Minireview:Therapeutic potential of myricetin in diabetes mellitus
Yong Li,Ye Ding
Department of Nutrition and Food Hygiene,School of Public Health,Peking University,Beijing 100191,China
Abstract Epidemiological studies have demonstrated that diabetes mellitus(DM)is a serious health burden for both governments and healthcare providers.Myricetin,a natural fl vonol with hydroxyl groups at 3,5,7,3',4' and 5' positions,is commonly ingested through human diets such as fruits,vegetables,tea,berries and red wine.Although few epidemiological and clinical studies have reported the health benefit of myricetin on DM,increasing evidences from in vitro and animal studies have confirme its hypoglycemic effect.Importantly,myricetin has the function to ameliorate insulin resistance.Moreover,myricetin can execute the functions including anti-inflammation anti-oxidative stress,anti-aldose reductase,antinon-enzymatic glycation and anti-hyperlipidemia.All of these functions may provide the contribution to the prevention of DM and diabetic complications.In this article,a comprehensive discussion to address the potential benefit of myricetin on DM and its underlying mechanisms has been conducted.
Keywords: Myricetin;Diabetes mellitus;Diabetic complications
1.Introduction
Diabetes mellitus(DM)is a metabolic disorder with increasing prevalence all over the world.According to the International Diabetes Federation,there was approximately 366 million people suffered from DM(aged 20–79 years)in 2011 and this figur would climb up to 552 million by the year of 2030[1].All forms of DM are characterized by hyperglycemia and the development of diabetes-specifi complications.In addition to infection and premature death,diabetic complications include macrovascular and microvascular diseases such as cerebrovascular disorders,myocardial infarction,limb amputation,blindness,renal failure,and a variety of debilitating neuropathies[2].All these complications can result in disastrous consequences of economic and social systems,but many synthetic drugs used today failed to complete a long-term glycemic control and alter the course of diabetic complications.Clinically,novel treatments with fewer side effects are desirable for the control of DM and its complications.
Interest in the use of plant extracts that possess widespread biological functions has increased in recent years.Myricetin(3,5,7,3',4',5'-hexahydroxyfl vone cannabiscetin) (Fig.1) is a natural fl vonol from fruits,vegetables,tea,berries,red wine and medical plants[3].The dietary intake of myricetin from our foods is about 0.98–1.1 mg per day,which is quite higher than some other fl vonols[4].Moreover,this fl vonol has a unique chemical structure.The combined contribution of hydroxyl groups at 3,5 positions and three continuous hydroxyl groups at position 3',4' and 5' can increase the antioxidant effectiveness of myricetin,but the presence of six hydroxyl groups can decrease its hydrophobicity,which may be the negative factor [5,6].Recently,the health benefit of myricetin have been demonstrated.Apart from antioxidative and cytoprotective effects,anti-carcinogenic actions,antiviral and antimicrobial properties,and anti-platelet activity,various studies have illustrated that myricetin is one of hypoglycemic components from plant sources[7–12].
2.Epidemiological evidence
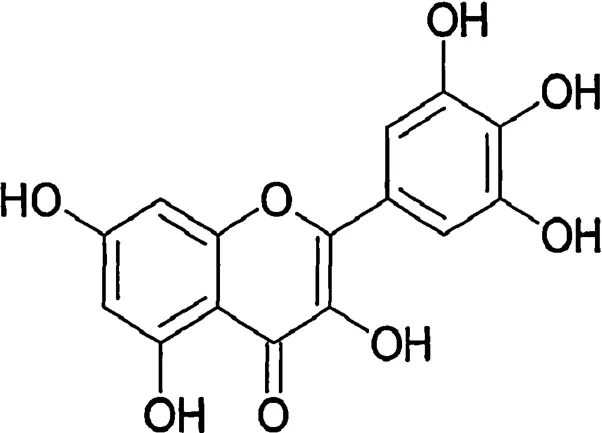
Fig.1.Chemical structure of myricetin.
