基于半导体压力传感原理的钐一硫化物在冻土区压力测量中的应用
Bolshev K.N.,Ivanov V.A.,Kaminskii V.V.,Lebedev M.P.,Stepanov A.A.
(俄罗斯科学院西伯利亚分院北极物理技术研究所,雅库茨克194021,俄罗斯)
0 Introduction
Despite the large number of existing methods,devices,instruments,automated systems,new problems are constantly introduced.Solution of such problems is not always possible by means available.This is especially relevant for solving problems related to the specifics of the Russian Far North.This paper deals with the problem of measuring the pressure in wet freezing particulate medium.
1 Materials and Methods
Baroresistors-samarium monosulfide(SmS)based semiconducting local pressure sensors,co-developed by the Ioffe Physical Technical Institute(St.Petersburg)and Institute of Physical Technical Problems of the North(Yakutsk).The sensor itself is a thin polycrystalline film of SmS,deposited on a glass substrate with metal pads on it which are used to electrically connect the sensor.The operation principle of these sensors is based on the dependence of the semiconducting layer resistance on pressure and temperature,which allows to calculate the pressure if the temperature of the sensor is known.The dependence of the resistance logarithm on temperature and pressure is linear.This linearity simplifies the calculation of the pressure and increases the reliability of results[1].
The significant advantage of these sensors is that they can be placed inside the object observed and measure the pressure in its various areas.SmS has the highest sensitivity to deformation among known materials.Application of SmS will create a new class of instruments(pressure sensors,force,torque,acceleration,etc.)having a high output signal and the minimum inaccuracy.The main element of a baroresistor is thin(0.5 micron)rectangular semiconducting film of polycrystalline SmS,deposited on a glass substrate.Typical sensor size is 0.5~2 mm.Before starting measurements with SmS based sensors,it is necessary to determine two coefficients for every particular sensor.The temperature coefficient of resistance(TCR) is:

R—resistance(Ohm);T—temperature,degrees(℃).
And the pressure coefficient of resistance(PCR) is:

P—uniform compression pressure(Pa).
Typical values for the baroresistors considered are α ~1.5×10-3deg-1and β~2×10-3MPa-1.
