鸡西盆地城子河组泥岩有机质保存条件研究①
樊 馥 张永生 高福红 蔡进功 崔海娜 于 鹏
(1.中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所 北京 100037;2.同济大学海洋地质国家重点实验室 上海 200092; 3.吉林大学地球科学学院 长春 130061;4.吉林油田勘探开发研究院 吉林松原 138000;5.北京科技大学土木环境工程学院 北京 005201)
鸡西盆地城子河组泥岩有机质保存条件研究①
樊 馥1,2张永生1高福红3蔡进功2崔海娜4于 鹏5
(1.中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所 北京 100037;2.同济大学海洋地质国家重点实验室 上海 200092; 3.吉林大学地球科学学院 长春 130061;4.吉林油田勘探开发研究院 吉林松原 138000;5.北京科技大学土木环境工程学院 北京 005201)
鸡西盆地作为我国东北地区重要的煤炭基地,已在多口钻井中发现油气显示。早白垩世城子河组为一套夹数个海相泥岩层的含煤岩系,形成于滨浅湖-沼泽的沉积环境,为该盆地主力烃源岩层。本次对该层位泥岩样品的常、微量元素全分析结果表明,水体盐度指标Sr/Ba在0.11~0.38之间,碱度指标(Ca+Mg)*20/(Si+Al)为0.22~ 1.33,氧化还原性指标V/Cr在1.17~3.23之间;生物标志物分析中反映沉积水体环境特征的指标Pr/Ph在2.4~2.8之间,平均值为2.2;伽马蜡烷/C30-藿烷(G/C30H)平均值为0.11,均未显示出遭受海侵影响的典型咸化水体及强还原性沉积环境特点,反映对有机质的保存不利。结合城子河组煤岩与泥岩相比具有高的氢指数和产烃潜量特点,认为该区大量的油气显示应该与广泛发育的煤岩关系更为密切。
鸡西盆地 泥岩 城子河组 有机质保存
0 引言
鸡西盆地为中-新生代残余盆地,是我国东北地区重要的煤炭基地。近年来,煤田钻孔87-20发生天然气井喷,鸡D2井钻遇六层含油粉砂岩,在其它的多口钻井中也见到了油气显示[1],说明其具有油气勘探前景。该区穆棱组剥蚀比较严重[2],城子河组作为该区早白垩世主力烃源岩层,形成于滨浅湖-沼泽的沉积环境,由粉砂岩、泥岩、煤层、沉凝灰岩组成。前人在该层位部分层段泥岩层中发现了半咸水的双壳类化石及海相沟鞭藻,确定它为一套夹数个海相层的含煤岩系[3]。国内外许多陆相含油气盆地中重要生烃层位的形成与海侵有密切的关系。例如中欧盆地三叠系,它是一套典型的海陆过渡相沉积;松辽盆地青山口一段、嫩江组一、二段;苏北-南黄海盆地的泰州组二段、阜宁组;另外,渤海湾盆地纯化镇组、沙河街组和东营组存在水体咸化特征,是否遭受过海侵问题一直以来也被广泛探讨[4~6]。研究认为大范围的海侵提供丰富的成烃母质,并且形成较深的水体有利于缺氧环境的形成,这对有机质的形成和保存是十分有益的[7]。本区城子河组的海侵是否改善了泥质烃源岩的沉积保存环境,这是需要进一步探讨的问题。目前,对于城子河组暗色泥岩的讨论,除以地层对比为目的的一些沟鞭藻研究外,缺乏反映沉积环境的地球化学证据。本文主要通过对样品常、微量元素全分析,对城子河组泥岩沉积时水体的盐度,碱度及保存的氧化还原环境进行讨论,希望为该区的油气勘探起一定的指导作用。
1 采样及样品测试
1.1 样品采集
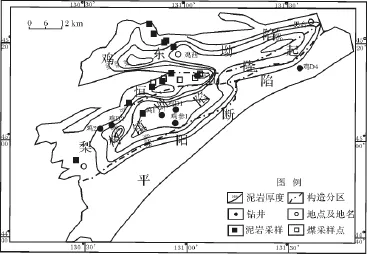
图1 鸡西盆地城子河组泥岩分布及采样位置图Fig.1 The distribution and the sampling location ofmud stone in Chengzihe Formation
鸡西盆地可划分为鸡东坳陷、恒山隆起、梨树镇凹陷和平阳断陷四个构造单元。城子河组泥岩在该区分布广泛,在鸡东坳陷和梨树镇凹陷内厚度最大,最大泥岩厚度超过400 m(图1)。地层岩性发育情况见图2。由于受城子河组地表出露情况的限制,本次采样点位于盆地西缘(图1),主要分布于鸡东坳陷,恒山隆起周缘及梨树镇坳陷边部。样品采自于城子河组砂泥岩互层的野外剖面,岩石类型为表面新鲜的灰黑色泥岩和页岩,出露的最大单层厚度为50 cm,部分夹菱铁矿结核及煤线。暗色泥岩最大厚度为3 m。共采集13块样品用于各项分析测试。

图2 鸡西盆地城子河组地层柱状图Fig.2 The stratigraphic column of Chengzihe Formation in Jixi basin
1.2 分析测试
常量元素分析:用去离子水对暗色泥岩样品进行表面清洗,50℃烘干后用瓷质研钵研磨至200目,其后采用标准压片法,制成X射线荧光光谱分析样品片,进行荧光光谱分析。
