非接触电导检测器的设计与联用技术进展
朱西雷,葛叶刚,康琪,申大忠
(山东师范大学化学化工与材料科学学院,山东济南 250014)
非接触电导检测器的设计与联用技术进展
朱西雷,葛叶刚,康琪,申大忠*
(山东师范大学化学化工与材料科学学院,山东济南 250014)
毛细管电泳中的非接触电导检测技术自1998年问世以来受到了广泛的关注。随着理论研究的深入,检测器的设计不断改进以提高其响应灵敏度,同时使它更便于和已有的仪器设备联用,并应用于微流控芯片电泳中。分析对象也从最初的小无机离子拓展到有机组分和生物大分子,随着商品化检测器的出现,该技术趋于成熟。该文侧重介绍近年来有关该传感器的设计改进、与其它检测器联用、与样品富集技术联合方面的研究和应用进展。
非接触电导检测;毛细管电泳;微流控芯片电泳;联用技术
combination technique
0 引言
1998年Zemann[1]与do Lago[2]同时报道了一种可用于毛细管电泳的电容耦合非接触电导检测器(Capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detector,C4D),使非接触电导法这一被冷落了近半个世纪的检测技术再次受到关注。C4D的检测灵敏度与紫外(UV)检测器大致相同,但是紫外检测需在毛细管上制备透光的窗口,去除保护层的毛细管很脆弱,并要求检测光路的精密校准。而C4D所用管状电极,可以套在毛细管保护层外使用,并根据需要能沿毛细管滑动,制备更为简便,并可以用于内径10 μm的毛细管上,因此在检测离子组分特别是那些缺乏紫外、荧光、电化学活性的无机小离子、有机离子组分方面具有一定的技术优势。与接触电导检测器相比,C4D的电极安放在毛细管外,既避免了在毛细管上钻孔安放传感电极的技术难题,同时还解决了与分离电压隔离的问题。电极不与溶液接触,避免了溶液与电极表面的化学反应、气泡附着、结垢等影响电极稳定性与重现性的问题,因此在微通道这种特定环境下,C4D更具优势。
近年来有关C4D的研究与应用的文献报道很多,不少学者从不同角度对C4D的研究进展进行了总结[3~11]。该文选取部分有代表性的研究工作,简要介绍近几年C4D在改进构造设计、与其它检测器联用和与样品处理技术联用方面的研究和应用进展。
1 C4D的构造设计
图1为do Lago课题组所报道的C4D检测池的结构示意图,它与Zemann所报道的检测池的差异在于在两敏感电极之间增设了接地屏蔽板,这种构造有效地降低了两电极之间通过空气的泄漏电流,能够提高C4D的信噪比,成为后来C4D设计改造的基础。
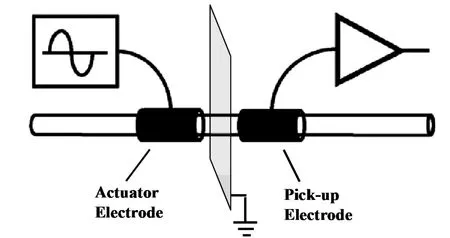
图1 用于毛细管电泳检测的C4D的构造与原理示意图(非比例尺)Fig.1Schematic diagram of a C4D cell in capillary electrophoresis(not to scale)
由图1可见,在CE中使用的C4D,其检测池的构造已大体固定,可变化的因素并不多,通常仅对电极长度、电极间距、毛细管内径、外径可以进行优化,因此有关C4D的设计改造偏向更便于在已有的毛细管电泳仪中使用和更好的响应性能。
Tuma等[12]设计了如图2所示的半圆电极型C4D检测池,其特点是更换或移动毛细管方便,尤其是采用电极在同侧的构造(I)时传感电极位置不发生改变,它的检测灵敏度略低于两电极在异侧的构造(II),这种构造的毛细管稳定性良好,其固定模具有利于安放光导纤维实现C4D和UV检测联用。
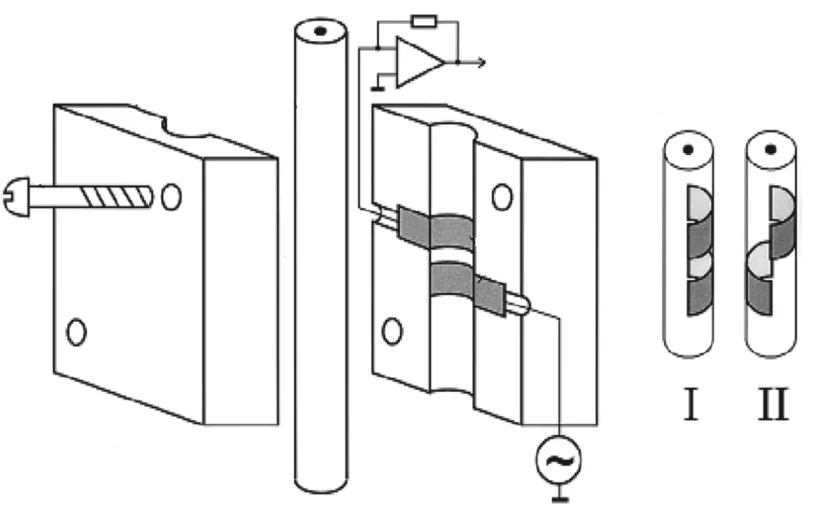
图2 半圆电极型C4D的构造示意图[12]Fig.2Scheme of C4D cell using semicircular electrodes and the electrode configuration[12]
Vuorinen等[13]将C4D集成在商品化毛细管电泳仪中的测试架内,在不影响UV检测的情况下,同时获得C4D的响应信号,测定其中无UV吸收的组分。Macka等[14]将C4D进行了微型化设计,使C4D更便于和其它检测器联用,检测系统更加紧凑(见图3)。

图3 常规C4D(左)与微型化C4D(右)[14]Fig.3Photographs of conventional C4D(left)and micro-C4D(right)[14]
do Lago等[15]制造了一款非常紧凑的微型化C4D检测系统,将电极对和整个电路整合到一块双面印刷电路板上,整个检测器的体积只有6.5 cm3。Knjazeva等[16]应用PEEK材料毛细管-C4D分析检测了肽、蛋白质等其它生物样品,并将其与传统的石英毛细管柱进行了比较,研究表明PEEK毛细管的阴极电渗流(EOF)非常低,即使在极限pH值下也非常稳定,分离效率和分辨率要好于石英毛细管,保留时间、峰面积的重现性也优于石英毛细管,并且PEEK毛细管所需实验条件也比较简单,不需要对管壁进行复杂的修饰。
Yang等[17]将电感耦合式非接触电导检测器应用于CE,该系统由高频信号发生器、磁环、线圈、取样电阻构成(见图4),该文对磁环直径、毛细管的位置、线圈的匝数、激励信号的电压、频率、取样电阻等参数的影响进行了测试和优化,并用于无机离子、氨基酸的分离检测。Pham等[18]构建了利用C4D同时分别测定阴阳离子的双通道CE系统,并成功检测了地下废水中的铵盐。
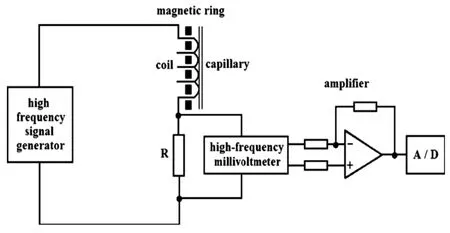
图4 电感耦合非接触电导检测器的原理图[17]Fig.4The electric circuit of the electromagnetic induction detector[17]
和CE中C4D结构变化有所不同,在微流控芯片电泳(MCE)中C4D可以和芯片的设计与加工同时进行,因此改进方案较多。2002年,Bastemeijer等[19]将非接触电导检测用于微芯片电泳,他们在玻璃基底上制备了一种四电极C4D检测池(见图5),敏感电极上覆盖30 nm SiC绝缘层确保与溶液中的分离电压隔离,因为这种装置绝缘层薄,因此有良好的响应灵敏度和线性关系,但电极加工制作工艺复杂而且要求很高,造价不菲。

