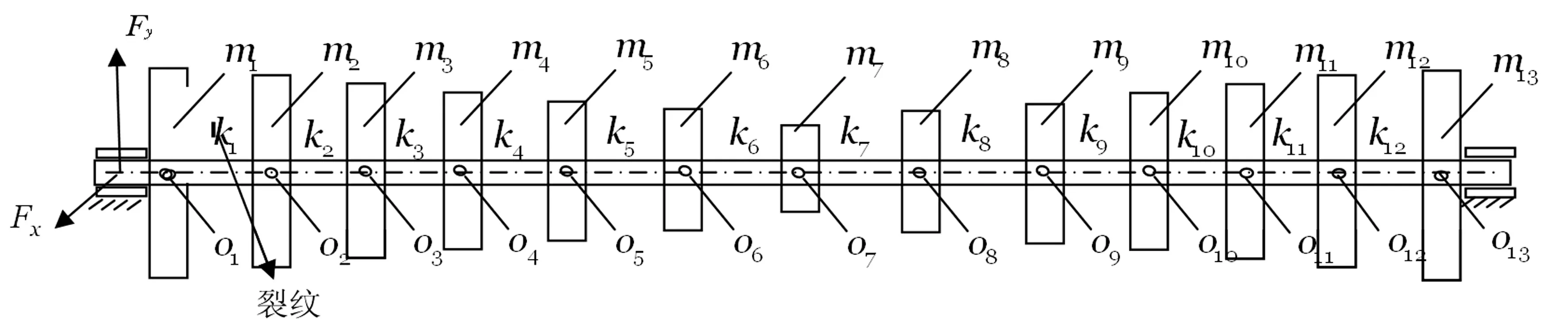
图2 26自由度裂纹转子模型
2 系统降维
2.1 降维系统
我们采取以下步骤对26个自由度含裂纹故障系统进行降维:
(1) 调整含裂纹故障系统的参数,使得系统分岔图呈规律性模式(如图3(a));
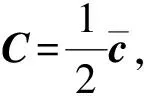
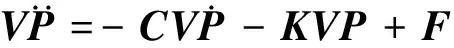
(5)
(3) 在给定初始条件和转速下,通过实验或者数值仿真,获取系统(5)各个自由度的过渡过程位移信息,记为z1(t),z2(t),…,zM(t),其中每个自由度产生的N个点等时间间隔位移序列,记为zi=(zi(t1),zi(t2),…,zi(tN))T,i=1,…,M,这些时间序列可形成矩阵χ=[z1,z2,…,zM],χ为N×M阶。计算自相关矩阵T=χTχ。求出其特征向量为φ1,φ2,…,φM,对应的特征值为λ1>λ2>…>λM。
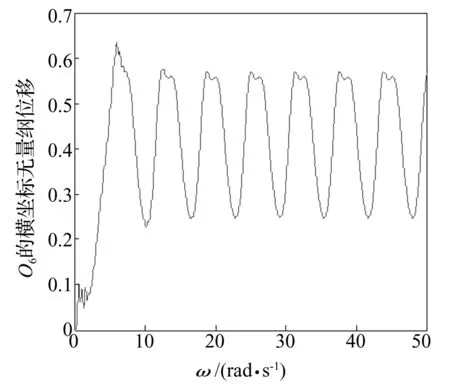
图3 在给定初始条件下时间历程图
(4) 设T=χTχ的前n阶特征向量组成矩阵V对系统坐标Z进行坐标变换,获得一组新坐标P,Z=VP,带入方程(5):
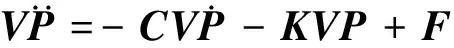
(6)
两端左乘(VTV)-1VT:

(7)
设
CR=(VTV)-1VTCV,KR=(VTV)-1VTKV
FR=(VTV)-1VTF
则有:
(8)
方程(8)即为降维后系统。
2.2 本文模型降维系统
通过图3可以看出,系统在给定初始条件下,0-6π时间内,系统处于过渡过程,按照3.1节中的步骤,获得的坐标变换矩阵为

按2.1节步骤,可获得降维系统的方程为
(9)
3 降维效果比较
图4给出原系统与降维系统分岔图的对比。从对比可以看出降维系统基本保持原系统的动力学特性,尤其较好的保留了原系统二分之一亚谐故障特性,得到较好的降维效果。
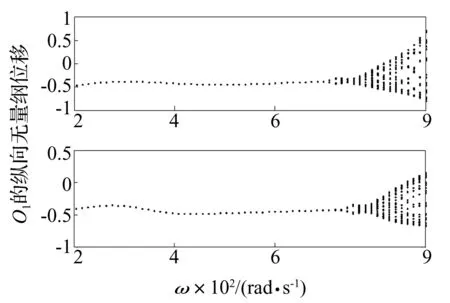
图4 分岔图(a) 原故障系统系统 (b)降维系统
4 C-L方法
4.1 二分之一亚谐共振