To determine the TCR,we used CRYO-VT-05-01 cryostat with the reference platinum resistance thermometer of the first class,PCR was determined in the pressure chamber with compressed gas.
Pressure change during the experiment was calculated by the following formula:

R0,T0—resistance and temperature at the initial moment of the experiment,respectively.
In this paper,we present the application of the baroresistors for measuring pressure in freezing ground.Fig.1 shows an automated setup for measuring the temperature and pressure at one-dimensional cryogenic freezing of wet particulate medium.
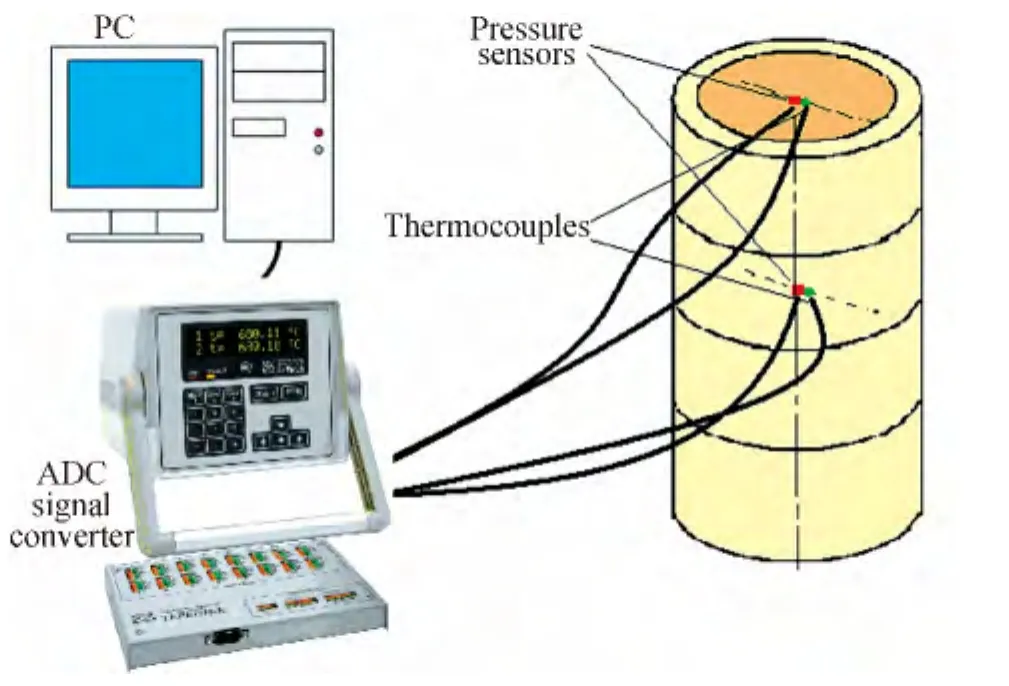
Fig.1 Apparatus for measuring the temperature and pressure at one-dimensional cryogenic freezing of wet particulate medium
The installation includes a personal computer,precision signal converter“TERKON”which can acquire data from resistance thermometers and thermocouples and test vessel in which particulate medium is placed.
The test vessel is a 15 cm high plastic cylinder with an inner diameter of 5 cm,in which thermocouples and pressure sensors are placed(Fig.2).
The thermocouples and pressure sensors are located as close as possible to each other.This allows us to calculate the pressure applied to the sensor using the temperature value obtained with a thermocouple.Wet river sand is used as a test medium.
At the beginning of an experiment,wet river sand is placed in a test vessel,containing pre-calibrated pressure sensors and thermocouples at room temperature.Then,all sides of the vessel are thermally insulated except for the top and placed in the freezer.During the experiment,data from sensors are obtained with the use of“TERKON”signal converter and transferred to a personal computer.Pressure,initially registered on sensors,is assumed to be zero.Computer program saves data on changes of the baroresistors'resistance and temperature registered by the thermocouples.The experiment ends when the temperature reachs the lowest point and remains constant.

Fig.2 The test vessel
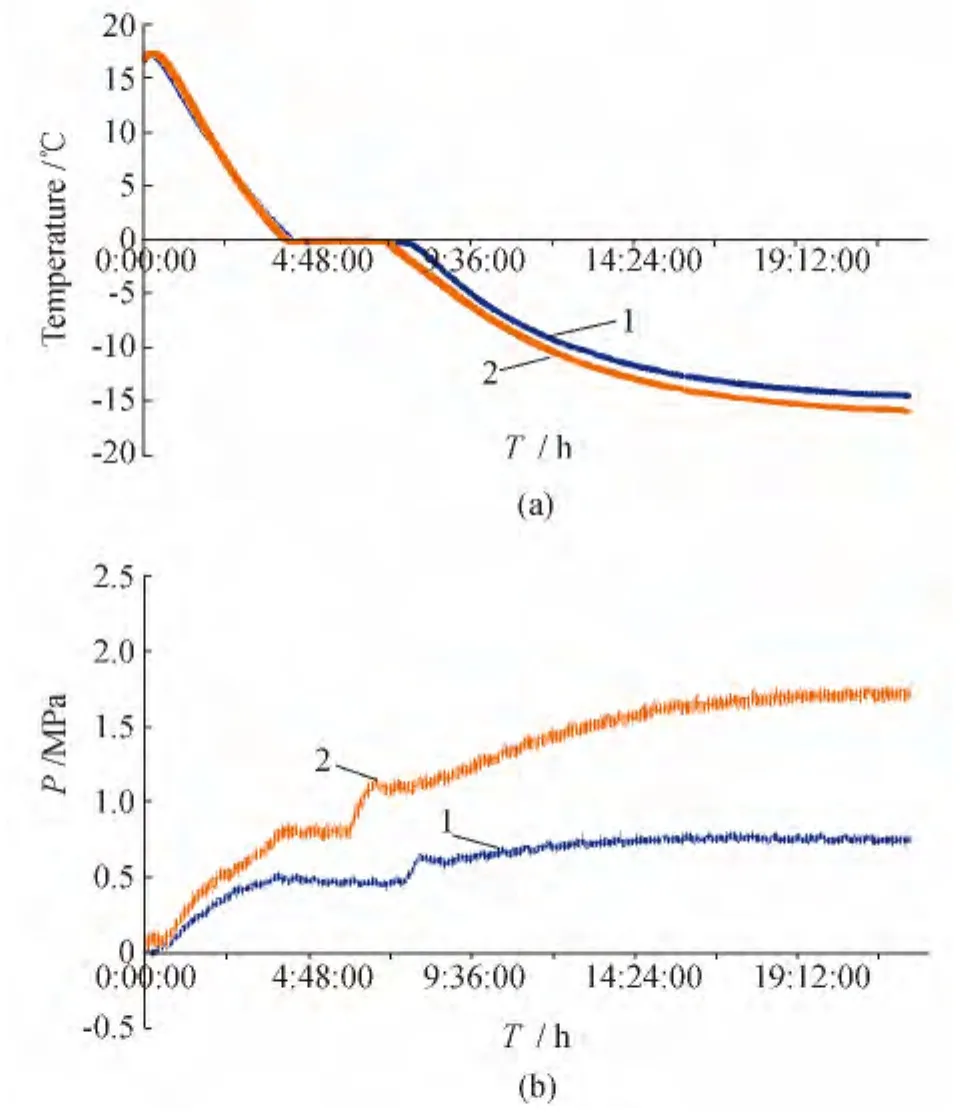
Fig.3 Temperature(a)and pressure(b)versus time at freezing