图5 用于MCE中的四电极C4D检测器实物照片与构造示意图[19]Fig.5Schematic diagram of the four-electrode C4D in microchip electrophoresis[19]
相比之下,Wang等[20]提出的如图6所示的C4D设计构造,具有制备简单的优点,在MCE中得到了推广应用,该设计中使用金属箔为电极,贴在微流控通道之上,不需要专门设计的芯片。
Kubáň等[21]研究了检测池的尺寸、电极放置方式和操作参数对微流控芯片中C4D的输出电压、峰高和信噪比的影响,结果表明反向平行电极能得到更好的灵敏度。在C4D电极反向平行的情况下,绝缘层厚度从125 μm增大到425 μm,分析信号下降了75%。出于机械强度方面的考虑,MCE中盖片不能太薄(>0.1 mm),但盖片太厚会使C4D的灵敏度受到影响,因此,使用薄的绝缘层成为改进C4D灵敏度的方式之一。如Tanyanyiwa等[22]使用如图7(B)所示的沟槽盖板构造C4D,配合500 V的激励电压,有效提高了信噪比,测定K+、Na+、Mg2+的检测下限分别达到0.49、0.41、0.35 μmol/L。
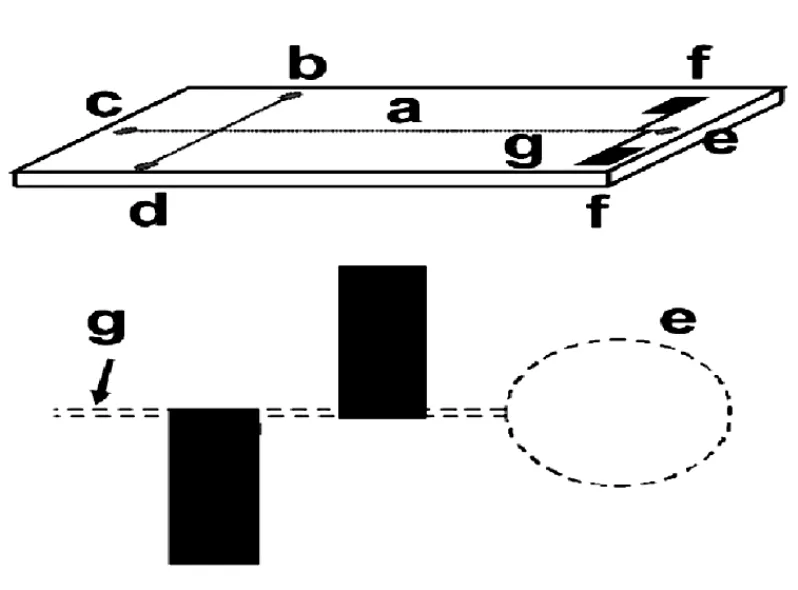
图6 用于微流控芯片的C4D示意图[20]Fig.6Microchip electrophoretic system with C4D[20]
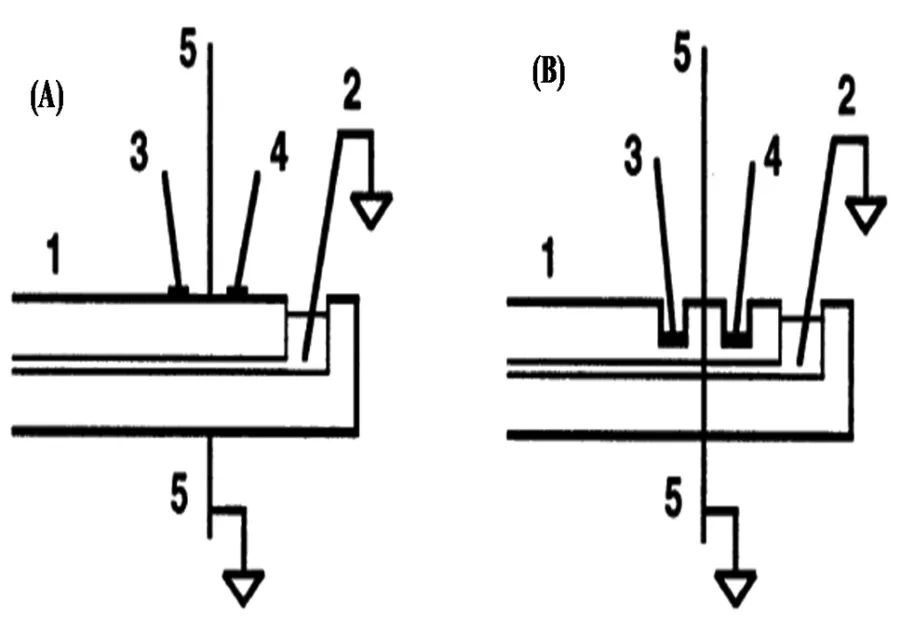
图7 盖玻片上制备C4D(A)和沟槽C4D(B)[22]Fig.7Cross-sectional view of the two cell arrangements without(A)and with(B)troughs for the detector electrodes[22]
Chen等[23]设计了如图8的C4D检测系统,芯片与检测器独立便于更换芯片,它们采用薄的玻璃覆盖板降低管壁阻抗,比较了正弦、方波、三角波信号源对C4D响应的影响,表明使用正弦波得到了最好的信噪比。Lichtenberg等[24]设计了如图9所示的内嵌电极式C4D,传感电极与分离通道之间的绝缘层厚度仅10~15 μm,且电极宽度只有400 μm,不仅灵敏度高,而且池体积也小,但存在加工要求高的不足。Xu等[25]将绝缘层的厚度进一步减小到1 μm,使C4D的检测灵敏度与接触电导法相同。
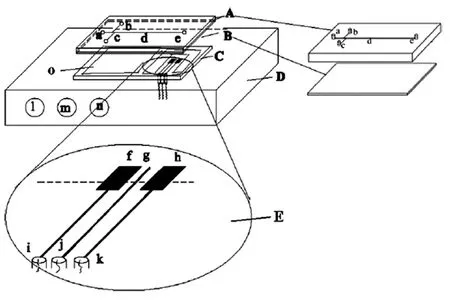
图8 可替换MCE的C4D设计示意图[23]Fig.8Schematic illustration for glass microchip system[23]
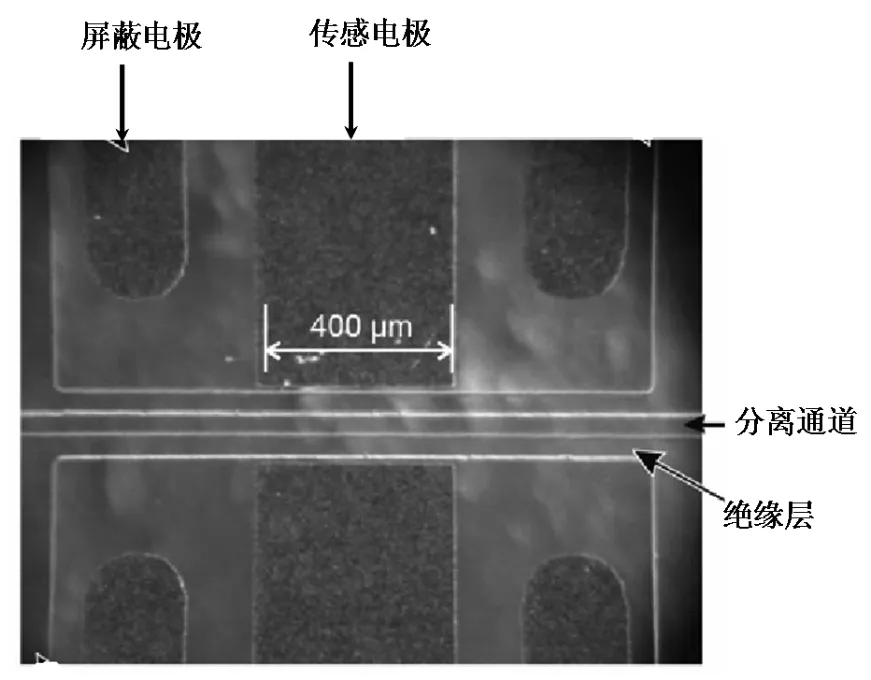
图9 内嵌电极式C4D的构造结构图[24]Fig.9Schematic diagram of the integrated in-plane electrodes C4D[24]
Wang等[26]报道了一种适用于聚甲基异丙烯酸酯(PMMA)微芯片电泳非接触电导检测器的银墨电极制备新方法,该方法使用丝网印刷技术,可批量制备。Liu等[27]设计了一款绝缘层厚度可控的聚二甲基硅氧烷(PDMS)电泳芯片非接触电导检测器,它是将一层PDMS旋转涂覆在一块带有Pt微电极的玻璃片上形成绝缘层,然后与另一块带有PDMS通道的盖板粘合在一起形成微芯片,绝缘层的厚度可精确控制在微米以下,实验结果表明当绝缘层厚度为0.6 μm时,Na+检测下限为0.07 μmol/L。
Mahabadi等[28]采用顶-底双电极构造,增加了敏感电极与溶液的耦合区间,相比单面C4D,其电力线在分离通道中的分布更为均匀,因此灵敏度也较单面C4D有所提高。Fercher等[29]报道了如图10所示的差分C4D检测系统,在分离通道的两端分别设置两个不同的检测区域,将两C4D的输出信号放大后相减,以差分信号用于分析测定,这种方式的优点是可以抵消因杂散电容引起的高基线水平,减小基线漂移,从而提高信噪比和灵敏度30~60倍。
Kumar等[30]设计了一款微型化的便携式MCE-C4D检测系统,将芯片、检测电路都设计到一个便携式的小盒子中,整个装置尺寸为19 cm×12 cm×8 cm,C4D电极被集成在聚合物(PMMA)电泳芯片上,用USB与便携式电脑相连接,用来提供电能、读取数据和控制系统,C4D检测所用的高压频率为3.6 MHz。用该装置在30 s内分离了肼、甲基肼、1,1-2甲基肼,检出限分别为12、36、340 ng/mL。Kang等[31]基于谐振原理的阻抗湮灭方法,将一压电石英晶体谐振器引入非接触电导检测器中,使检测电路总阻抗的虚部在谐振条件下为零,大大降低了整个电路的阻抗值,使检测灵敏度得到较大提高,获得了与接触电导法相近的灵敏度。Huang等[32]开发了一种适合在毫米级管内测电导的新型C4D传感器,引入串联谐振原理和新的屏蔽结构后,大大降低了在测量电导时耦合电容和杂散电容的不利影响,改进了C4D传感器的性能,可以在较大管道内(内径为7.8 mm)实现电导测量。

图10 双C4D差分测量装置及检测电路示意图[29]Fig.10Exploded view(A),enlarged detector areas(B,C)of the LTCC device(not to scale)and differential measurement setup with postamplification stage[29]
Wang等[33]设计了一种应用于MCE的壁面射流型C4D电导检测器,并用该装置分离检测了爆炸相关物质甲基铵、铵、钠离子,与普通的非接触电导检测相比灵敏度提高了10倍以上。Blanco等[34]采用一种简易的连续注射CE-C4D装置,快速分析简易爆炸装置(IEDs)中残余物的无机阴离子,分析时间为90 s,检测下限为23~50 μg/L。Zhao等[35]设计了一种新型基于氧化铟锡(ITO)镀膜玻璃的MCE-C4D,该芯片通过丝网印刷和蚀刻技术制成,具有很高的稳定性和重现性,用该芯片检测复方药物中的氨基比林、咖啡因,两种物质可在1 min内得到完全分离,检出限分别为8、3 μg/mL。