(10)
式中
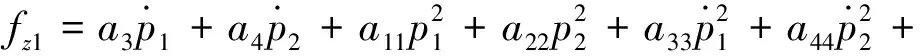
(11)

(12)
并取如下坐标平移公式
(13)
则方程(9)可化为

(14)
其中
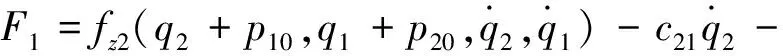
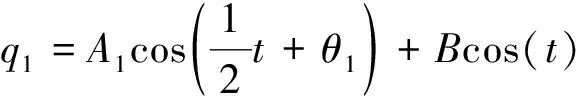
其中,A1,A2,θ1,θ2为时间t的慢变函数。
采用平均法,得到平均方程:

令等号右端等于0,忽略掉小项,消去θ1,θ2,可得分岔方程
F7=0
F8=0
(15)
4.2 二分之一亚谐共振模式分析
为进一步讨论原系统的动力学特性,全面分析系统参数与系统动态行为的关系,参照C-L方法,选取裂纹影响系数α与裂纹转盘处无量纲阻尼c2,其两个状态变量的转迁集为[34]:


表1 α—c2平面分岔情形
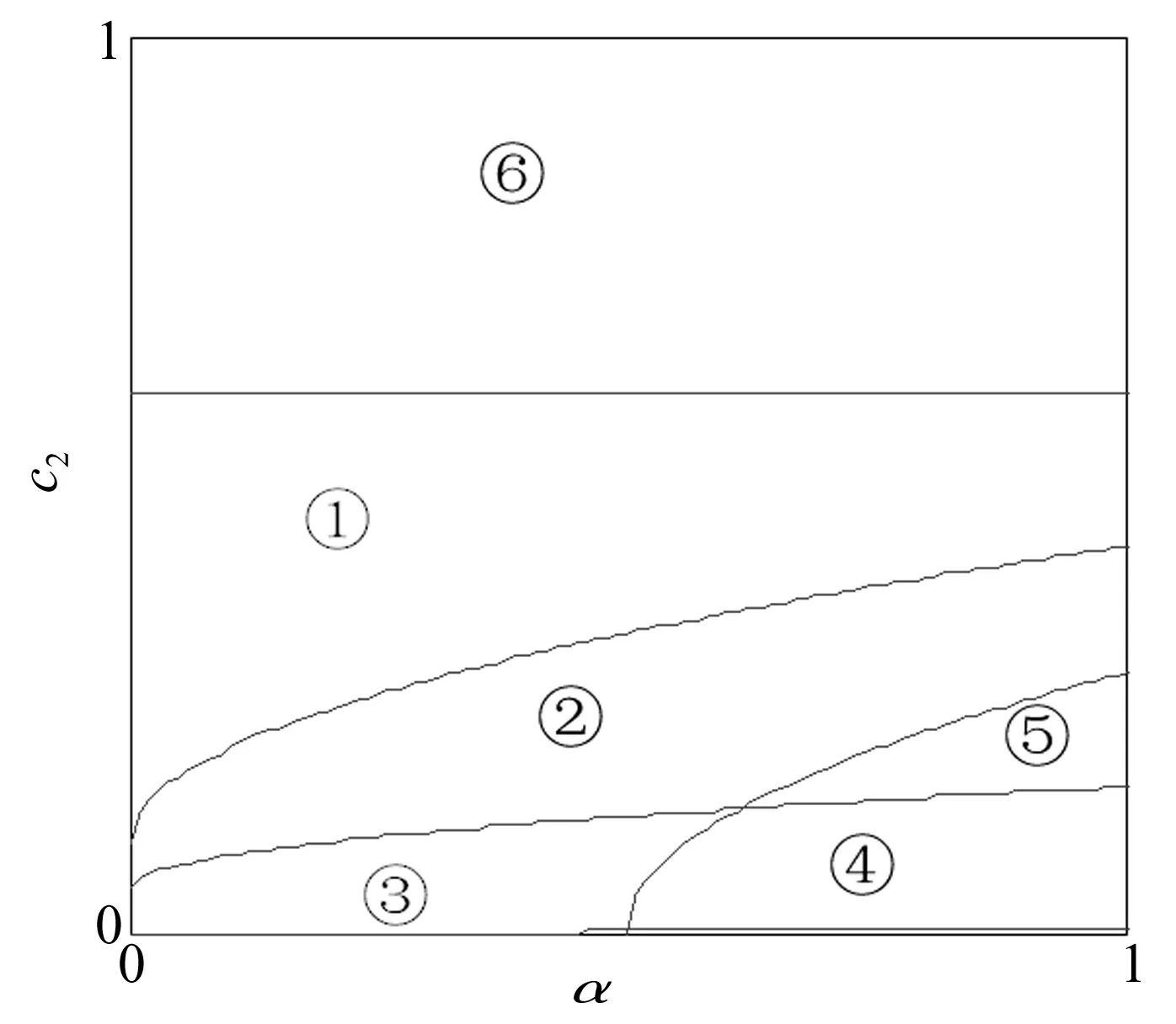
图5 α-c2转迁集
本文首次利用C-L方法对降维后两个自由度含裂纹故障的转子系统进行分岔分析,讨论了系统参数与系统动态行为之间的关系,得到了二分之一亚谐共振附近系统不同的分岔模式(见表1)。从图中,系统在系统二分之一亚谐共振处,随着系统参数的变化,存在分岔、滞后等复杂的非线性动力学现象,进而反映了实际系统可能出现的各种复杂动力学现象。该分析为26个自由度含裂纹转子系统的参数优化及设计提供理论指导。
5 结 论
本文研究了含裂纹故障的某低转子动力学行为,根据实际系统建模后,引入改进的POD方法成功将26个自由度系统降维为2个自由度等效模型,通过数值对比,说明降维方法的有效性,为实际大型系统的降维提供一条途径。为研究该系统的动力学行为,利用C-L方法对降维后系统进行分岔分析,讨论了系统参数与系统动态行为之间的关系,得到了裂纹转子系统二分之一亚谐共振附近系统不同的分岔模式,为转子-轴承系统的裂纹故障诊断及其治理,以及非线性动力学设计提供理论依据。
参 考 文 献
[1]Gasch R. A survey of the dynamic behavior of a simple rotating shaft with a transverse crack[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1993, 160 (2): 313-332.
[2]Meng G. The nonlinear influences of whirl speed on the stability and response of a cracked rotor[J]. Journal of Machine Vibration, 1992, 4: 216-230.
[3]Sekhar A S and Prabhu B S. Condition monitoring of cracked rotors through transient response[J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 1998, 33 (8): 1167 -1175.
[4]高建民,朱晓梅. 裂纹转子的动力特性研究[J]. 西北工业大学学报,1992,10 (4):434-439.
GAO Jian-min, ZHU Xiao-mei. O n dynamic behavior of cracked rotors[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechincal University, 1992, 10(4): 434-439.
[5]赵玉成,李舜酩,许庆余. 裂纹转子的弯扭耦合振动特性分析[J].应用力学学报,1999,16 (1) :60-64.
ZHAO Yu-cheng, LI Shun-ming, XU Qing-yu. Analysis on bending-torsional coupled vibration of cracked rotor[J]. Chinese journal of Applied Mechanics, 1999, 16(1): 60-64.
[6]Zheng J B, Meng G. Bifurcation and chaos response of a nonlinear cracked rotor[J]. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 1998 , 8 (3) : 597-607.
[7]史东锋,屈梁生. 转子横向裂纹故障的诊断信息提取[J]. 化工机械, 1998, 25 (5):275-279.
SHI Dong-feng, QU Liang-sheng. Extraction of diagnostic information of transverse crack faults of rotors[J]. Chemical Engineering and Machinery, 1998, 25(5): 275-279.
[8]Meng G, Han E J. Dynamic response of a cracked rotor with some comments on crack detection[J]. Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, 1997, 119 (2): 447-455.