微量元素分析:将样品在100℃烘箱中烘干,在玛瑙研钵中磨至200目,称取30~45 mg样品,置入Teflon溶样器中,加入1m l1∶1 HNO3,5 min后加3 ml纯HF,然后放到加热板上保温7 d,在此期间每天超声1次,每次约40 min,将样品蒸干,然后加入1∶1 HNO34 m l,再超声波振荡30min;用2%HNO3将样品稀释至样品重量的1 000倍,在稀释1 000倍后的溶液中取出4 g左右,稀释10倍,作为微量元素待测溶液进行ICP-MS测试。
相关常、微量数据见表1。
2 分析结果
2.1 常、微量元素
选取常、微量元素中Sr/Ba、(Ca+Mg)*20/(Si +Al)及V/Cr,Ni/Co等参数分别作为本次研究中反映水体盐度、碱度及还原性的指标。各样品相关参数的具体数值见表1。
城子河组泥岩样品Sr/Ba的变化范围在0.11~ 0.38之间,平均值为0.26。研究表明:Sr和Ba两者在海水中的富集程度有着巨大的差别,卡钦科夫曾提出Sr/Ba>1为海相,Sr/Ba<1为陆相。王璞王君认为,Sr/Ba作为盐度指标是直接和有效的,而作为划相标志是间接的,且其相对值较其绝对值更有意义[8]。本区城子河组泥岩Sr/Ba特点反映沉积水体盐度较低。
测试样品的(Ca+Mg)*20/(Si+Al)范围在1.26~2.00之间,平均值为1.68。因为Ca和Mg在海水中明显富集,而Si和Al却明显贫化。并且现代沉积物的研究结果表明,泥质岩石中的元素含量与水介质中该元素的浓度呈显著的正相关[8]。因此泥岩(Ca+Mg)*20/(Si+Al)的数值即反映了沉积水体的碱度情况。城子河组泥岩(Ca+Mg)*20/(Si+Al)数值特点反映该区泥岩沉积时水体的碱度偏低。

表1 样品常、微量元素分析数据Table1 Themajor element and trace element data of samp les
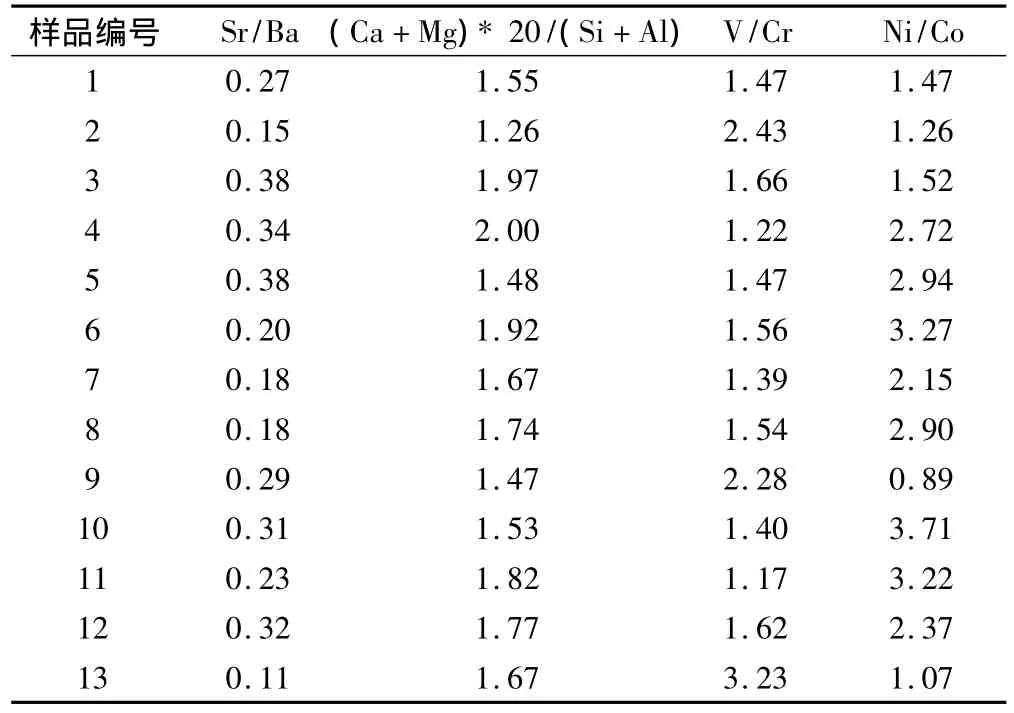
表2 泥岩样品地球化学参数特征Table2 The character of geochem ical indexes from mudstone samp les
城子河组泥岩V/Cr在1.17~3.23之间,平均值为1.73.i/Co的范围为0.89~3.71,平均值为2.27.ones等(1994)通过对西北欧晚侏罗世沉积古氧相地球化学的研究,认为V/Cr,Ni/Co是比较可靠的指标,并首次提出相关元素比值与氧化-还原条件的对应关系(表2)[9]。与Jones提出的标准对比,城子河组泥岩V/Cr及Ni/Co数值反映了富氧的水体环境特征。

表3 古氧相地球化学指标对比Table3 The geochem ical index of the paleo-oxidation phase
3 讨论
从相关元素比值所反映的泥岩沉积保存时的水体盐度和碱度特点来看,松辽盆地泉头至嫩江组典型海侵层序的共生泥岩序列中Sr/Ba在0.28~1.73之间,平均值为0.69[8]。本区城子河组泥岩样品Sr/Ba的变化范围在0.11~0.38之间,平均值为0.26,与嫩江组相比盐度明显偏低。在碳酸盐存在的情况下,该比值受碳酸盐含量的控制,随碳酸盐含量升高而增加[10]。嫩江组发育大套碳酸盐结核,而本区剖面只发现少数泥岩层夹菱铁矿结核。二者Sr/Ba比值也可能与碳酸盐含量差异有关。嫩江组(Ca+Mg)*20/(Si+Al)在0.29~9.42之间,平均值为1.70[8]。本次鸡西盆地研究层位(Ca+Mg)*20/(Si+Al)的范围在1.26~2.00之间,平均值1.68,也反映碱度明显低于嫩江组的特点。上述对比表明,与松辽盆地湖侵层序相比,城子河组的盐度和碱度偏低,可能是由于松辽盆地早白垩世三次海侵的规模较大,持续时间长,致使该套地层整体的盐度、碱度背景值都明显偏高。而鸡西盆地早白垩世城子河组尽管也存在海侵,但由于规模较小,并且只是以海相夹层出现,因此对该区泥岩整体盐度和碱度的提高影响不大。从泥岩沉积时的氧化还原环境来看,在松辽盆地白垩系层序的共生泥岩中,发育指示沉积水体还原环境的闪锌矿和镍黄铁矿[8]。而本区泥岩中仅发育少量菱铁矿。相关研究表明,这种矿物可以形成于轻度还原环境(亚氧化带)到强还原环境(甲烷形成带)[11],所代表指示环境范围十分宽泛,综合城子河组V/Cr(数值范围1.17~3.23)之间和Ni/Co(数值范围0.89~ 3.71)较低的数值特点(范围为0.89~3.71),反映泥岩沉积保存于偏氧化的环境。综上所述,城子河组泥岩总体表现为低盐度、低碱度且偏氧化的沉积保存环境特点。
