代谢指纹分析及其在食品科学中的应用
梁强,郭晓晖,周蓓莉,赵国华,2
1(西南大学食品科学学院,重庆,400715)2(重庆市农产品加工技术重点实验室,重庆,400715)
代谢指纹分析及其在食品科学中的应用
梁强1,郭晓晖1,周蓓莉1,赵国华1,2
1(西南大学食品科学学院,重庆,400715)2(重庆市农产品加工技术重点实验室,重庆,400715)
代谢指纹分析是代谢组学的重要研究手段之一,它具有快速、高通量、全局分析的特点。文中在总结国内外近几年来有关代谢指纹分析研究开发与应用文献的基础上,对其概念与分类、分析流程及其在营养代谢性标记物研究、物质代谢规律研究、膳食调查与评价、食品原料差异性鉴别、食品质量评价与追溯等方面的应用,并对该技术在食品科学中应用进行了综述。
代谢指纹分析,食品科学,溯源
代谢组指的是一个细胞、组织或器官中,所有代谢物组分的集合,尤其指小分子代谢物。代谢组学是继基因组学、转录组学和蛋白质组学之后,出现的一个相对较新“组学”研究领域,它能实现对代谢组中小分子(<1 500 u)代谢物的高通量的定性和定量分析[1]。代谢指纹分析是代谢组学的重要研究手段,通过对代谢物的整体分析,比较图谱差异进行样品快速鉴别和分类[2]。代谢指纹分析技术已经广泛的应用于植物学、医学、生物、环境及微生物等领域[2-4],在食品科学研究[5-8]也展现出诱人的潜力,但我国在这方面的研究才刚起步。本文在介绍代谢指纹分析基本原理与流程的基础上,对它在国内外食品科学领域中的应用进行了综述。
1 代谢指纹分析
1.1 代谢指纹分析概念与分类
代谢组学的出现可以追溯到20世纪80年代,而真正得到发展是在 20世纪末[5]。早期研究中,Nicholson[9]和 Fiehn[10]等曾分别提出了动态代谢组学(metabonomics)和静态代谢组学(metabolomics)的概念。随研究的深入,学术界对代谢组学进行了统一的定义。当前广为接受的代谢组学是指通过对生物系统在给定时间和条件下所有小分子代谢物质进行定性和定量分析,从而从整体上揭示该生物系统内物质代谢规律的科学。
代谢组学中对小分子代谢物质的分析通常分为目标分析和非目标分析[6]。目标分析主要是针对特定的代谢物进行定性和定量分析,包括代谢物靶分析和代谢轮廓(谱)分析;代谢物靶分析是对一个或少数几个已知结构和分析方法特定目标成分进行定性和精确定量分析;代谢轮廓(谱)分析是对结构、性质或代谢路径相关的一组化合物进行定性和近似定量分析。非目标分析是对全部代谢物进行的模糊分析,通常借助于指纹图谱,又称为代谢指纹分析。该方法通过不同因素条件下代谢物的指纹图谱差异,对代谢过程进行全方位描述。与代谢物靶分析和代谢轮廓(谱)分析相比,代谢指纹分析能更为真实地反映生物系统内预期或不可预期的变化规律。
1.2 代谢指纹分析流程
代谢指纹分析包括生物分析和数据分析两部分[1-11],生物分析主要包括样品制备(研磨、冷冻、干燥、稀释等)、代谢物萃取、衍生化作用、代谢物检测获得可供分析的大量有效数据(图谱);常用的生物分析技术包括液相色谱-质谱(GC-MS)、气相色谱-质谱(LC-MS)、毛细管电泳-质谱(CE-MS)、傅里叶变换红外光谱-质谱(FTIR-MS)及核磁共振技术(NMR)等。这些技术各有优缺点和适用对象[5]。数据分析主要包括原始数据进行预处理、指纹图谱比较或化学计量学统计分析,挖掘数据信息,寻找变化规律,从而反映代谢的进程。预处理的目的去掉代谢物之外的背景干扰;常用的化学计量分析包括主成分分析(PCA)和偏最小二乘法-判别分析(PLS-DA)。代谢指纹分析流程图见图1。