Lima等[36]将同轴电极整合到了微芯片上,并证明将这种电极应用到压力驱动流平台的C4D上可有效提高灵敏度和检测能力。Thredgold等[37]在聚二甲基硅氧烷(PDMS)微芯片上为C4D制备了注入式金属镓电极,具有制造工艺快速、简便的优点。Zheng等[38]设计了可获得更高灵敏度的双输入电容耦合非接触电导检测器(DIC4D)装置,该检测器由两个输入电极和一个输出电极组成,当对每个输入电极施加具有相同幅度和不同相位的两个交流电压时,利用不同相位的两个信号的叠加,减小了输出电极的等效电阻,提高了检测灵敏度。
2 C4D与其它检测器联用
C4D的传感电极不与待测溶液接触,无需光学检测窗口,位置可以移动,这些特点使它与其它检测器具有良好的兼容性,在CE或MCE中将C4D与其它检测器联用,可以检测同种或不同种类的组分,提供更多的化学信息,提高分析方法的选择性,近年来这方面的研究报道呈增长趋势。Wang等[39]设计了一种应用于芯片毛细管电泳的非接触电导/安培双检测器装置,在一个分离通道上的这两种检测模式可以同时检测被分析物的离子和电活性特征,有利于提高重现性,增强峰确认能力,两个检测器相互独立进行相关组分检测。Tuma等[40]比较了C4D和二极管矩阵光度检测器(DAD)的性能,实验条件是以乙酸为背景电解质,CE分离肌胺酸酐、精氨酸以及3-甲基组氨酸,研究发现两种检测器的实验条件类似,可以作为CE的双重检测器。乙酸浓度的变化对C4D的噪声影响要小于DAD检测器,但对它的响应影响要大,乙酸浓度高时C4D的检测效果要好于DAD,反之DAD的检测效果更好。Vázquez等[41]改进了C4D/安培双检测器检测系统设计,分析检测过氧化亚硝酸盐的降解产物NO2-、NO3。
Zikmundova等[42]应用UV/非接触电导检测器同时测定了膳食食品中的脯氨酸、酪氨酸,这两种物质在毛细管中未完全分离,但其中一种物质在两个检测池中都有响应,而另一种物质仅在一个检测池中有信号。Shen等[43]报道了一种使用于微流控芯片系统的复合检测装置(见图11),激光诱导荧光检测器(LIF)的检测位点与C4D的检测位点一致。激光诱导荧光检测器采用共聚焦原理,非接触电导检测器可以移动,检测中两种检测方式取长补短,相互支持。
Liu等[44]报道了一种适用于微芯片电泳的荧光(FD)/C4D便携式检测装置,该装置中两检测器检测位置一致并且同时响应,荧光检测器采用二极管为光源,采用平面光电二极管采集荧光,两个检测器的同时使用并且可同时检测样品的荧光和带电性质。Ryvolova等[45]将C4D检测器、UV检测器、荧光检测器安装在同一检测池上,可将其应用于CE、毛细管电色谱、液相色谱上进行多信号同时检测。
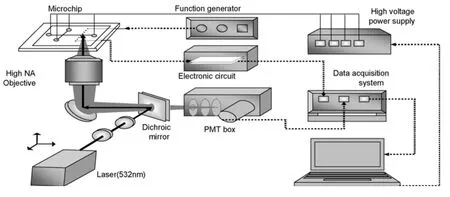
图11 共聚焦LIF-C4D系统结构示意图[43]Fig.11Schematic setup of confocal LIF-C4D system[43]
3 C4D与样品处理技术联用
C4D与样品处理技术特别是在线样品处理技术联用,提高分析的灵敏度、选择性、分析速度、准确度等,这是近年来C4D研究工作的主要方向。
Sedyohutomo等[46]设计了一种离子色谱的新型抑制单元,用来降低背景电导以提高检测物的响应信号,用C4D进行离子检测,六种常规离子F-、Cl-、NO2-、Br-、NO3-、SO42-的检测下限在ng/mL水平。Braz等[47]建立了基于气体扩散-C4D检测的铵离子测定系统,注射体积为100 μL,检测限为0.8 μmol/L。Ding等[48]将固相微萃取(SPE)用于MCE-C4D系统来分析游泳池水消毒时产生的二氯乙酸、三氯乙酸,检出限分别为38、62 mg/L,分析时间小于3 min。Teerasong等[49]报道了一种无试剂顺序注射检测方法,用以同时检测软饮料中的含糖量、色度和二氧化碳含量,通过蒸发液相中的二氧化碳,再使其溶解到接受器水流中,其电导率发生变化,由C4D在线检测电导率。Coelho等[50]设计了一种能与CE匹配的毛细管膜扩散洗涤器,用来处理空气样品,然后将其与CE-C4D分离检测系统相连,可测定室外空气中的甲醛、甲酸、乙酸、氨含量。
Mark等[51]建立了一种通过超声辅助萃取、顶空单滴微萃取(SDME)来净化和浓缩样品,然后利用MCE-C4D技术来测定海产品降解过程中产生的不稳定脂肪胺的新方法,用分离通道长度为8.7 cm的PMMA芯片分离了五种不稳定的短链脂肪胺,分离时间小于40 s,检测限低于0.4 pg/mL。Wei等[52]联用SPE方法在线浓缩水杨酸和山梨酸,使检测下限达到0.05和0.08 μmol/L,并用于酱油中水杨酸和山梨酸的含量测定。Mai等[53]将SPE在线浓缩装置加入该系统中,富集因子在百倍以上,整个装置可以在无人干预下运行,用于布洛芬等药物分析,直接测定的检测下限在5 μmol/L,在线富集后达到nmol/L量级。随后该课题组对顺序进样装置进行了微型化设计,采用压缩空气为动力自动上样,整个装置集成在45 cm×35 cm×15 cm的手提箱中,总重量约8 kg,在电池供电模式下能连续工作9 h,并根据具体情况分析任务,优化上样系统,以达到快速高效分离。完成分离4种阴离子(Cl-,NO3-,SO42-, NO2-)仅需16 s,检测下限在1 μmol/L以下[54]。Liu等[55]利用膜电解萃取技术(EME)作为一种新颖样品准备技术纯化和富集了唾液样品中的盐酸丁二胺、1,5-戊二胺、亚精胺和精胺,亚精胺的富集因子可达106,检出限范围在1.4~7.0 ng/mL。Wu等[56]利用连续缓冲液-液萃取和聚酰胺聚合物辅助CE-C4D测定了食物油中的游离脂肪酸,在18 min内分离出了10种脂肪酸,检出限范围为0.46 ~3.28 μmol/L。Lemos等[57]通过超声萃取将原生橄榄油中的Na+、K+、Ca2+和Mg2+提取到水溶液中,并利用CE-C4D进行分析,3 min内很好的分离了这些金属离子,Na+、K+、Ca2+和Mg2+的检出限分别为0.029、0.029、0.033和0.044 mg/kg。
