Effect of APS on Hormones Regulating Blood Glucose in Active Rats
ZHU Yuhui


Abstract
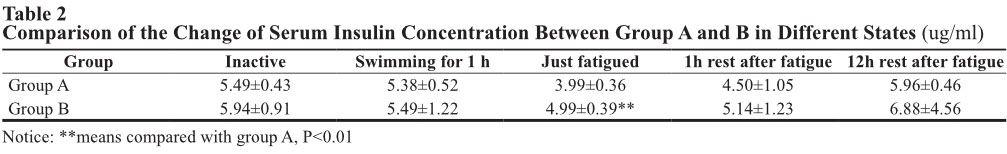
The paper aims to discuss the influence of Astragalus Polysacharin (APS) on hormones regulating blood glucose in active rats. The experiment was conducted to detect the plasma insulin and glucagon concentrations in swimming rats in different states. The result of the experiment showed that the ASP-injected rat group had higher plasma insulin and glucagon concentration, compared with that of the purewater-drinking rat group (control group). After one-hour swimming, the APS-injected rat group had higher glucagon concentration than that of the control group (P <0.05); when just fatigued, the APS-injected group showed evidently higher plasma insulin concentration, compared with the control group (P <0.01). The conclusion is drawn that APS can enhance the release of plasma insulin and glucagon in active rats; promote their compatibility effect in the process of glycogen synthesis and storage, hence increasing glycogen reserves. It can delay fatigue caused by hypoglycemia, and accelerate physical recovery from exercise-induced fatigue. Key words: APS; Insulin; Glucagon; Rats
INTRODUCTION
According to traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), spleen is the core of human activities, generating “qi” (or vitality). Spleen determines the performance of limbs and muscle, therefore, is closely related to physical activities. Astragalus is a representative Chinese medicine for tonifying spleen and reinforcing “qi”, frequently used in clinical medicine. Astragalus is slightly sweet, slightly warm in nature. It can reinforce “qi”, enhance immunity, induce diuresis to reduce edema, and eliminate toxins. According to modern pharmacology, astragalus provide 14 microelements necessary for health, including polysaccharides, saponins, flavonoids, alkaloids, various amino acids, vitamins, selenium, zinc, and iron. Among them, astragalus polysaccharides(APS), is regarded as the major bioactive component of astragalus. Experiments and clinical researches (Shao, Xu, & Dai, 2004) have shown that APS can increase immunity, reduce blood pressure, and regulate blood sugar level. It also has anti-stress, anti-tumor, anti-virus, anti-radiation, anti-oxidant functions. With the means of an experiment, the paper aims to discuss the influence of APS in astragalus on hormones regulating blood glucose in swimming rats, in the hope of providing scientific evidence for clinical application of astragalus in the field of sports medicine.
1. MATERIALS AND METHOD
 Advances in Natural Science2013年4期
Advances in Natural Science2013年4期
- Advances in Natural Science的其它文章
- Biological Significance of Spicy Essential Oils
- Nuclear Energy From the Fission Process as an Alternative Source of Energy
- Spectrophotometric Determination of Methyl Paraben in Pure and Pharmaceutical Oral Solution
- Simulating Optimum Design of Handling Service Center System Based on WITNESS
- Population and Mutagenesis or About Hardy and Weinberg One Methodical Mistake
- Classical and Quantum Explanation of the Magnetic Focusing