[9]郑艳萍 朱厚军. 具有弹性支撑的裂纹转子的动力特性分析 [J]. 汽轮机技术,2009,51(5):353-356.
ZHENG Yan-ping, ZHU Hou-jun. Analysis of the dynamic behavior of a cracked rotor with elastic bearings[J].Turbine Technology, 2009, 51(5): 253-356.
[10]Wu M C, Huang S C. Vibration and crack detection of a rotor with Speed-dependent bearings[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Science, 40 (6): 545-555.
[11]郑吉兵. 裂纹转子的动态响应、稳定性及分叉与混沌[D]. 西安:西北工业大学, 1996.
[12]Prabhu B S, Sekhar A S. Severity estimation of cracked shaft vibration with fluid film bearings[J]. Tribology Transactions, 1995, 38(3): 583-588.
[13]Sekhar A S. Vibration characteristics of a cracked rotor with two open cracks[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1999, 223 (4): 497-512.
[14]Tsai T C, Wang Y Z. The vibration of a multi-cracked rotor[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Science, 1997, 39 (9): 1037-1053.
[15]Sekhar A S,Prabhu B S. Vibration and stress fluctuation in cracked rotor[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1994, 169 (5):655-667.
[16]Papadopoulos C A, Dimarogonas A D. Stability of cracked rotors in the coupled vibration mode[J]. Journal of Vibration, Acoustics, Stress, and Reliability in Design, 110: 356-359.
[17]Sekhar A S,Prabhu B S. Crack detection and vibration characteristics of cracked shafts [J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration,1992 ,157 (2) : 375-381.
[18]Bachschmid N,Diana G. The influence of unbalance on cracked rotors[C]. Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on fault of Vibration in Rotor. Mach., 1984: 193-198.
[19]Mayes I W,Davies, W G R. A method of calculating the vibrational behavior of coupled rotating shafts containing a transverse crack [C]. 2nd International Conference on fault on Vibration in Rotor. Mach., 1980:17-27.
[20]Tsai T C,Wang Y Z. The vibration of a multi-cracked rotor[J].International Journal of Mechanical Science, 1997, 39 (9) : 1037-1053.
[21]Huang S C, Huang Y M, Shieh S M. Vibration and stability of a rotating shaft containing a transverse crack[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1993, 162 (3):387-401.
[22]朱厚军,赵玫,王德洋. Jeffcott 裂纹转子动力特性的研究[J]. 振动与冲击,2001,20(1),1- 4.
ZHU Hou-jun, ZHAO Mei, WANG De-yang. A study on the dynamic of a cracked Jeffcott rotor[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2001, 20(1) : 1- 4.