See等[58]利用无极性变换的大体积进样、场放大样品堆积两种在线富集技术,富集了饮用水中草甘膦、抗草丁膦、氨基磷酸,并用CE-C4D进行了分离和检测,在优化的条件下,采用大体积进样的CE-C4D方法,灵敏度提高48~53倍,检出限在1.7~11 mg/L之间,而用场放大CE-C4D方法的检出限达到0.1~2.2 mg/L,灵敏度增大25 0~1 000倍。Lau等[59]利用场放大样品注射在线富集技术富集了实际样品中的Cr3+,Pb2+,Hg2+, Ni2+等四种重金属离子,并用CE-C4D进行了分离和检测,富集倍数达9万倍,检测限达到0.005~ 2.32 μg/L。See等[60]利用阳离子载体聚合膜结合电场驱动富集目标阴离子,再结合大体积进样堆积技术,提高了毛细管电泳C4D检测的灵敏度,对草甘膦和甲胺磷酸的检测下限达到0.8和1.5 ng/mL。Tuma等[61]利用新型大体积堆积进样(LVSS)的CE-C4D检测了中脑导水管周围灰质(PAG)微透析液中的神经递质氨基丁酸、甘氨酸和谷氨酸,检出限分别为9、10和15 nmol/L。Gao等[62]利用CE-C4D通过强场样品注射(FESI)在线预富集方法测定了四种β2-兴奋剂:盐酸特比萘芬、异丙喹喘宁、福莫特罗和盐酸班布特罗,检测限达到0.02 mg/L,比传统无预富集过程的CE-C4D的检测灵敏度提高了30~40倍。Ji等[63]利用有效的样品处理和场放大进样富集在线技术与CE-C4D联用分析牛奶样品中三聚氰胺的含量,检测限为0.015 mg/kg,相对标准偏差在6%以下。
Partyka等[64]利用瞬间等速电泳预富集(t-ITP)毛细管电泳分离研究了季铵盐标记的阳离子衍生低聚糖,在15 min内实现25种低聚糖的分离与C4D检测,检测下限达到1×10-8mol/L。Li等[65]利用CE-C4D结合壳聚糖与表面活性剂辅助样品堆积技术,在线毛细管电泳富集了高原紫花苜蓿根系的四种有机酸即乌头酸,没食子酸,柠檬酸和L-苹果酸,检测限在2.4~54 ng/mL,富集倍数在3×102~1.5×104。Keyon等[66]利用逆流瞬时等速电泳(TITP)-CZE-C4D技术,将样品中高浓度钠离子作为主导离子,L-丙氨酸作为终止电解质(TE)和背景电解质,分析了麻痹性贝类毒素(PSTs),检测限分别为0.07~1 μg/mL,可测得海鲜样品中的PSTs。Strychalski等[67]将C4D用于梯度淋洗移动边界电泳(GEMBE)中检测复杂生物样品如细胞核血样中的无机阴离子,在梯度淋洗中通过微分信号得到各组分的色谱峰。Strieglerova′等[68]利用电隔膜技术净化和预富集人体液中的锂离子后,用CE-C4D技术进行分离和检测,检出限为9 nmol/L,采用此方法测定了尿液、血浆、血清、血液整体中的锂离子含量。采用电膜萃取人体液样品中的17种未衍生的氨基酸,用CE-C4D进行了分离检测,对人血清、血浆、全血中的12种氨基酸进行了分离检测[69]。
Kiplagat等[70]将一个开管预处理柱直接与毛细管柱相连,然后将血清、血浆等样品直接注入开管柱,经表面修饰的熔融石英毛细管柱会选择吸附干扰基质,小的无机阳离子则会进入到分析柱进行直接测定。Pham等[71]用CE-C4D检测了人血清中的游离丙戊酸和总丙戊酸,样品用量为140 μL,在毛细管电泳分离前,先用分散液液微萃取去除样品中的生物基质,其中游离丙戊酸与蛋白结合丙戊酸通过离心超滤法分离,滤液酸化后萃取;总丙戊酸采用直接将血清酸化后萃取测定,检测下限是0.08 μg/mL,可以用于儿科病人的常规药物检测。Santos等[72]将薄层电化学流通池-毛细管电泳-非接触电导检测联用,实现了脂肪醇类中性组分的测定,在电化学池中脂肪醇被氧化成对应的脂肪酸,衍生化过程仅需1 min,然后将靠近电极表面的溶液以压力进样方式导入毛细管,2.5 min内分离四种脂肪酸,全自动的流通系统分析速度达到12样/h,检测下限为5×10-5mol/L。
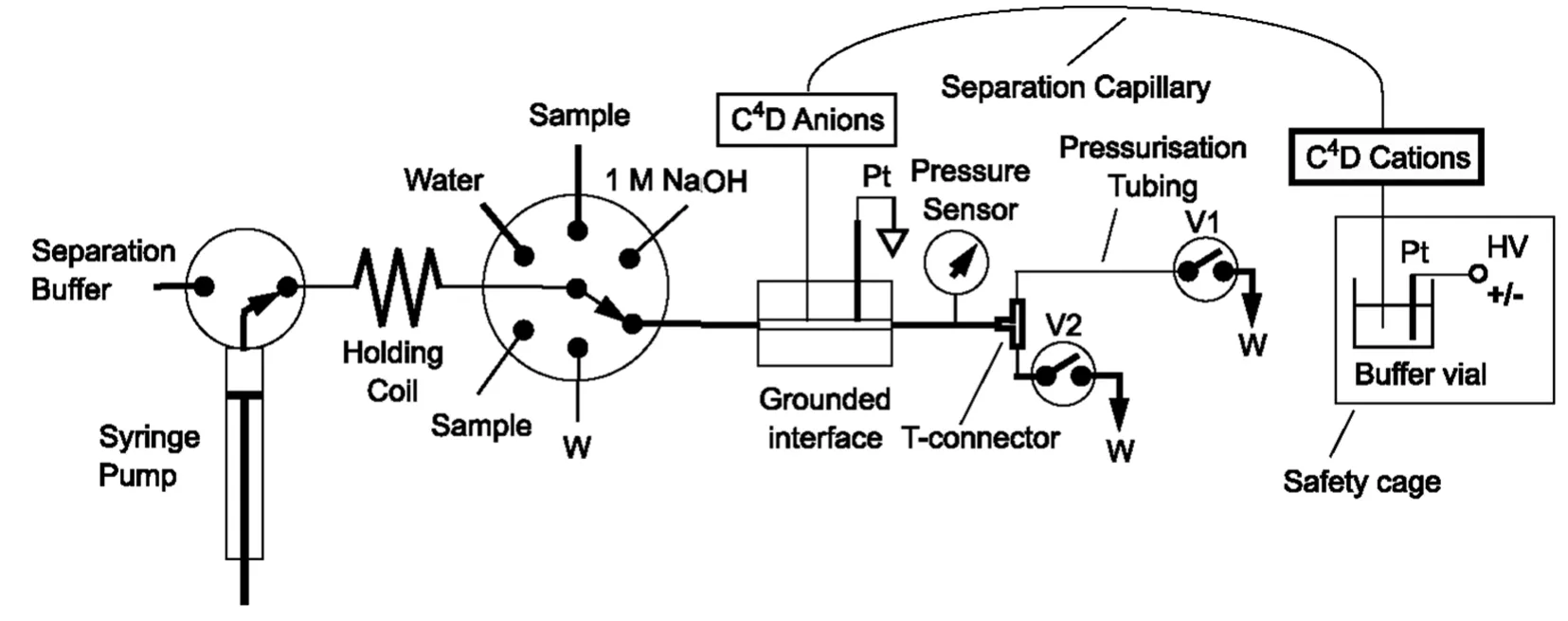
图12 顺序进样压力辅助CE-C4D结构框图[74]Fig.12Schematic drawing of the SIA–CE-C4D-system for pressure-assisted capillary electrophoresis[74]
Hauser课题组[73]设计了如图12的顺序上样装置,可实现阴、阳离子的同时测定,所用毛细管内径为10 μm,有效地减少了样品带的扩散,该系统可以组合出几种进样与测量方式,如将样品用压力推到毛细管中间,在电泳下阴、阳离子分别在毛细管两端检测;阴、阳离子两端进样,C4D在毛细管中间检测与对应两端分别检测,以及压力辅助的电泳分离模式。当同时存在压力驱动和电驱动两种力场,对于分离度良好的峰,可以优化分析时间,对于分离不好的体系则可以延长分离时间以改善色谱峰分离效果[74]。
Kiplagat等[75]设计了一种便携式开管毛细管柱离子色谱C4D检测装置,通过USB与手提电脑相连,进行检测和数据采集,用低电导率的有机酸做洗脱液,同时分离了一价、二价阳离子,在30 min内分离了六种常见阳离子,检测下限小于μg/mL。Kubáň等[76]设计了一种结构紧凑的C4D仪器装置,用来分析实际的化学降解剂与分解产物,该装置可以从各种固体基质如混凝土、砖块、土壤、植物中提取样本,并从中萃取出甲氟膦酸异丙酯、甲氟磷酸异己酯、甲硫膦酸丙胺乙酯进行原位分析检测,整个过程包括仪器启动、样品萃取、完成分析检测总用时5 min,该装置的进样方法重现性良好。Nguyen等[77]研制了带有微型高压C4D的便携式半自动化CE仪器,此CE-C4D系统利用气动操作控制溶液冲洗过程,通过转动电子开关控制不同的操作,如:冲洗毛细管、接口冲洗和电泳分离,与其它复杂系统相比,此方法是一个经济简单实用的操作方案。
Kubáň等[78]开发了一种直接注入人体血样分析甲酸盐的方法,用于快速识别甲醇中毒,把包含渗析膜的样品预处理装置结合到CE-C4D上,将血样中的小离子经渗透膜电动注入分离毛细管,渗透膜将红细胞、蛋白质、脂类和其它高分子化合物等基质组分保留在处理室内,不干扰随后的CE分离,将甲酸盐从其它小阴离子中分离出来,在原始血样中甲酸盐的检测限和定量限分别为15 μmol/L和50 μmol/L。Anouti等[79]基于中心切割技术应用两个C4D检测器建立了一种分析氨基酸对应异构体的新方法,该方法应用一根毛细管和手性、非手性两种电解质,在第一维方向上氨基酸在非手性电解质中进行分离,选择合适区带的分析物在第二维上进行手性氨基酸的分离,此法可用于分离多种氨基酸的对应异构体。
