Plateau Iris in Whites versus Asians
Thidarat Leeungurasatien, Sunita Radhakrishnan,Travis Porco Goufu Huang,4, Senad Osmanovic,Jehn-Yu Huang,Shan Lin,*
1.Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco, School of Medicine,
San Francisco,California, USA
2.Department of Ophthalmology, Chiang Mai University Hospital, Chiang Mai, Thailand
3.Glaucoma Center of San Francisco and Glaucoma Research& Education Group,San Francisco,California,USA
4.State Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology, Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center,
Sun Yat-sen University,Guangzhou,China
5.Northwestern University,Feinberg School of Medicine,Chicago, Illinois, USA
6.University of California, Davis, School of Medicine, California, USA
7.National Taiwan University Hospital,Taiwan
Introduction


Materials and methods
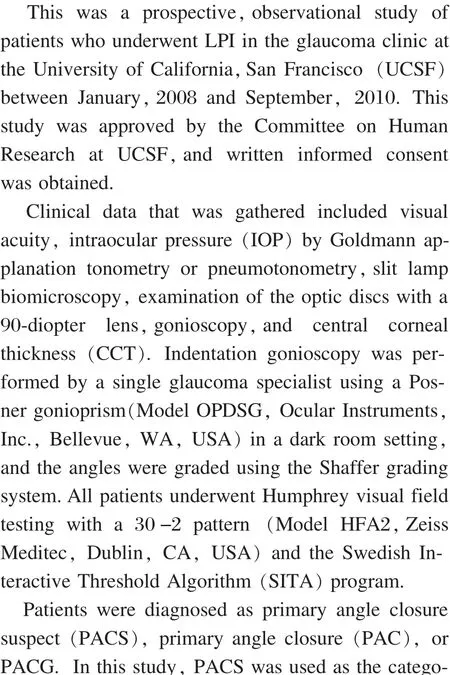
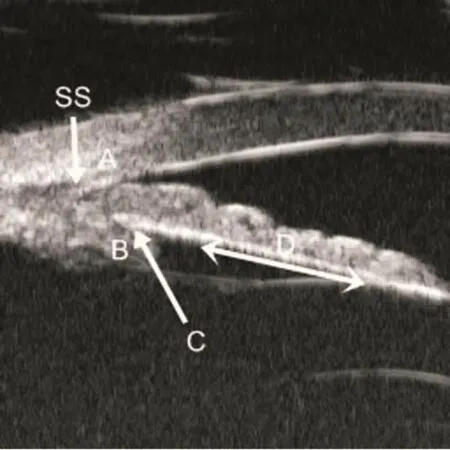
Figure 1 Ultrasound biomicroscopy image from an eye with plateau iris showing iridotrabecular contact(A), anterior displacement of ciliary process (B), loss of the ciliary sulcus(C), and flat central iris plane (D).SS=Scleral spur.

Figure 2 Ultrasound biomicroscopy image from an eye with plateau iris showing “slit” angle between peripheral iris and cornea