高红梅(2007)对同一批城子河组泥岩样品进行与沉积环境相关的生物标志化合物分析,结果表明, Pr/Ph在2.4~2.8之间,平均值为2.2,反映了偏氧化的沉积保存环境特征;伽玛蜡烷/C30-藿烷(G/C30H)平均值为0.11,反映了水体化学分层不十分明显;孕甾烷+升孕甾烷/C27甾烷的均值为0.88,C27重排甾烷/C27甾烷均值为0.34,反映水体盐度不高[12]。由此可以看出,泥岩中反映沉积环境特征的有机地化参数与无机地球化学指标Sr/Ba、(Ca+Mg)*20/(Si +Al)及V/Cr及Ni/Co比值反映的环境特征基本一致,并未显示出城子河组遭受海侵后高盐度、强还原的沉积水体特点。同时,高福红(2007)对该盆地发现城子河组海相泥岩的鱼亮子沟剖面取样研究,也未找到典型海侵层位应该具有的极高盐度和反映强还原特征的地球化学证据[13]。尽管一些沉积相的研究证据提出,城子河组沉积期,盆地的水域面积达到最大,可能与北部的勃利盆地和东北部的虎林盆地为统一盆地,并且遭受了东部的海侵[14],但从鸡西盆地城子河组大量煤岩发育的岩性特征以及本次泥岩样品及前人研究得出的地球化学证据来看,海侵对于该盆地泥岩沉积保存环境的改善并不明显,城子河组泥岩并未处于一个有利于有机质保存的沉积环境。
先前对这批泥岩样品生烃潜力研究反映,暗色泥岩TOC在0.11%~3.87%之间;同时,对煤岩和碳质泥岩分析反映TOC为18.85%~80.27%,不同岩石类型有机质丰度差别明显,这主要与暗色泥岩通常为分散型的有机质保存形式,而煤岩为富集有机质保存形式有关。但同时,暗色泥岩IH为0.02~144.00 mg/g,S1+S2为0.04~4.16 mg/g;而煤和碳质泥岩IH为53.8~207.00 mg/g,S1+S2为16.93~179.99 mg/g,不论是氢指数IH还是产烃潜量S1+S2均反映了煤和碳质泥岩生烃能力要好于暗色泥岩样品。并且热解相关参数反映煤和碳质泥岩的有机质类型(Ⅱ2型)也好于暗色泥岩(Ⅲ型)[15]。同时,发生气喷的87-20井气样进行CH4、N2、O2、He、CO2、δ13C分析,结果显示气体成分主要是甲烷,二氧化碳含量低,属煤型气[16]。城子河组暗色泥岩较差的有机质保存环境特征、与煤岩对比显示较差生烃能力特点,气态烃类煤型气的特征,说明盆地内油气显示可能与煤岩关系更为密切。
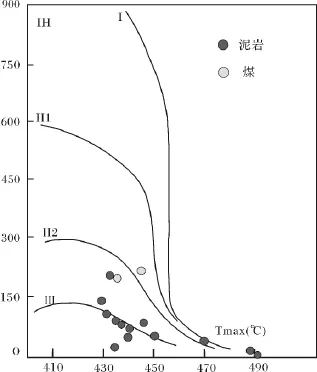
图3 城子河组泥岩和煤的有机质类型[15]Fig.3 The organicmatter type of themuddy rock and the coal in Chengzihe Formation
4 结论
对鸡西盆地早白垩世城子河组泥岩常、微量元素分析表明:泥岩沉积时水体的盐度,碱度偏低,有机质保存环境的还原性差,与有机地球化学指标的相关分析结果反映的环境特征基本一致,说明海侵对于该盆地泥岩沉积保存环境的改善并不明显。同时,泥岩与煤岩相比,在有机质类型及生烃能力方面均未呈现优势特征,加之,部分钻井气态烃类煤型气特点,说明该区油气显示可能与煤岩关系更为密切。
References)
1 朴太元,蔡华伟,姜宝玉。黑龙江省东部白垩纪含煤地层简介[J]。地层学杂志,2005,29(增刊):589-595[Piao Taiyuan,Cai Huawei,Jiang Baoyu.On the Cretaceous coal-bearing strata in eastern Heilongjing[J].ournal of Stratigraphy,2005,29(Suppl。):589-595]
2 王建国,王林凤。鸡西盆地含煤沉积盆地特征及早期油气勘探[J]。古地理学报,1999,1(4):61-69[Wang Jianguo,Wang Linfeng.Characteristics and early stage petroleum exploration in Jixi coalbearing basin[J].ournal of Palaeogeography,1999,1(4):61-69]
3 祝幼华,何承全。黑龙江省东部中侏罗世至早白垩世沟鞭藻组合序列[J]。地层学杂志,2003,27(4):282-288[Zhu Youhua,He Chengquan.Themiddle Jurassic to early Cretaceous dinoglagellate assemblage sequence from eastern Heilongjiang[J].ournal of Stratigraphy,2003,27(4):282-288]