4 C4D的其它应用
除用于电泳及色谱检测器外,C4D的非分析测定应用也有文献报道。如利用移动式C4D对毛细管整体柱色谱固定相进行无损扫描分析,可以探测固定相的均匀性。这种无损新检测技术可应用于毛细管柱、微流控芯片固定相化学和物理性质的研究,还可应用于液相、气相色谱,毛细管区带电泳或电色谱,用以评估表面的化学改性以优化步骤、评估覆盖度及化学或物理活性等[6]。Nehme′等[80]将沉积5层聚电解质的毛细管充满水后,利用C4D进行了评价,通过连续扫描发现,相比较未修饰的毛细管,电导率有明显提高,然后随时间延长电导率有所降低,但10 min后电导率降低速率明显减小,说明由于聚电解质长链缠绕涂覆在壁上使电介质层加厚。Walsh等[81]通过光引发反应制备了聚苯乙烯-二乙烯苯整体柱,制造过程中依靠C4D来优化改进制造方法,用C4D测定流体电阻数据来评估整体柱的渗透性,用沿毛细管轴向的电导剖面图来评估侧面的均匀性,结果表明整体柱在聚合过程中沿轴向旋转,在整个长度上分布均匀。Collins等[82]利用C4D监测了石英毛细管内聚合整体柱固定相的聚合过程,在固定相生长过程中,聚合物生长减少了溶液在毛细管中所占比例,而溶液与聚合物的阻抗存在差异,因此可用C4D监测其生长过程,并通过移动C4D了解其均匀性。Wang等[83]用C4D检测技术测定了毫米粗的管道内气液两相流中单个气泡的移动速率,该新方法结合了C4D检测和速率测量的相关原理,采用五电极构成双C4D,利用速率测量与速度测量相互关联的理论,结合电导检测器获得的两个电导信号实现了气泡速率的测量。
5 结论
C4D作为一种通用型离子检测器,虽然灵敏度与荧光尤其是激光诱导荧光检测器、安培检测器、质谱检测器相比偏低,和UV的灵敏度大抵相当,但传感器构造简单,对于一些常见的无机离子,特别是缺乏紫外吸收、荧光、或电化学活性的离子,有一定的技术优势。C4D所用管状电极,可以套在毛细管保护层外使用,制备更为简便,并可以用于内径10 μm的毛细管上。与接触电导检测器相比,C4D的电极套在毛细管外,既避免了在毛细管上钻孔安放传感电极的技术难题,同时还解决了与分离电压隔离的问题,电极不与溶液接触,避免了溶液与电极表面的化学反应、气泡附着、结垢等影响电极稳定性与重现性的问题,因此在微通道这种特定环境下,C4D更具优势。此外,C4D无需光学检测窗口,位置可以移动,这些特点使它与其它检测器具有良好的兼容性,在CE或MCE中将C4D与其它检测器联用,可以检测同种或不同种类的组分,提供更多的化学信息,提高分析方法的选择性。近年来C4D研究工作的主要方向是与样品处理技术特别是在线样品处理技术联用,提高分析的灵敏度、选择性、分析速度、准确度等。
[1]Zemann A J,Schnell E,Volgger D,et al.Contactless conductivity detection for capillary electrophoresis[J]. Anal.Chem.,1998,70:563~567.
[2]Da Silva J A F,do Lago C L.An oscillometric detector for capillary electrophoresis[J].Anal.Chem.,1998,70: 4 339~4 343.
[3]Kubáň P,Hauser P C.A review of the recent achievements in capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection[J].Anal.Chim.Acta,2008,607:15~29.
[4]Kubáň P,Hauser P C.Ten years of axial capacitively coupled contactlessconductivity detection for CZE-a review[J].Electrophoresis,2009,30:176~188.
[5]Elbashir A A,Aboul-Enein H Y.Applications of capillary electrophoresis with capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection(CE-C4D)in pharmaceutical and biological analysis[J].Biomed.Chromatogr.,2010,24: 1 038~1 044.
[6]Connolly D,Floris P,Nesterenko P N,et al.Non-invasive characterization of stationary phases in capillary flow systems using scanning capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection(sC4D)[J].Trac-Trends in Anal. Chem.,2010,29:870~884.
[7]Kubáň P,Hauser P C.Capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection for microseparation techniques–recent developments[J].Electrophoresis,2011,32:30~ 42.
[8]Opekar F,Stulik K.Some important combinations of detection techniques for electrophoresis in capillaries andon chips with emphasis on electrochemical principles[J]. Electrophoresis,2011,32:795~810.