There are some epidemiological and clinical studies related to the myricetin on DM.Several reports state that myricetin is associated with reduced risk of DM.It was proposed that myricetin was a primitive fl vonoid inChrysobalanaceaefamily used for traditional medicine to control the glycemia of diabetic patients in northern Brazil [13,14].As part of Finnish Mobile Clinic Health Examination Survey,information on habitual food consumption from a random sample of 10,054 participants suggested that the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus(T2DM)might be lower due to higher intake of dietary myricetin[10].In the United States,researchers used a composition,including myricetin,as an application for treating DM and metabolic disorders[15,16].Nevertheless,the intake of myricetin still reveals a neutral effect.The follow-up study (333,905 person-years) of a large cohort of US middle-aged and older women in the Women’s Health Study did not provide a strong support for the hypothesis that high intake of myricetin could protect against the development of T2DM (RR:0.95;95% CI:0.81,1.12;pfor trend=0.38)[17].These contradictory conclusions may be explained by racial and gender differences,irrational DM and diet assessment,insufficien myricetin dose,short therapeutic duration,or poor timing for supplementation initiation.Therefore,studies are still needed to address the pharmaceutical actions and mechanisms of myricetin in this regard.
Although the epidemiological evidences are weak,in vitroand animal studies provide the evidence in support of the hypoglycemic effect of myricetin.In the present review,the connection between myricetin and DM is focused on the basis of current studies.The underlying mechanisms have also been discussed,which will provide possible guidance during the treatment of DM.
3.In vitro and animal evidences
As mentioned above,DM is characterized by chronic hyperglycemia and the maintenance of normoglycemia is one of primary treatment goals.Increasing evidences have confirme that myricetin can regulate glycemia inin vitroand animal studies [18–20].It was reported that myricetin could significantl attenuate hyperglycemia through promoting glucose uptake in soleus muscle and liver,and enhancing hepatic glycogen synthase I activity and glycogen synthesis in hepatocytes of diabetic rats[18,19].Moreover,myricetin might modulate glucose and fructose transport inXenopus laevisoocytes by inhibiting the expression of apical,or luminal,facing-facilitated glucose transporter 2 (GLUT2),a major pathway of sugar absorption [20].As a result,myricetin may inhibit or delay glucose absorption and can reveal substantial impact on the management of normoglycemia.These finding not only support the hypothesis that myricetin can reduce hyperglycemia and ameliorate glycogen metabolism,but also stimulate the exploration of underlying mechanisms of myricetin on anti-diabetic function.
3.1.Myricetin and amelioration of insulin resistance(IR)
IR is the most common etiology of DM.Improving insulin sensitivity and ameliorating IR seem to be crucial for the protection of DM.In Liu’s study,repeated intravenous injection of myricetin for 14 days was found to significantl increase the whole-body insulin sensitivity and decrease the higher degree of IR in fructose chow-fed rats[21].Similar functions of myricetin were observed in obese Zucker rats[22].The essential mechanisms of myricetin for improving insulin sensitivity might be the amelioration of impaired signaling intermediates downstream of insulin receptors through enhancing the secretion of β-endorphin,which in turn led to the activation of peripheral μ-opioid receptors.Then,myricetin treatment correspondingly affected the phosphorylation of insulin receptors,insulin receptor substrate-1(IRS-1),the p85 regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase,protein kinase B (PKB/Akt)and Akt substrate of 160 kD,with subsequent effects on glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) translocation [23].Moreover,in our studies,myricetin intervention also revealed the attenuation for the inhibitory effect of hyperinsulinemia on glucose uptake through increasing AMP-activated protein kinase activity in C2C12 myotubes[24].Although further studies are still needed to explore the mechanisms of myricetin on insulin sensitivity,these finding already provide a new aspect of the pharmacological actions of myricetin,which might be used as a promising therapeutic category for the treatment of IR and T2DM.