Typical result of the experiment for two pressure sensors is shown on Fig.3.The baroresistor indicated by number(1)is located at the top of the test vessel.Baroresistor,which is on a lower position is designated by number(2).The“a”graph shows the temperature change registered by thermocouples corresponding to the baroresistors(1)and(2).The“b”graph shows pressure versus time calculated for the corresponding sensors.The experiment lasted for about 22 hours total.
2 Discussion and Conclusions
Without going into the physics details of this type of soil freezing,we can say that the main features of such process on Fig.3 reflect correctly.This is true to the shape of the curve during freezing at temperatures near 0℃ and unstable behavior of the pressure in the temperature range between the freezing point of water and bound water from 0℃to-20℃.This allows us to believe that SmS-based baroresistors reflect the change of pressure adequately with pressures as low as 1 MPa.
Previously,baroresistors have been used for registering high pressures encountered during the durability tests of high pressure vessels and pipes[2].This experiment shows that,with appropriate calibration,SmS-based baroresistors can be applied for measuring low pressures which arise in the frozen soil.
[1] Ivanov V A,Bolshev K N,Alekseev A A,et al.The crack branching research methodology at low temperature field tests[J].Nauchnoe priborostroyenie,2010,20,(2):120-125.
[2] Kaminskiy V V,Soloviev S M,Stepanov N N,et al.The features of the semi-conductive tenzo-and baroresistors based on samarium monosulfide[A].Proceedings of the VI International conference[C]//Orenburg:Strength and failure of the materials and constructions.2010,261-269.
- 黑龙江大学工程学报的其它文章
- The harm of perennial frozen soil to the pipeline exporting the crude oil from Mohe county to Daqing city
- Overview of research methods of frozen soil hydrology in Heilongjiang Province
- Environmental geochemistry of urban areas in Yakutia
- A permafrost factor in the development of deformations on the Amur Highway
- The problem of project statement of construction principles of buildings and facilities in permafrost
- The forecast of a temperature regime of soils containing the pile foundation of a pithead on diamond-mining mines of cryolithic zone

