Process Parameter Optimization on Pneumatic Bulging for Abnormity Thin-wall Pot
SONG Zhiping,CUI Shuping,HUANG Te
1.Shanxi Institute of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering,Changzhi 046011,China;2.Yongkang Vocational and Technical School,Yongkang 321300,China
1.Introduction
Abnormity thin-wall pot is a metal container of different shapes made through partial expansion or rolling designs. Abnormity thin-wall pot is well known for its unique appearance to consumers,and it is popular with manufacturers for being effective in raising added value of products.It has broad market demand and developing space at home and abroad[1].
Abnormity thin-wall pot has thinner thickness(δ=0.17 ~0.28 mm[1]),sometimes it should bear a certain amount of pressure and corrosion,and it also has higher quality requirements for forming parts,which is hard to achieve through traditional molding methods.The pneumatic bulging is a new process and technology with great prospects[2].As the forming process is affected by material performance,earthenware size,mould shape,friction status and many other factors[3-4],improper parameter will not get ideal thickness distribution and will have such forming defects as corrugation and breakage.Therefore,it is necessary to make further research on pneumatic bulging process parameter.
2.The finite-element model and numerical simulation scheme
Using metal forming stimulation special software DYNAFORM,to build the finite-element model of abnormity pot semi-finished product and the mould,as shown in Fig.1.
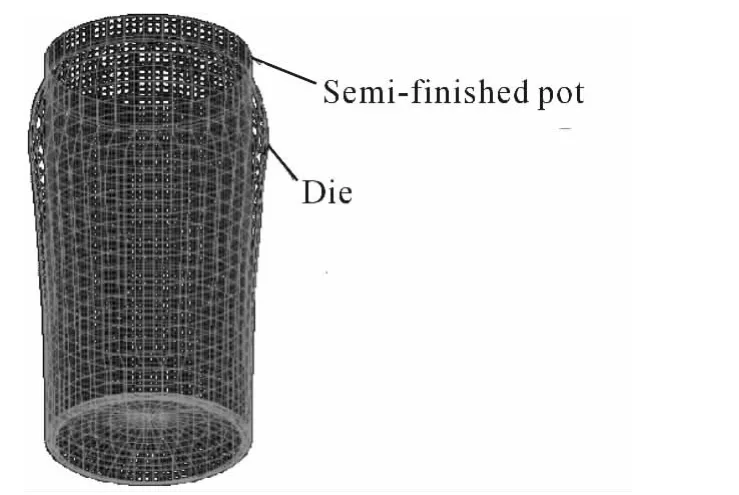
Fig.1 Finite-element model of semi-finished pot and mould
Tin plated steel is commonly used as the material of the abnormity pot semi-finished product.The material model chooses the Bartlat material model,the mould deformation is treated as rigid materials.The constitutive equations σ =Kεn,K=521.32 MPa,n=0.144 are satisfied.In the numerical simu-lation process,by adopting the method of fixing other parameters and changing individual parameter,we studied the influence of friction factor,mould round angle,pot wall thickness and bulging pressure on the stress of bulging area and the wall thickness reduction which will lead to forming defects such as corrugation or breakage.Specific programs are shown in Tab.1.The simulation includes 20 steps together,at last the formed part entirely attaches to the surface of the mould.

Tab.1 Program of Numerical Simulation
3.Discussion about the Numerical Simulation Result
3.1.Different friction factors’influence
Changing the friction factor μ respectively,the semi-finished materials have pasted the mould completely,and the simulation result data is obtained.As shown in Fig.2,the friction factor μ between the mold and the pot semi-finished product increases,the reduction rate of wall thickness will increase obviously,particularly remarkable in the step μ =0.01 ~0.05;When μ > 0.10,it almost becomes the horizontal straight line,and its influence isn’t obvious.The maximum stress value tends to rise along with the increase of friction factor.Therefore,the increase of the friction is not favorable for the bulging,and the friction should be reduced as far as possible.Considering the realistic lubrication condition and the lubrication efficiency,the reasonable value of the friction factor μ is situated between 0.05 ~0.10.
3.2.The influence of die radius of curvature
Changing the die radius of curvaturer,the simulation result is obtained as shown in Fig.3.It shows that with the increase of the die radius of curvature,axial contraction almost becomes a linear going up,which is very beneficial to pneumatic bulging.If the die radius of curvature is too small,the pot base at the die radius of curvature will have the stress concentration area and then lead to its quick breakage.Therefore,small die radius of curvature should be avoided in the design of actual products,the reasonable value should be the maximum one on the premiser> 4δ(δ is pot wall thickness).