2 代谢指纹分析在食品科学中的应用
2.1 营养代谢性疾病标记物研究
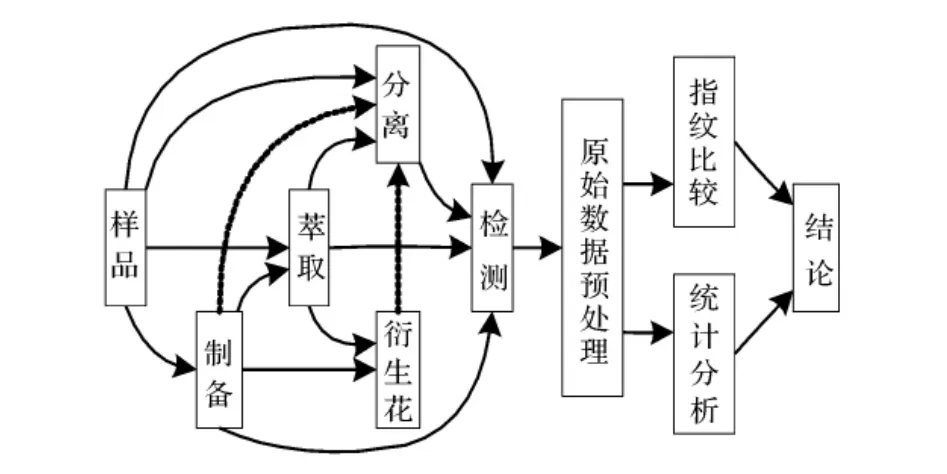
图1 代谢指纹分析流程图
代谢指纹分析已用于糖尿病、肥胖病、慢性炎症等营养性代谢性疾病及其并发症的研究,对机体的代谢物(如血液、尿液、粪便等)进行全面分析,从指纹图谱上快速的区分不同的代谢途径,再与代谢物数据库比对,找到相关的生物标记物。许多研究(表1)表明,该分析技术可以作为发现机体代谢异常和寻找潜在的生物标记物的有效工具,为医学疾病的诊断提供有效的信息。

表1 代谢指纹分析在营养代谢性疾病标记物的应用
2.2 物质代谢及膳食结构研究
传统研究膳食结构的方法是食物问卷调查或饮食日记,由于参与者主观性强很难准确完整的记录他们每天的膳食情况,因此,此方法具有局限性,而代谢指纹分析是一个有效的客观的饮食结构分析方法。有报告指出代谢指纹分析能准确地区分标准早餐和测试早餐[17],同时也用于分析物质在机体内的代谢。从这些研究(表2)可以看出,代谢指纹分析用于分析物质代谢及膳食结构具有潜在的前景,进一步研究饮食与健康的关系,提出更加合理的膳食指南。
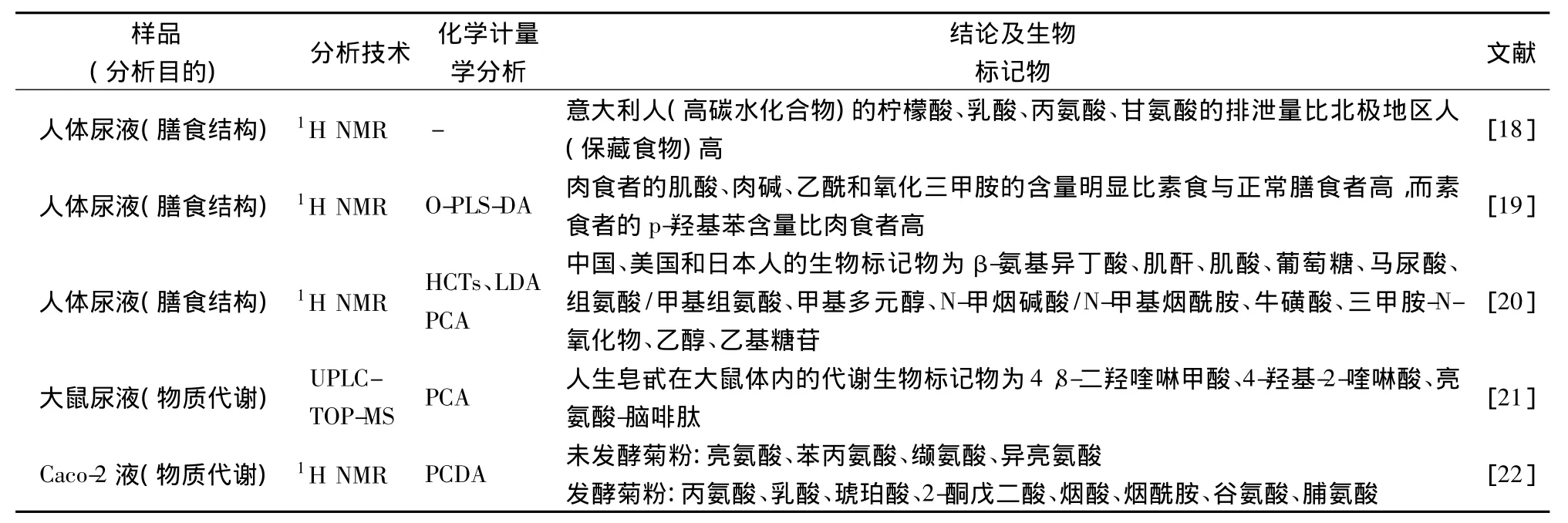
表2 代谢指纹分析在物质代谢和膳食结构的应用
2.3 食品原料鉴别分类
代谢指纹分析常用于食品成分分析,可以追溯原料的品种、来源地、生长环境及养殖方式,从而判断原料的安全性。Luthria等人[23]利用紫外光谱和方差分析-主成分分析对花椰菜进行分析,发现不同品种之间和生长条件下花椰菜的指纹图谱存在明显差异,能够快速鉴别分类。Davis等人[24]发现非转基因和转基因大麦的成分存在明显的不同。类似的研究见表3,这些研究都说明了,在鉴别食品原料的品种、质量、产地、生长环境的差异和成熟度时,代谢指纹分析是一个有效的研究策略。

表3 代谢指纹分析在鉴别食品原料的应用
2.4 食品质量评价及溯源
许多研究者将代谢指纹分析应用于食品质量安全的检测(见表4)。它能提高食品检测的速度、准确性及重现性。从这些研究看出,此分析技术能有效地对产品进行分级,鉴定产品品质,鉴别产品是否掺假,评价食品质量安全,更为重要是应用于食品生产过程的动态监管,确保每批产品的一致性。

表4 代谢指纹分析在食品质量安全的应用
2.5 其他方面的应用
代谢指纹分析也应用于食品加工中化学和微生物变化的研究。Chen等人[37]发现,不同保藏方式的肉类(火鸡、牛肉、猪肉、羊肉、鱼)和菠菜的指纹图谱存在明显的差异,进一步研究发现,冷冻肉在-20℃下也被大肠杆菌污染。Lee等人[38]发现,发酵茶的儿茶素、没食子儿茶素、表儿茶素-3-没食子酸、没食子儿茶素-3-没食子酸、奎尼酸、咖啡因和蔗糖的含量比绿茶低,而没食子酸和葡萄酸含量高,鉴别不同加工工艺的茶叶。Del Bove等人[39]采用FI-IR对意大利10个地域奶酪中22种酵母菌进行分析,通过免费软件“R”(http://cran.r-projet.org/)对酵母菌进行快速鉴别和表型分类。从这些研究可以看出,代谢指纹分析在鉴别食品保藏方式、食品加工工艺及分析食品中有益和有害微生物具有潜在的前景,在食品工业上,可以用来优化食品生产工艺,减少生产成本,控制加工过程减少每批产品的差异性,提高食品风味口感,确保食品质量安全。