4 王璞珺,Schneider Werner,Matern Frank,等。陆相盆地中的海侵层序特征:中欧盆地三叠系与松辽盆地白垩系对比研究[J]。矿物岩石,2002,22(2):47-53[Wang Pujun,SchneiderWerner,Matern Frank,et al.The characters of transgressive sequence of terrigenous basin:correlation between the Triassic in centraleuropen basin and the cretaceous in songliao basin of China[J].ournal of Mineral and Petrology,2002,22(2):48-53
5 傅强,李益,张国栋,等。苏北盆地晚白垩世-古新世海侵湖泊的证据及其地质意义[J]。沉积学报,2007,25(3):380-385[Fu Qiang,Li Yi,Zhang Guogong,etal.Evidence of transgression lake of Subei basin during late Cretaceous and Paleocene epoch and its geological significance[J].cta Sedimentologica Sinica,2007,25(3): 380-385]
6 袁文芳,陈世悦,曾昌民。济阳坳陷古近系沙河街组海侵问题研究[J]。石油学报,2006,27(4):40-49[Yuan Wenfang,Chen Shiyue,Zeng Cangmin.Study on marine transgression of Paleogene Shahejie Formation in Jiyang depression[J]。2006,27(4):40-49。
7 黄第藩,李晋超,顾信章,等。陆相有机质演化和成烃机理[M]。北京:石油工业出版社,1984:109-143[Huang Difan,Li Jinchao, Gu Xinzhang,etal.Mechanism of Evolution and Generating Hydrocarbon on Terrigenous Organic Matter[M].eijing:Petroleum Industry Press,1984:109-143]
8 王璞珺,刘万洙。事件沉积导论、实例、应用[M]。长春:吉林科学技术出版社,2001:42-64[Wang Pujun,Liu Wangzhu.Depositional Events:Introcuction,Example and Application[M].hangchun:Jilin Science and Technology Press,2001:51-71]
9 施春华,黄秋,颜佳新。广西来宾栖霞组缺氧沉积环境地球化学特征[J]。地质地球化学,2001,29(4):35-39[Shi Chunhua, Huang Qiu,Yan Jiaxin.Geochemistry of the dysaerobic sedimentary environments of the Qixia Formation in Laibing,Guanxi[J].eology Geochemistry,2001,29(4):35-39]
10 孙镇城,杨藩,张枝焕,等。中国新生代咸化湖泊沉积环境与油气生成[M]。北京:石油工业出版社,1997:115-142[Sun Zhengcheng,Yang Fan,Zhang Zhihuan,et al.Sedimentary Environment and Oil Generation of Salty Lake in Mesozoic and Cenozoic in China[M].eijing:Petroleum Industry Press,1997:125-142]
11 Mozley P S,Wersin P,宋新宇。作为沉积环境指示剂的菱铁矿同位素组成[J]。地质地球化学,1994,4(8):42-49[Mozley P S, Wersin P,Song Xinyu.The isotope elementof siderite as the indicator of sedimentary environment[J].eology Geochemistry,1994,4 (8):42-49]