[9]Elbashir A A,Aboul-Enein H Y.Recent advances in applications of capillary electrophoresis with capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection(CE-C4D):an update[J].Biomed.Chromatogr.,2012,26:990~1 000.
[10]Coltro W K T,Lima R S,Segato T P,et al.Capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection on microfluidic systems-ten years of development[J].Anal.Methods,2012,4:25~33.
[11]Kubáň P,Hauser P C.Contactless conductivity detection for analytical techniques:Developments from 2010 to 2012[J].Electrophoresis,2013,34:55~69.
[12]Tuma P,Opekar F,Jelínek I.A contactless conductometric detector with easily exchangeable capillary for capillary electrophoresis[J].Electroanalysis,2001,13:989~ 992.
[13]Vuorinen P S,Jussila M,Siren H,et al.Integration of a contactless conductivity detector into a commercial capillary cassette Detection of inorganic cations and catecholamines[J].J.Chromatogr.A,2003,99:45~52.
[14]Macka M,Hutchinson J,Zemann A,et al.Miniaturized movable contactless conductivity detection cell for capillary electrophoresis[J].Electrophoresis,2003,24:2 144 ~2 149.
[15]Francisco K J M,Lucio C,do Lago C L.A compact and high-resolution version of a capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detector[J].Electrophoresis,2009, 30:3 458~3 464.
[16]Knjazeva T,Kulp M,Kaljurand M.CE separation of various analytes of biological origin using polyether ether ketone capillaries and contactless conductivity detection [J].Electrophoresis,2009,30:424~430.
[17]Yang X J,Chen Z G,Liu C,et al.Electromagnetic induction detector for capillary electrophoresis and its application in pharmaceutical analysis[J].Talanta,2010,82: 1 935~1 942.
[18]Pham T T T,Mai T D,Nguyen T D,et al.Automated dual capillary electrophoresis system with hydrodynamic injection for the concurrent determination of cations and anions[J].Anal.Chim.Acta,2014,841:77-83.
[19]Bastemeijer J,Lubking W,Laugere F,et al.Electronic protection methods for conductivity detectors in micro capillary electrophoresis devices[J].Sens.Actotors B, 2002,83:98~103.
[20]Pumera M,Wang J,Opekar F,et al.Contactless Conductivity Detector for Microchip Capillary Electrophoresis [J].Anal.Chem.,2002,74:1 968~1 973.
[21]Kubáň P,Hauser P C.Effects of the cell geometry and operating parameters on the performance of an external contactless conductivity detector for microchip electrophoresis[J].Lab Chip,2005,5:407~412.
[22]Tanyanyiwa J,Hauser P C.High-voltage capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection for microchip capillaryelectrophoresis[J].Anal.Chem.,2002,74: 6 378~6 382.
[23]Chen Z,Li Q,Li O,et al.A thin cover glass chip for contactless conductivity detection in microchip capillary electrophoresis[J].Talanta,2007,71:1 944~1 948.