3.3.Pot wall thickness δ its influence
Changing pot wall thickness,the simulation result is obtained as shown in Fig.4.The chart shows that when pot wall thickness increases,the maximum reduction rate,the maximum stress value and the axial contraction all reduce.The thicker the semi-finished product is,the more beneficial it is to forming.But this contradicts with the lightweight and material economy.Therefore,based on satisfying the operation requirements and guaranteeing the formed quality,it is economical to select smaller pot wall thickness.
3.4.The influence of bulging pressure
Changing bulging pressureprespectively,the simulation result data is obtained as shown in Fig.5.Figure 5 indicates that with the increase of bulging pressure, wall thickness reduction quantity, the stress value and the axial contraction will increase too,but the increase is not much enough to have an obviouseffect. Therefore,the bulging pressure should be a small value in the condition that bulging is sufficient.
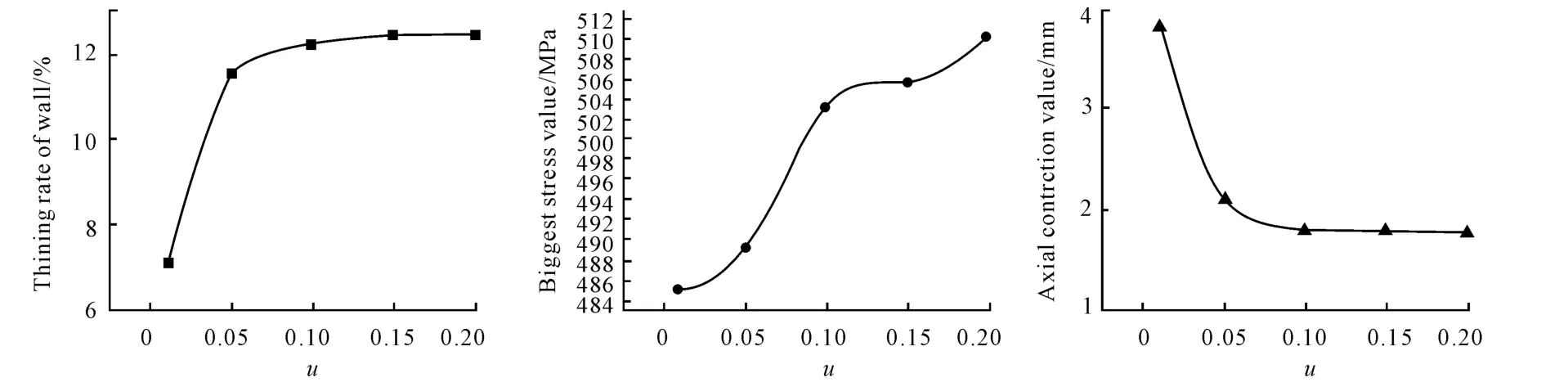
Fig.2 Different Friction Factors’Influence
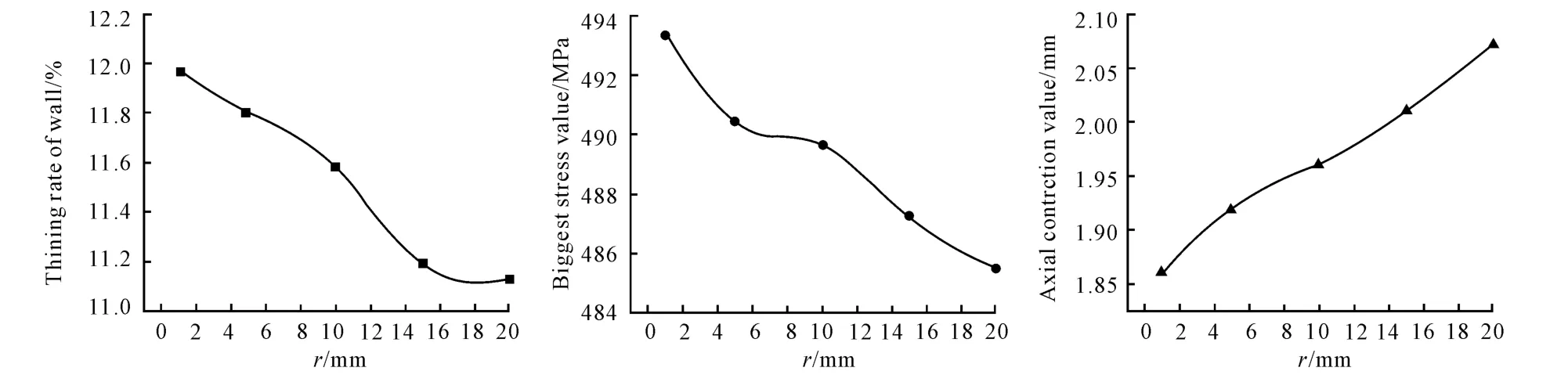
Fig.3 Influence of Die Radius of Curvature
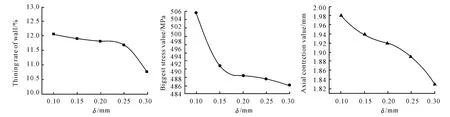
Fig.4 Influence of Pot Wall Thickness

Fig.5 Influence of Bulging Pressure
4.Process parameter optimization
Considering such factors as pot wall thickness,friction factor,the die radius of curvature,the loading intrinsic pressure,material economy,the process parameter is optimized as:The material is tin-plate steel;Thickness δ=0.20 mm;Friction factor μ =0.06;Die radius of curvaturer=15 mm;Bulging pressurep=6 MPa.Through the numerical simulation optimization,the wall thickness distribution and the stress distribution of the simulation result are compared as shown in Fig.6.