12 高福红,高红梅,樊馥。鸡西盆地下白垩统烃源岩生物标志物地球化学特征[J]。石油实验地质,2007,29(2):188-198[Gao Fuhong,Gao Hongmei,Fan Fu.Geochemical characteristics of biomarkers extracted from the lower Cretaceous coalmeasure rocks in Jixi basin[J].xperimental Petroleum Geology,2007,29(2):188-198]
13 高福红,刘立,马瑞,等。黑龙江鸡西盆地鱼亮子沟城子河组海相泥岩有机地球化学特征[J]。世界地质,2007,26(2):194-198 [Gao Fuhong,Liu Li,Ma Rui,et al.Organic geochemistry of Yuliangzigou marine mudstone in Chengzihe formation of Jixi basin [J].lobal Geology,2007,26(2):194-198]
14 王杰。鸡西盆地早白垩世沉积特征及物源分析[D]。吉林大学, 2007:68[Wang Jie.Characters of sediments and provenances of Jixi basin in early Cretaceous[D].ilin University,2007:68]
15 樊馥,高福红,高红梅。鸡西盆地下白垩统煤系烃源岩生油潜力[J]。新疆石油地质,2007,28(1):36-39[Fan Fu,Gao Fu-hong, Gao Hongmei.Genetic potential of coal-measure source rocks of lower Cretaceous in Jixi basin[J].injiang Petroleum Geology,2007,28 (1):36-39]
16 唐金生。鸡西盆地煤层气勘探方向[J]。天然气工业,1996,16 (3):3-4[Tan Jinsheng.Exploration orientation of coal-bed gas in Jixi basin[J].atural Gas Industry,1996,16(3):3-4]
Organic M atter Preservation of M udstone from Chengzihe Formation in Jixi Basin
FAN Fu1,2ZHANG Yong-sheng1GAO Fu-hong3CAIJin-gong2CUIHai-na4YU peng5
(1.Institute of M ineral Resources,Chinese Academ y of Geological Sciences,Beijing 100037; 2.The State Key Laboratory of Marine Geology in Tongji University,Shanghai 200092; 3.School of Earth Science,Jilin University,Changchun 130061; 4.Institute of Oil Exp loration and Development in Jilin Field,Songyuan,Jilin 138000; 5.Beijing University of Science and Technology Beijing,Civil and Environment Engineering School,Beijing 005201)
Jixi basin is the Mesozoic-Cenozoic residue basin and the important coal base in the northeast China.At present,several drilling wells in the coal fields discovered the oil and gas shows in this area.Chengzihe Formation is the coal-bearing formation in the lower Cretaceous of the Jixi basin,which deposited in the circumstance of coastalshallow lake.The previous studies found themussels fossil of brackish water and a lotof dinoflagellates ofmarine facies,which reflected themarine interlayer existed in the