3.2.Myricetin and insulinomimetic effect
Insulin has many physiological functions including accelerating glucose oxidation,promoting glucose uptake and storage and stimulating lipogenesis.As a compensatory adaptation to IR,insulin is sufficientl increased in nondiabetic subjects,whereas in subjects with DM,the adaptation is insufficient In addition to the improvement of insulin sensitivity,the treatments of DM should also focus on the discovery of novel compounds with insulinomimetic effects.
Our group demonstrated a facilitated effect of myricetin on glucose uptake in C2C12 myotubes under normal and insulinstimulated conditions [24].Furthermore,it was determined that myricetin was the only compound to stimulate lipogenesis and enhance insulin-stimulated lipogenesis among 30 biofl vonoids during a drug screening study.An insulinomimetic effect of myricetin on glucose transport in adipocytes of rats with non-insulin-dependent DM was also observed.The EC50was approximately 65 μmol/L[25].
Molecular mechanisms potentially contributing to the insulinomimetic effect of myricetin were studied.Previous studies had demonstrated that insulin could stimulate glucose transport in adipocytes through the translocation of GLUT4,in which tyrosine phosphorylation played a crucial role in the signal-transduction pathway [26].However,immunoblot analysis of GLUT4 in rat adipocyte plasma membrane revealed that the stimulation of glucose transport by myricetin was not a consequence of GLUT4 translocation.Instead,the stimulation in glucose uptake was probably due to a direct interaction of myricetin with GLUT4[25],which was confirme by computer simulation in Strobel’s study[27].In this study,however,myricetin inhibited the insulin-stimulated uptake of methylglucose (a substrate that enters the cells through the facilitative hexose transporter GLUT4) by adipocytes over the concentration range of 10–100 μmol/L.Moreover,this fl vonol could not inhibit glucose transport by inhibiting the tyrosine kinase activity acting on IRS-1,and this characteristic further indicated a direct interaction of myricetin with GLUT4.In conclusion,these results show that the effects of myricetin are still elusive,but myricetin might directly interact with GLUT4.
3.3.Myricetin and anti-inflammatory effect
Inflammatio is characterized by abnormal cytokine expression,increased acute phase reactants and other mediators,and the activation of inflammator signal pathways.A large number of studies have linked chronic“inflammation” or the networks integral to inflammator responses,to the development of IR and β-cell dysfunction,which will eventually lead to DM[28].
Myricetin,as a bioactive component,was reported to execute the inhibitory function for the production of inflamma tory cytokines.In lipopolysaccharide(LPS)-stimulated primary macrophages and RAW264.7 macrophages,myricetin could significantl inhibit the production of interleukin-12 in a dosedependent mannerviathe down-regulation of transcription factor nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) binding activity [29].Myricetin was also reported to inhibit interleukin-1β(IL-1β)-induced inflammator mediators in SW982 human synovial sarcoma cells [30].Moreover,in Blonska’s study,myricetin revealed a significan reduction on IL-1β mRNA level in RAW264.7 macrophages under the stimulation of LPS and interferon-γ(IFN-γ),although it was no impact on the synthesis and release of cytokines.However,the most potent inhibitor of IL-1β synthesis and release in this study was chrysin,which decreased the concentration of IL-1β by (59.2±4.2)%in cell lysates and by(51.9±1.0)%in cell-culture supernatants(P<0.001)[31].
On the other hand,myricetin could also affect inflamma tory signal pathways.According to Kim’s observation,myricetin inhibited tumor necrosis factor-α(TNF-α)-induced expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in JB6 P+ mouse epidermal cells by targeting mitogen-activated protein kinase 4,as well as MEK1 (mitogen-activated protein or extracellular signal-regulated kinase) [32].In another study,the impacts of six fl vonoids on NF-κB/inhibitor-κB (I-κB) system in TNF-α-activated ECV304 cells were also examined.Myricetin could strongly inhibit endothelial cell proliferation through inhibiting I-κB kinases [33,34].Moreover,myricetin could inhibit anti-Fas IgM-induced apoptosis and block the synergetic effect of anti-Fas IgM with TNF-α or IL-1β on cell death in human osteoblastic cell line MG-63.The mechanisms might be associated with the inhibition of Fas expression induced by TNF-α and IL-1β,and enhancement of Fas-associated death domain protein-like IL-1β-converting enzyme that were in the charge of caspase-8 and caspase-3 activation[35].Therefore,a potential application of myricetin in preventing angiogenesis-related diseases and diabetic osteopathy might be achieved.