Statistical analysis

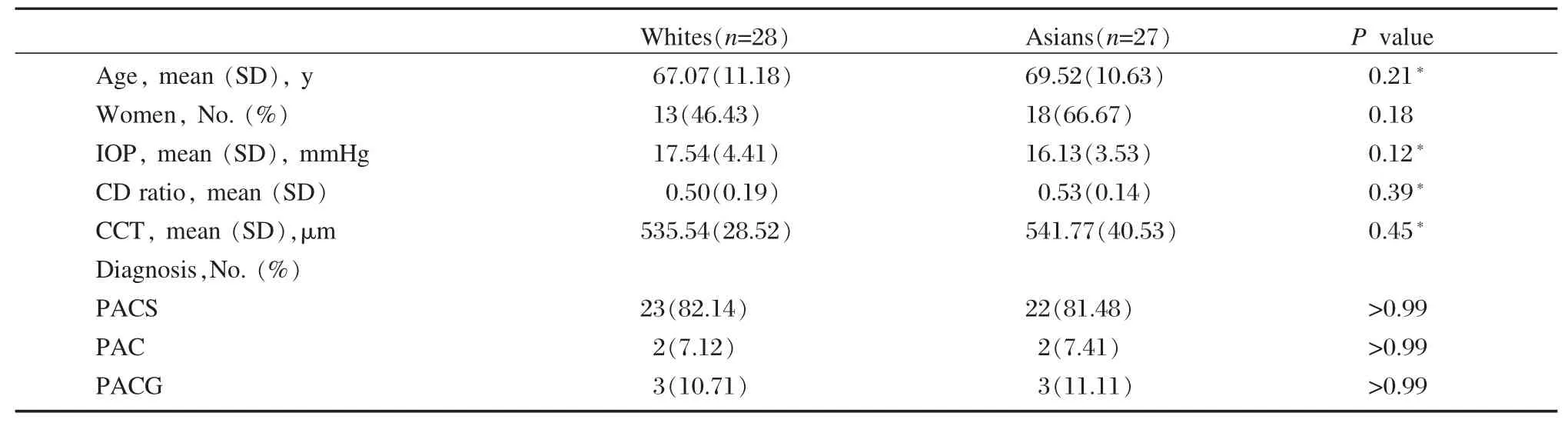
Table 1 Clinical characteristics and biometric parameters of White and Asian subjects
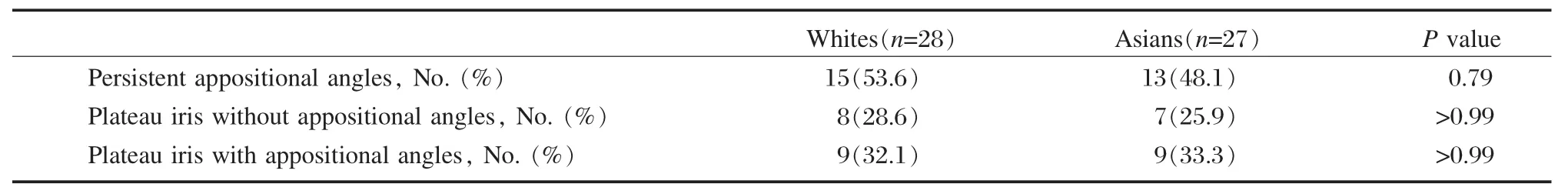
Table 2 Persistent appositional angles, plateau iris without appositional angles, and plateau iris with appositional angles in White and Asian subjects
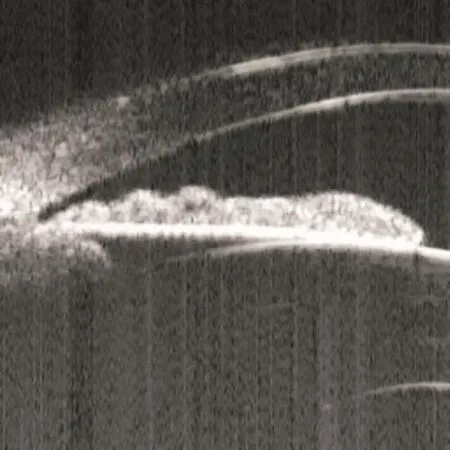

Figure 3 Ultrasound biomicroscopy image from an eye with features of plateau iris after laser peripheral iridotomy showing anterior ciliary process, absent ciliary sulcus, and flat central iris plane without iridotrabecular contact.

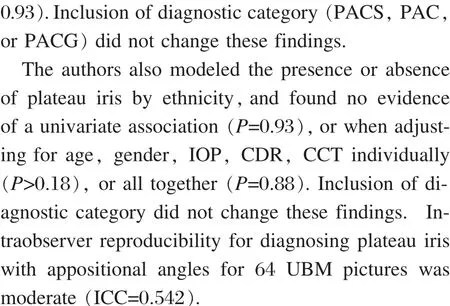
Discussion


- 眼科学报的其它文章
- Development of Clinical Visual Physiology in China during Past Fifty Years
- Comparison on Visual Function after Implantation of an Apodized Diffractive Aspheric Multifocal or Monofocal Intraocular Lens
- Complications of Fibrin Glue in Pterygium Surgery with Amniotic Membrane Transplant
- Efficacy of Phacovitrectomy Combined with Internal Limiting Membrane Peeling for Macular Diseases
- Relationship between the Alignment of a Non-Mydriatic Fundus Camera,Anterior Chamber Depth and Axial Length
- Efficacy of Removing Dislocated Lens using Intravitreal Phacoemulsification