Chengzihe Formation.It infers that the transgression occurred in this period.At home and abroad,many studies indicate that themain source rock layers in themajority of oil and gas bearing basin are related closely with the transgression.We choose somemud rocks from the Chengzihe Formation and perform analysis on themajor elementand trace element,combiningwith the previous organic geochemistry data, to reveal the character ofwater circumstancewhen themud rock of Chengzihe Formation deposits,and discuss how the transgression influences on the water circumstance and organic matter preservation.The analysis result indicates that the values of Sr/Ba which is salinity index ranging from 0.11 to 0.38,0.26 average;the(Ca+Mg)*20/(Si+Al),as the alkalinity index,is from 0.22 to 1.33,1.68 average;as the oxidation-reduction indexes,V/Cr is 1.17 ~3.23,and Ni/Co is 0.89~3.71.ompared with the typical transgression sequence from Quantou Formation to Nenjiang Formation in Songliao basin,the values are low obviously in the Chengzihe Formation,which reflects the sediment and preservation circumstances of low salinity,low alkalinity and weak oxidation.In recent years,the analysis results on the biomarkers from the Chengzihe Formation indicate that as the oxidation-reduction index,the value of Pr/Ph is2.4~2.8,2.2 average;the G/C30H which indicates the salinity stratification ofwater column is0.11 average;the pregnane+homopregnane/C27sterane is0.88 average,C27diasterane/C27sterane is0.34 average,reflecting the salinity of water is low,which is coincide with the analytical result of the major element and trace element.All kinds of indexes do not show the character of the typical transgression sequence,such as the high salinity water and the strong reducive sediment circumstance.It indicates that the sediment environment is not fit for the organic matter preservation.It is coincidentwith the Gaofuhong(2007)'study on the typical transgression sequence of Yuliangzigou section in the Chengzihe Formation.