[24]Lichtenberg J,De Rooij N F,Verpoorte E.A microchip electrophoresis system with integrated in-plane electrodes for contactless conductivity detection[J].Electrophoresis,2002,23:3 769~3 778.
[25]Xu Y,Liang J,Liu H T,et al.Characterization of a capacitance-coupled contactless conductivity detection system with sidewall electrodes on a low-voltage-driven electrophoresis microchip[J].Anal.Bioanal.Chem., 2010,397:1 583~1 593.
[26]Wang J,Chen G,Chatrathi M P,et al.Screen-Printed Contactless Conductivity Detector for Microchip Capillary Electrophoresis[J].Electroanalysis,2008,20:2 416 ~2 421.
[27]Liu J S,Xu F,Wang S F,et al.A polydimethylsiloxane electrophoresis microchip with a thickness controllable insulating layer for capacitatively coupled contactless conductivity detection[J].Electrochemistry Communications,2012,25:147~150.
[28]Mahabadi K A,Rodriguez I,Lim C Y,et al.Capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection with dual topbottom cell configuration for microchip electrophoresis [J].Electrophoresis,2010,31:1 063~1 070.
[29]Fercher G,Haller A,Smetana W,et al.End-to-end differential contactless conductivity sensor for microchip capillaryelectrophoresis[J].Anal.Chem.,2010,82: 3 270~3 275.
[30]Kumar A,Burns J,Hoffmann W,et al.Determination of hydrazines by chip electrophoresis with contactless conductivity detection[J].Electrophoresis,2011,32:920~ 925.
[31]Kang Q,Shen D Z,Li Q L,et al.Reduction of the impedance of a contactless conductivity detector for microchip capillary electrophoresis:compensation of the electrode impedance by addition of a series inductance from a piezoelectric quartz crystal[J].Anal.Chem.,2008,80:7 826~7 832.
[32]Huang Z,Long J,Xu W,et al.Design of capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection sensor[J].Flow Measurement and Instrumentation,2012,27:67~70.
[33]Wang J,Chen G,Muck A.Wall-jet conductivity detector for microchip capillary electrophoresis[J].Talanta, 2009,78:207~211.
[34]Blanco G A,Nai Y H,Hilder E F,et al.Identification of inorganic improvised explosive devices using sequential injection capillary electrophoresis and contactless conductivity detection[J].Anal.Chem.,2011,83:9 068~ 9 075.
[35]Zhao J,Chen Z G,Li X C,et al.A novel microchip based on indium tin oxide coated glass for contactless conductivity detection[J].Talanta,2011,85:2 614~2 619.
[36]Lima R,Piazzetta M,Gobbi A,et al.Highly sensitive contactless conductivity microchips based on concentric electrodes for flow analysis[J].Chem.Commun.,2013, 49:11 382~11 384.
[37]Thredgold L,Khodakov D,Ellis A,et al.On-chip capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection using“injected”metal electrodes[J].Analyst,2013,138: 4 275~4 279.
[38]Zheng H,Li M,Dai J Y,et al.Double input capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detector with phase shift [J].Anal.Chem.,2014,86:10 065~10 070.
[39]Wang J,Pumera M.Dual conductivity/amperometric detection system for microchip capillary electrophoresis[J]. Anal.Chem.,2002,74:5 919~5 923.
[40]Tuma P,Opekar F,Samcová E,et al.A comparison of the properties of contactless conductivity and diode-array photometric detectors in analyses of low-molecular,biologically active substances by capillary electrophoresis in acetic acid solutions[J].Electroanalysis,2008,20:477~ 484.
[41]Vázquez M,Frankenfeld C,Coltro W K T,et al.Dual contactless conductivity and amperometric detection on hybrid PDMS/glass electrophoresis microchips[J].Analyst,2010,135:96~103.
[42]Zikmundová J,Tuma P,Opekar F.A dual spectrophotometric/contactless conductivity detector for CE determination of incompletely separated amino acids[J].J.Sep. Sci.,2008,31:353~355.
[43]Shen F,Yang M,Yu Y,et al.Simultaneous laser-induced fluorescence and contactless-conductivity detection for microfluidic chip[J].Chin.Chem.Lett.,2008,19:1 333~ 1 336.
[44]Liu C,Mo Y Y,Chen Z G,et al.Dual fluorescence/contactless conductivity detection for microfluidic chip[J]. Anal.Chim.Acta.,2008,621:171~177.
[45]Ryvolova M,Preisler J,Foret F,et al.Combined contactless conductometric photometric and fluorimetric single point detector for capillary separation methods[J].Anal. Chem.,2010,82:129~135.
[46]Sedyohutomo A,Lim L W,T Takeuchi.Development of packed-column suppressor system for capillary ion chromatography and its application to environmental waters [J].J.Chromatogr.A,2008,1203:239~242.
[47]Braz H L,Ito D T,Silva J A F,et al.Trace levels determination of ammonium by flow injection analysis using gasdiffusion and capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection[J].Electroanalysis,2008,20:477~484.
[48]Ding Y S,Rogers K.Determination of haloacetic acids in water using solid-phase extraction/microchip capillary electrophoresis with capacitively coupled contactless conductivitydetection[J].Electrophoresis,2010,31: 2 602~2 607.
[49]Teerasong S,Chan-Eam S,Sereenonchai K,et al.A reagent-free SIA module for monitoring of sugar,color and dissolved CO2content in soft drinks[J].Anal.Chim. Acta,2010,668:47~53.
[50]Coelho L H G,Melchert W R,Rocha F R,et al.Versatile microanalytical system with porous polypropylene capillary membrane for calibration gas generation and trace gaseous pollutants sampling applied to the analysis of formaldehyde,formic acid,acetic acid and ammonia in outdoor air[J].Talanta,2011,83:84~92.
[51]Mark J J P,Kumar A,Demattio H,et al.Combination of headspace single-drop microextraction,microchip electrophoresis and contactless conductivity detection for the determination of aliphatic amines in the biodegradation process of seafood samples[J].Electroanalysis,2011, 23:161~168.
[52]Wei R X,Li W H,Yang L R,et al.Online preconcentration in capillary electrophoresis with contactless conductivity detection for sensitive determination of sorbic and benzoic acids in soy sauce[J].Talanta,2011,83:1 487~ 1 490.
[53]Mai T D,Bomastyk B,Duong H A,et al.Automated capillary electrophoresis with on-line preconcentration by solid phase extraction using a sequential injection manifold and contactless conductivity detection[J].Anal. Chim.Acta.,2012,727:1~7.
[54]Mai T D,Pham T T T,Pham H V,et al.Portable capillaryelectrophoresis instrument with automated injector and contactless conductivity detection[J].Anal.Chem., 2013,85:2 333~2 339.
[55]Liu Y,Zhang X L,Guo L,et al.Electromembrane extraction of salivary polyamines followed by capillary zone electrophoresis with capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection[J].Talanta,2014,128:386~392.
[56]Wu J Q,Ge Y,Qin W D.Combination of Running-Buffer-Mediated Extraction andPolyamidoamine-Dendrimer-Assisted Capillary Electrophoresis for Rapid and Sensitive Determination of Free Fatty Acids in Edible Oils[J].J.Agric.Food Chem,2014,62:4 104~4 111.