However,all these studies were not based on the diabetic models.According to the description of de Prati,myricetin with three hydroxyl groups in the 3',4',5' positions of the B ring had a strong and specifi inhibitory activity on signal transducer and activator of transcription 1[36],which was always induced by inflammator cytokines to reveal the harmful effect on the development of DM [37–39].In a 4-week randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial,300 mgblueberinsupplement (containing 50 mg myricetin) was administered in T2DM patients 3 times per day.The results showed thatblueberinsupplement significantl reduced the fasting glucose from(143±5.2) mg/L to (104±5.7)mg/L (P<0.001) in diabetic group,which was correlated with the reduction of serum Creactive protein from (5.18±1.4) mg/L to (2.14±1.8) mg/L(P<0.05)[40].Furthermore,anin vitrostudy from our laboratory showed that myricetin could increase cell viability,reverse insulin secretion,and decrease cell apoptosis under the induction of the cytokine mixture with TNF-α(10 ng/mL),IL-1β(5 ng/mL) and IFN-γ(1000 IU/mL) in RIN-m5f β cells [41].Therefore,myricetin may possess relevant anti-inflammator properties.But so far,few researches in this area are conducted so that the anti-inflammator role of myricetin in diabetic models and the relevant mechanisms need to be further elucidated.
3.4.Myricetin and anti-oxidative stress
Oxidative stress,which are regulated through the balance of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and antioxidant enzyme activity,play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of DM and its complications [42].There was strong evidence that myricetin could effectively remove a variety of ROS and execute the anti-oxidative activity due to a large number of active hydroxyl groups [41,43].It was also reported that myricetin could significantl reduce the increased production of free radicals during cell swelling and ischemic injury,and improve oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced potential decline in mitochondrial membrane[44].Moreover,several studies determined the protective effect of myricetin against ROS-induced cell death.For example,preincubation with fl vonoids such as myricetin,quercetin and rutin revealed significan protection on Caco-2 and HepG2 cells against hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced DNA damage [45].Anotherin vitrostudy found that myricetin,quercetin and morin had protective effects on the apoptosis of cardiomyocytes induced by H2O2,which was mainly due to their capacity to increase Bcl-2/Bax ratio,and inhibit the activation of caspase-3[46].
Numerous studies also have evaluated the antioxidant capacity of myricetin under chemical-induced environments.The application of 2-deoxy-d-ribose could induce the oxidative damage of osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells;in contrast,myricetin executed the role of anti-oxidative damage through increasing cell survival and decreasing the contents of MDA,protein carbonyl and advanced oxidation protein products [47].Similarly,myricetin also suppressed the production of intracellular ROS,restore the potential of mitochondrial transmembrane,increase Bcl-2/Bax ratio and decrease caspase-3 activation in 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium-treated MES23.5 cells [48].Moreover,hyperactive molecules such as ROS can cover the surface of erythrocytes to result in the decrease of oxygen-carrying ability in blood,which is correlated with diabetic complications in T2DM patients.Pandey and colleagues found that myricetin revealed significantl protective effect on the increase of tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced oxidative stress parameters including malondialdehyde(MDA)and protein carbonyl group in erythrocytes from T2DM patients(P<0.01)[49].