In addition,the previous study on the potential of generating hydrocarbon reveals the TOC value of the blackmud rock is between 0.11%and 3.87,which is lower than the value of the coal and the carbonaceousmud rock,the TOC ofwhich ranges from 18.58%to 80.27%.esides,the hydrogen index(HI)of the black mud stone is 0.02~ 144.00 mg/g,and the generating hydrocarbon potential(S1+S2)is between 0.04~4.16 mg/g,all ofwhich is lower than the value of the coal and the carbonaceousmud rock that the IH is53.8 mg/g~207 mg/g,and the S1+S2is 16.93~179.99 mg/g.The organicmatter type(ⅡB)of the coal and carbonaceousmuddy rock is better than the organicmatter type(Ⅲ)of the black mud rock.It indicates that the coal and carbonaceousmud rock have the advantageous potential of generating hydrocarbon。
Some evidence of sedimenary facies study indicate that the water area reached themaximum during the whole periods in this basin,and it is probably that the Jixi basin,Boli basin in the north and the Hulin basin in the northeast form the uniform basin,suffering the transgression from the east.However,a lot of coal in Chengzihe Formation of Jixi basin and the geochemical evidence from the previous and present studies indicate that the transgression do not improve sediment environment evidently.Contrasting with Songliao basin,the scale of transgression is smaller in the Jixi basin,which do not improve the salinity and alkalinity evidently,so the water environment of the Chengzihe Formation is not good for the organicmatter preservation.Due to the advantageous generating hydrocarbon potential of the coal and carbonaceousmud rock,it infers the oil and gas show in this area is probably related to the coal and carbonatemud rock。
Jixi Basin;mud rock;Chengzihe Formation;organic matter preservation
樊馥 女 1982年出生 博士后 油气地球化学 E-mail:fanfu2005612033@sina.com
P593
A
1000-0550(2011)05-0980-06
①国家自然科学基金项目(批准号:40872089和41072089)和国家油气重大专项(2008ZX05006-003)、中国石油化工股份有限公司科技局基金(P08039)资助。
2010-08-18;收修改稿日期:2010-12-16