As we can see from the figure,the thinnest thickness increases from 0.176 mm to 0.187 mm after the optimization.Through calculating,we can see that the maximum wall thickness reduces from 0.024 mm to 0.013 mm,and the maximum reduction rate reduces from 11.8%to 6.6%,which is a big improvement.Meanwhile,the maximum stress value reduces from 492.5 MPa to 481.8 MPa,the stress distribution is also improved to some extent.
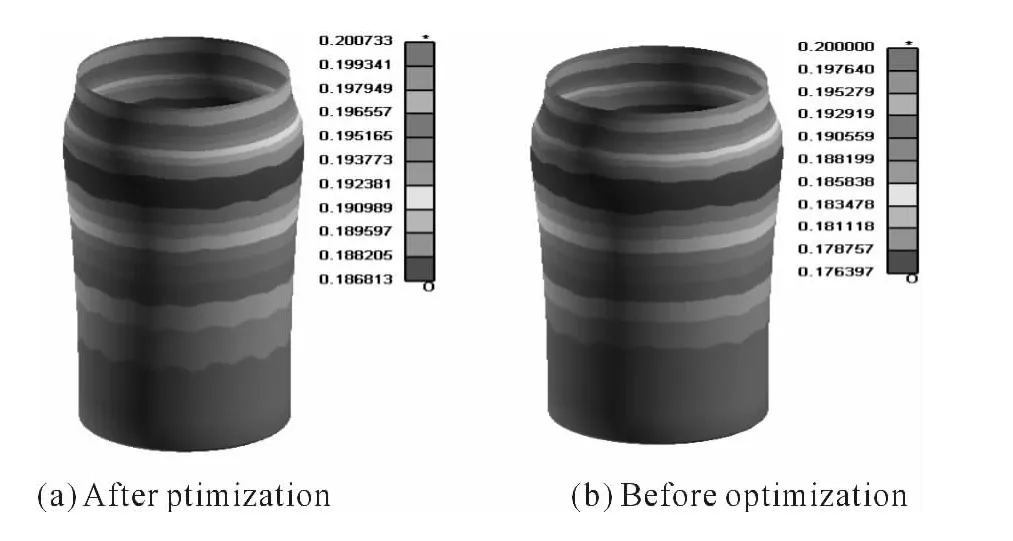
Fig.6 Comparison of the Result of Wall Thickness Distribution
5.Experimental confirmation
The test specimen is T3 tin-plate steel pot,wall thickness δ=0.2 mm,friction factor μ =0.06,die radius of curvaturer=5 mm,loading intrinsic pressurep=6 MPa.The DERUN pneumatic pressure bulging machine is used to carry on the experiment.Figure 7 shows the comparison of the test specimen before and after forming.Figure 8 is the cut test specimen.Fig.9 is the thickness distribution map of the numerical simulation test specimen under the same condition.
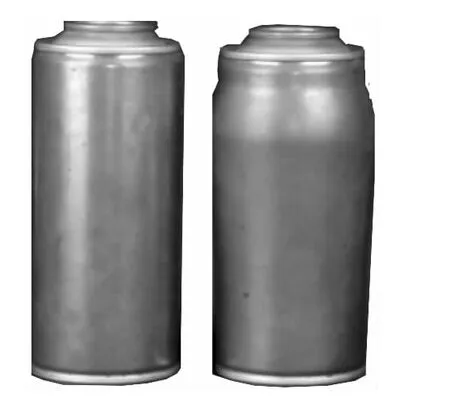

Fig.7 Experimental test specimen before and after forming
Taking 3 cut test specimen,and comparing the measured values of the pot wall thickness and the simulation data,the biggest error is smaller than 10%,the numerical simulation result coincides the test result well,which proves the feasibility of numerical simulation.