3 展望
代谢指纹分析是代谢组学重要研究内容之一,它是从全局的角度去研究代谢物组,对样品进行快速的鉴别和分类,如果要对各信号所代表的代谢物进行定量和结构鉴定,还需要借助目标分析方法。目前出现许多改进技术,如超高液相色谱-质谱(UHPLCMS2)、二维气相-飞行时间质谱(GC×GC-TOF-MS),液相-飞行时间质谱(LC-TOP-MS)、实时直接分析飞行时间质谱(DART-TOP-MS)和混合四极飞行时间质谱(Q-TOP-MS)、超高液相色谱-飞行时间质谱(UPLC-TOP-MS)、2D-NMR等为代谢指纹分析的广泛应用提供了技术平台。
纵观当前代谢指纹分析的研究,还可以进一步利用该技术建立食品代谢物数据库和人体代谢物数据库;建立一个标准化、可接受、重现性好的人类营养学研究方案;食品加工和食品变化的标记物筛选;食品功能成分及有害物质代谢物标记物筛选与鉴定;食品中危害物定性与定量测定;食品生产过程控制等。由此可见,代谢指纹分析在食品科学中是应用前景广阔。
[1] Wishart D S.Metabolomics in monitoring kidney transplants[J].Current Opinion in Nephrology and Hypertesion,2006,15(6):637-642.
[2] Ellis D I,Dunn W B,Griffin J L,et al.Metabolic fingerprinting as a diagnostic tool[J].Pharmacogenomics,2007,8(9):1 243-1 266.
[3] Mattolt L,Cangi F,Matdecchi A,et al.Metabolomic fingerprinting of plant extracts[J].Journal of Mass Spectrometry,2006,41(12):1 534-1 545.
[4] Krastanov A.Metabolomics-the state of art[J].Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment,2010,24(1):1 537-1 543.
[5] Wishart D S.Metabolomics:applications to food science and nutrition research[J].Trends in Food Science &Technology,2008,19(9):482-493.
[6] Cevallos-cevallos J M,Reyes-de-corcuera J I,Etxebbrria E,et al.Metabolomic analysis in food science:a review[J].Trends in Food Science & Technology,2009,20(11):557-566.
[7] Antignac J P,Courant F,Pinel G,et al.Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics applied to the chemical safety of food[J].Trends in Analytical Chemistry,2011,30(2):292-301.