Besides ROS,reactive nitrogen species(RNS)also play a key role in the development of DM.Many inflammator cytokines and mediators can induce the synthesis of inducible nitric oxide synthase(iNOS)in animals and humans with DM,resulting in the generation of a large number of nitric oxide(NO).Several studies demonstrated that NO-derived peroxynitrite had obvious toxic effects on β-cells.However,myricetin could attenuate the LPS-induced outburst of iNOS gene expression and decrease NO production in intact rat liver [50].In our study,myricetin revealed the reduced generation of cytokine-induced NO due to the inhibition of NF-κB-dependent iNOSexpression in RIN-m5f β cells[41].
Taken together,myricetin is an effective antioxidant inin vitrostudies.This property might make myricetin indirectly improve IR,reduce β-cell apoptosis and promote insulin secretion.
3.5.Myricetin and anti-aldose reductase(AR)effect
Glucose at high level in diabetic tissues can lead to the accumulation of sorbitolviaAR pathway or polyol pathway [51],which plays an important role in the development of vascular and neurological complications [52,53].Several studies have revealed the improvement of retinal,renal,cardiac and neuronal function in diabetic patients subjected to the treatment with AR inhibitors.Myricetin can inhibit AR activity and might play an important role in the development of DM and its complications[54].For example,cultured human red blood cells in high glucose increased intracellular concentration of sorbitol.However,myricetin isolated from leaves ofAnthocep halus chinensis L amkat the concentration of 94.3 μmol/L significantl decreased sorbitol level with strong inhibition of AR in eye lens of pig (IC50:39.7 μmol/L) and rat (IC50:15.6 μmol/L)[55].In another study,myricetin 3',5‘-dimethylether 3-O-β-d-glucopyranoside (10 g/mL),a derivative of myricetin,was demonstrated as the AR inhibitory component fromNelumbo nucifera stamensfor the eye lens of rats with the inhibition of enzyme activity by 40.27%[56].
3.6.Myricetin and anti-non-enzymatic glycation of protein effect
Hyperglycemia,superimposed oxidative stress,and chronic inflammator components in diabetic tissues can cause the accumulation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and late-stage glycoxidation adducts of proteins in multiple tissues[51],which reveals too much toxicity on cardiovascular system,retina,kidney,peripheral limbs and other parts of the body,leading to diabetic complications[57].It was demonstrated that the increased hydroxyl groups at 3’,4’,5,and 7 positions of fl vonoids could result in strong inhibition of AGE formation[58].Interestingly,myricetin has multiple hydroxyl groups in these positions,which might provide a strong ability to inhibit the generation of AGEs.Indeed,Ghaffari’s investigation found that fi e f avonols such as quercetin,myricetin,kaempferol,rutin and morin could decrease LDL glycation and electrophoretic mobility of glycated LDL in a dose-dependent manner [59].In another study,collagen was incubated with glucose (250 mmol/L) in the presence of different fl vonoids.These fl vonoids (25 μmol/L or 250 μmol/L) markedly inhibited the cross-linking formation of advanced glycation end products and reduced pentosidine/hydroxyproline values in a concentration-dependent manner.Moreover,the decreasing inhibition order was observed from myricetin,quercetin,rutin,(+)catechin and kaempferol[60].Therefore,myricetin is a very potent inhibitor of AGEs,but the anti-non-enzymatic glycation effect of myricetin should be further studiedin vivo,especially in diabetic models.
3.7.Myricetin and anti-hyperlipidemia
Insulin has important regulatory effects on lipid and glucose metabolism so that DM is associated with abnormal lipid metabolism [61].An experiment with hyperlipidemic mouse models fed with high-fat diet for 3 weeks demonstrated that myricetin had a positive effect on lipid metabolism.The serum lipids including total cholesterol,triglycerides (TG) and low density lipoprotein-cholesterol(LDL-C)in hyperlipidemic mice revealed a significan difference after the administration of myricetin at the dose of 0.5 g/kg for 12 days when compared with the control group,especially the TG and LDL-C levels(p<0.05)[62].