[23]Sekhar A S, Prabhu B S. Transient analysis of a cracked rotor passing through critical speed [J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1994, 173, 15-21.
[24]Tsai T C, Wang Y Z. Vibration analysis and diagnosis of a cracked shaft [J]. Journal of Sound and vibration, 1996, 192(3):607-620.
[25]Gasch R. A survey of the dynamic behaviour of a simple rotating shaft with a transverse crack[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1993, 160(2):313-332.
[26]杨积东,许培民,闻邦椿. 裂纹扩展对转子动特性的影响[J]. 东北大学学报,2001,22(2): 203-206.
YANG Ji-dong, XU Pei-min, WEN Bang-chun. Character of a flexible rotor with crack propagation[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2001, 22(2):203-206.
[27]林言丽,褚福磊. 裂纹转子的刚度模型[J]. 机械工程学报,2008,44(1):114-120.
LIN Yan-li, ZHU Fu-lei. Stiffness models for the cracked shaft of the rotor system[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2008, 44(1): 114-120.
[28]曾复,吴昭同,严拱标. 裂纹转子的分岔与混沌特性分析[J]. 振动与冲击,2000,19(1):40-42.
ZENG Fu, WU Shao-tong, YAN Gogn-biao. Analysis of bifurcation and chaos on a cracked rotor[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2000, 19(1): 40-42.
[29]何成兵,顾煜炯,宋光雄.裂纹转子弯扭耦合振动非线性特性分析[J].振动与冲击,2012,31(9):33-38.
HE Cheng-bing,GU Yu-jiong,SONG Guang-xiong.Nonlinear analysis on coupled flexural and torsinal vibration of cracked rotor[J].Journal of Vibration and Shock,2012,31(9):33-38.
[30]Glosmann P, Kreuzer E. Nonlinear system analysis with Karhunen-Loeve transform[J]. Nolinear Dynamics, 2005, 41: 111-128.
[31]Steindl A,Troger H. Methods for dimension reduction and their application in nonlinear dynamics[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2001, 38: 2131-2147.
[32]Kerschen G, Feeny B F, Golinval J C. On the exploitation of chaos to build reduced-order models[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2003, 192: 1785-1795.
[33]Kappagantu R, Feeny B F. An "optimal" modal reduction of a system with frictional excitation[J]. Journal of Sound and vibration, 1999, 224(5): 863-877.
[34]李军,陈予恕. 低压-发电机转子系统弯扭耦合情况下的组合共振研究[J].应用数学和力学,2011,32(8):895-911.
LI Jun, CHEN Yu-shu. Study on combined resonance of low pressure cylinder-generator rotor system with bending-torsion coupling [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2011, 32(8): 957- 972.
[35]Chen Y S, Leung A Y T. Bifurcation and Chaos in Engineering [M]. London, Springer, 1998.