[57]Lemos M A T,Pinheiro A M,Cassella R J,et al.Simultaneous determination of potassium,sodium,calcium,and magnesium in virgin olive oils by capillary electrophoresis with capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection[J].Anal.Methods,2014,6:3 629~3 633.
[58]See H H,Hauser P C,Ibrahim W A W,et al.Rapid and direct determination of glyphosate,glufosinate,and aminophosphonic acid by online preconcentration CE withcontactlessconductivitydetection[J].Electrophoresis,2010,31:575~582.
[59]Lau H F,Quek N M,Law W S,et al.Optimization of separation of heavy metals by capillary electrophoresis withcontactlessconductivitydetection[J].Electrophoresis,2011,32:1 190~1 194.
[60]See H H,Hauser P C.Electric field-driven extraction of lipophilic anions across a carrier-mediated polymer inclusion membrane[J].Anal.Chem.,2011,83:7 507~ 7 513.
[61]Tuma P,Sustková-Fiˇserová M,Opekar F.Large-volume sample stacking for in vivo monitoring of trace levels of γ-aminobutyric acid,glycine and glutamate in microdialysates of periaqueductal gray matter by capillary electrophoresis with contactless conductivity detection [J].J.Chromatogr.A,2013,1303:94~99.
[62]Gao F,Wu M L,Zhang Y,et al.Sensitive determination of four β2-agonists in pig feed by capillary electrophoresis using on-line sample preconcentration with contactless conductivity detection[J].J.Chromatogr.B,2014, 973:29~32.
[63]Ji Y L,Chen X W,Zhang Z B,et al.Efficient sample clean-up and online preconcentration for sensitive determination of melamine in milk samples by capillary electrophoresis with contactless conductivity detection[J].J. Sep.Sci.,2014,37:3 000~3 006.
[64]Partyka J,Foret F.Cationic labeling of oligosaccharides for electrophoretic preconcentration and separation with contactless conductivity detection[J].J.Chromatogr.A, 2012,1267:116~120.
[65]Li X,Ju Y Y,Xu Y Y,et al.On-line capillary electrophoresis enrichment by combining chitosan trapping with surfactant assisted sample stacking for the ultratrace determination of organic acids in Plateau alfalfa roots[J]. Anal.Chim.Acta,2013,789:100~106.
[66]Keyon A,Guijt K,Bolch C,et al.Transientisotachophoresis-capillary zone electrophoresis with contactless conductivity and ultraviolet detection for the analysis of paralytic shellfish toxins in mussel samples[J].J. Chromatogr.A,2014,1364:295~302.
[67]Strychalski E A,Henry A C,Ross D.Expanding the capabilities of microfluidic gradient elution moving boundary electrophoresis for complex samples[J].Anal. Chem.,2011,83:6 316~6 322.
[68]Strieglerová L,Kubáň P,Bocek P.Rapid and simple pretreatment of human body fluids using electromembrane extraction across supported liquid membrane for capillary electrophoreticdeterminationoflithium[J].Electrophoresis,2011,32:1 182~1 189.
[69]Strieglerová L,Kubáň P,Bocek P.Electromembrane extraction of amino acids from body fluids followed by capillary electrophoresis with capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection[J].J.Chromatogr.A,2011, 1218:6 248~6 255.
[70]Kiplagat I K,Doan T K O,Kubáň P,et al.Use of disposable open tubular ion exchange pre-columns for in-line clean-up of serum and plasma samples prior to capillary electrophoretic analysis of inorganic cations[J].J.Chromatogr.A,2011,1218:856~859.
[71]Pham T T T,See H H,Morand R,et al.Determination of free and total valproic acid in human plasma by capillary electrophoresis with contactless conductivity detection [J].J.Chromatogr.B,2012,907:74~78.
[72]Santos M S F,Lopes F S,Vidal D T R,et al.From sample processing to quantification:A full electrochemical approach for neutral analyte derivatization,capillary electrophoresis separation,and contactless conductivity detection[J].Anal.Chem.,2012,84:7 599~7 602.
[73]Mai T D,Hauser P C.Simultaneous separations of cations and anions by capillary electrophoresis with contactless conductivity detection employing a sequential injection analysis manifold for flexible manipulation of sample plugs[J].J.Chromatogr.A,2012,1267:266~272.
[74]Mai T D,Hauser P C.Pressure-assisted capillary elec-trophoresis for cation separations using a sequential injection analysis manifold and contactless conductivity detection[J].Talanta,2011,84:1 228~1 233.
[75]Kiplagat I K,Kuban P,Pelcova P,et al.Portable, lightweight,low power,ion chromatographic system with open tubular capillary columns[J].J.Chromatogr.A, 2010,1217:5 116~5 123.
[76]Kuban P,Seiman A M,Makarotseva N,et al.In situ determination of nerve agents in various matrices by portable capillary electropherograph with contactless conductivity detection[J].J.Chromatogr.A,2011,1218: 2 618~2 625.
[77]Nguyen T A H,Pham T N M,Doan T T,et al.Simple semi-automated portable capillary electrophoresis instrument with contactless conductivity detection for the determination of β-agonists in pharmaceutical and pigfeed samples[J].J.Chromatogr.A,2014,1360:305~311. [78]Kubáň P,Bocek P.Direct analysis of formate in human plasma,serum and whole blood by in-line coupling of microdialysis to capillary electrophoresis for rapid diagnosis of methanol poisoning[J].Anal.Chim.Acta, 2013,768:82~89.
[79]Anouti S,Vandenabeele-Trambouze O,Cottet H.Heartcutting 2D-CE with on-line preconcentration for the chiral analysis of native amino acids[J].Electrophoresis, 2010,31:1 029~1 035.
[80]Nehme R,Perrin C,Cottet H,et al.Influence of polyelectrolyte capillary coating conditions on protein analysis in CE[J].Electrophoresis,2009,30:1 888~1 896.
[81]Walsh Z,Levkin P A,Jain V,et al.Visible light initiated polymerization of styrenic monolithic stationary phases using 470 nm light emitting diode arrays[J].J.Sep.Sci., 2010,33:61~67.
[82]Collins D A,Nesterenko E P,Brabazon D,et al.In-process phase growth measurement technique in the fabrication of monolithic porous layer open tubular(monoPLOT) columns using capacitively coupled contactless conductivity[J].Analyst,2013,138:2 540~2 545.
[83]Wang B L,Zhou Y,Ji H F,et al.Measurement of bubble velocity using capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection(C4D)technique[J].Particuology,2013, 11:198~203.
Proceedings of contactless conductivity detector in designs and combinations in detection and preconcentration techniques
Zhu Xi-lei,Ge Ye-gang,Kang Qi,Shen Da-zhong*
(College of Chemistry,Chemical Engineering and Materials Science,Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250014,China)
The popularity of contactless conductivity detection in capillary electrophoresis has been growing steadily since its introduction in 1998.Improvements have been made in the design of the detector in order to facilitate its handling,to allow easy incorporation into available instruments or to achieve higher sensitivity.The understanding of its fundamental working principles has been advanced and the detection approach has also been transferred to lab-on-chip devices.The range of applications has been extended greatly from the initial work on small inorganic ions to include organic species and biomolecules.Commercial devices are now available and the method can be considered a mature detection technique.In this article,the achievements in design of the detector, combination with other detection methods and sample preconcentration techniques are reviewed.
contactless conductivity detection;capillary electrophoresis;microchip capillary electrophoresis;
国家自然科学基金资助项目(21275091,21175084)
*通讯联系人,E-mail:dzshen@sdnu.edu.cn