3.8.Myricetin and anti-hypertension action
Hypertension is a common and important cardiovascular risk factor in DM,with major implications not only for increased morbidity and mortality,but also for healthcare costs.Several studies based on animal models suggest that myricetin can prevent the development of hypertension [63,64].The administration of myricetin (100 mg/kg and 300 mg/kg for 6 weeks) isolated fromVitis vinifera Linn(Vitaceae) was found to reduce systolic blood pressure (SBP) and vascular reactivity to catecholamines,reverse the metabolic alteration and result in the right shift of the cumulative concentration–response curve of angiotensin II in fructose-induced rats [63].In another study,similar functions of myricetin were observed in deoxycorticosterone acetate (DOCA)-induced rat models with hypertension.Chronic administration of myricetin(100 mg/kg and 300 mg/kg p.o.for 4 weeks)reduced SBP and vascular reactivity as well as reversed DOCA-induced heart rate increase[64].
3.9.Myricetin and inhibition of human pancreatic α-amylase(HPA)
HPA is a key enzyme in the digestive system and catalyzes the initial step in the hydrolysis of starch,a principal source of glucose in human diet.Previous studies have demonstrated that specifi inhibitors of HPA have potential for the control of blood glucose level during the treatment process of obesity and DM.In order to achieve the novel inhibitors,a library with 30,000 natural biological extracts from terrestrial and marine origins was screened.A number of inhibitory components were identified of which myricetin was a competitive inhibitor of HPA[65].
3.10.Other positive effects
The formation of islet amyloid deposits is common in patients with T2DM.Although the mechanism responsible for pancreatic β cell cytotoxicity during the process of islet amyloid formation is still unknown,amyloid formation is considered as an important factor in deterioration of islet function and reduction of β cell mass[66].Some polyphenol molecules have been demonstrated to inhibit the formation of fibrilla assemblies and their associated cytotoxicity.Hasegawa and coworkers confirme the inhibitory effect of several small molecules,and 12 polyphenol compounds,including myricetin,on the assembly of heparininduced Tau protein and β-amyloid1–40into filament [67].Furthermore,myricetin had higher binding affinit to oligomeric and filamentou Tau than to the monomeric form.As therapies based on amyloidogenic properties were beneficia for both T2DM and Alzheimer’s disease,it was hypothesized that myricetin might inhibit the formation of islet amyloid deposits.However,substantially more studies are highly desired for identifying the effect of myricetin on the inhibition of human islet amyloid polypeptide aggregation.
Since depression and DM are major contributors to the global burden of diseases,the bidirectional relationship between them is of special interest in the 21st century.Because of lack of physical activity,poor glycemic control,diabetic complications and poor self-care,DM increased risk for depression[68].Myricetin was successfully applied in traditional Chinese medicine to treat depression and anxiety[69].
4.Conclusion
The rapidly increasing prevalence of DM in all parts of the world,coupled with increasing life expectancy,will continue to challenge the resourcefulness of scientists and clinicians in refinin existing therapies and developing new approaches to control DM.A multitude of studies have been performed utilizing the beneficia properties of myricetin in cultured cells and diabetic animals.Based on current results and our knowledge,it is clear that myricetin has powerful effect at the cellular level and offers a great deal of promise as a novel approach for the prevention and management of DM and its complications.However,a wide diversity of questions remain open,furtherin vitroand animal studies are still highly desired for fully understanding of the identificatio of new molecular targets for protection against DM.Moreover,randomized trials should be conducted to determine whether myricetin can be recommended as a dietary strategy for reducing the risk of DM development in individuals with high-risk diabetes or as an early treatment of DM patients.
- 食品科学与人类健康(英文)的其它文章
- About the Beijing Academy of Food Sciences
- Inhibition of citrus fl vonoids on 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate-induced skin inflammatio and tumorigenesis in mice
- Hypothesis review:The direct interaction of food nanoparticles with the lymphatic system
- How functional foods play critical roles in human health
- GUIDE FOR AUTHORS
- Pharmacological potential of ampelopsin in Rattan tea