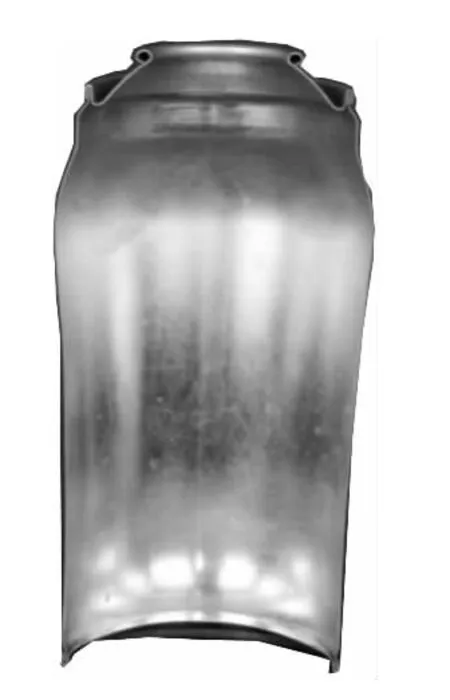

Fig.8 The chart of the cut experimental test specimen
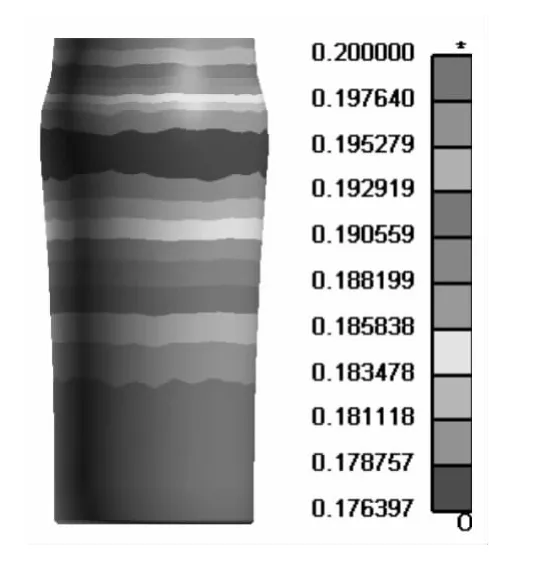
Fig.9 Thickness distribution map of simulation test specimen
6.Conclusions
Through analyzing the numerical simulation result of the abnormity thin-wall pot,the article studies the influence rules of friction factor,the die radius of curvature,pot wall thickness and the bulging pressure on the pneumatic pressure bulging forming:
1)Increasing the friction between the mould and the pot semi-finished product does not favor the bulging forming,so the friction factor should be reduced as far as possible,and the reasonable value is μ=0.05~0.10.
2)The increase of the die radius of curvature causes the linear reduction of the maximum reduction rate and the maximum stress value which is greatly advantageous to the bulging.The product design should avoid the radius of curvature being too small,it should be the maximum one on the premiser>4δ(δ is pot wall thickness).
3)The increase of the pot wall thickness is greatly advantageous to the forming.On the premise that forming quality is guaranteed,the pot wall thickness should be reduced as far as possible so as to consider the economy request.
4)Bulging pressure increases,the reduction rate of the pot wall thickness,the stress value and the axial contraction increases too.The Loading pressure should be the minimum one when sufficient bulging is guaranteed.
[1]HU J H.The Present and Future of Metal Packaging Industry in China[J].Packaging World,2006(3):36-43.
[2]Imaninejad M,Subhash G,Loukus A.Experimental and numerical investigation of free-bulge formation during hydro-forming of aluminum extrusions[J].Material Processing Technology,2004(147):247-251.
[3]Mustafa Yasar.Gas Detonation Forming Process and Modeling for Efficient Spring-back Prediction[J].Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2004,150:270-279.
[4]Yeang-Maw Hwang,Yi-Kai Lin.Analysis and Finite Element Simulation oftheTubeBulge Hydroforming Process[J].Journal of Processing Technology,2002(125):821-825.
[5]MAO J D.The Influence of Lubrication on Metal bulging and drawing performance[J].Machinery Manufacturing and Automation,2008(5):40-42.
- 机床与液压的其它文章
- Strength Analysis and Optimization of a Torsion Beam Rear Suspension
- Development of Vibration Signal Acquisition and Analysis System for Machine Tools Based on LabVIEW
- Numerical Analysis and Experimental Research on Micro Milling Process with Cycloidal Tool Path
- Analysis of the Optimization of Gear Pump Pulsation Based on Matlab
- Simulation Evaluation and Performance Analysis of a Double Coil Magnetorheological Valve
- Remote Condition-based Maintenance Approach to Hydraulic System of Construction Machinery