[8] Fave G,Beckmann M,Lloyd A J,et al.Development and validation of a standardized protocol to monitor human dietary exposure by metabolite fingerprinting of urine samples[J].Metabolomics,2011(doi:10.1007/s11306 -011-0289-0).
[9] Nicholson J K,Lindon J C,Holnes E.‘Metabonomics’:understanding the metabolic responses of living systems to pathophysiological stimuli via multivariate statistical analysis of biological NMR spectroscopic data[J].Xenobiotica,1999,29(11):1 181-1 189.
[10] Fiehn O.Metabolomics-the link between genotypes and phenotypes[J].Plant Molecular Biology,2002,48:155-171.
[11] Garcia-perez I,Vallejo M,Garcia A,et al.Metabolic fingerprinting with capillary electrophoresis[J].Journal of Chromatography A,2008,1 204(2):130-139.
[12] 蔡爽,霍韬光,徐静华,等.超高效液相色谱-质谱用于2型糖尿病大鼠粪样代谢物指纹图谱研究[J].沈阳药科大学学报,2009,26(10):811-816.
[13] Zeng Maomao,Liang Yizeng,Li Hongdong,et al.Plasma metabolic fingerprinting of childhood obesity by GC/MS in conjunction with multivariate statistical analysis[J].Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis,2010,52(2):265-272.
[14] Lamers R J A N,Degroot J,Spies-faber E J,et al.Identification of disease-and nutrient-related metabolic fingerprints in osteoarthritic guinea pigs[J].Journal of Nutrition,2003,133(6):1 776-1 780.
[15] Zhao Xinjie,Fritsche J,Wang Jiangshan,et al.Metabonomic fingerprints of fasting plasma and spot urine reveal human pre-diabetic metabolic traits[J].Metabolomics,2010,6(3):362-374.
[16] Barba L,Garcia-ramirez M,Hernandez C,et al.Metabolic fingerprints of proliferative diabetic retinopathy:an1H-NMR-based metabonomic approach using vitreous humor[J].Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science,2010,51(9):4 416-4 421.
[17] Primrose S,Draper J,Elsom R,et al.Metabolomics and human nutrition[J].British Journal of Nutrition,2011,105(8):1 277-1 283.
[18] Zuppi C,Messana I,Forni F,et al.Influence of feeding on metabolite excretion evidenced by urine 1H NMR spectral profiles:a comparison between subjects living in Rome and subjects living at arctic latitudes(Svaldbard)[J].Clinica Chimica Acta,1998,278(1):75 -79.
[19] Stella C,Hall B B,Clorec O,et al.Susceptibility of human metabolic phenotypes to dietary modulation[J].Journal of Proteome Research,2006,5(10):2 780 -2 788.
[20] Dumas M E,Maibaum E C,Teague C,et al.Assessment of analytical reproducibility of 1H NMR spectroscopy based metabonomics for large-scale epidemiological research:the INTERMAP study[J].Analytical Chemistry,2006,78(7):2 199-2 208.
[21] 汪江山,赵欣捷,郑育芳,等.超高效液相色谱/飞行时间质谱用于人生皂甙Rg3作用后大鼠尿液代谢物指纹图谱分析及标记物的鉴定[J].色谱,2006,24(1):5-9.
[22] Lamers R J A N,Wessels E C H H,Sandt J J M,et al.A pilot study to inverstigate effects of lnulin on Caco-2 cells through in vitro metabolic fingerprinting[J].The Journal of Nutrition,2003,133(10):3 080-3 084.
[23] Luthria D L,Mukhopadhyay S,Robbins R J,et al.UV spectral fingerprinting and analysisvariance-principal component analysis:ausefultoolforcharacterizing sources of variance in plant materials[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2008,56(14):5 457 -5 462.
[24] Davis R A,Chariton A J,Oehlschlager S,et al.Novel feature selection method for genetic programming using metabolomic H1NMR data[J].Chemometrics and Intelli-gent Laboratory Systems,2006,81(1):50-59.
[25] Mahdi H J,Andayani and Ishsk R,et al.Metabolic fingerprinting of three Malaysian Ginger(Zingiber officinale Rosecoe)using gas chromatography-mass spectromertry[J].American Journal of Applied Sciences,2010,7(1):17-23.
[26] Jung Y,Lee J,Kwon J,et al.Discrimination of geographical origin of beef by1H NMR-based metaolomics[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2010,58(19):10 458-10 466.
[27] Ali K,Maltese F,Zyprian E,et al.NMR metabolic fingerprinting based identification of grapevine metabolites associated with downy mildew resistance[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2009,57(20):9 599-9 606.
[28] Choi Y H,Sertic S,Kim H K,et al.Classification of I-lex species based on metabolomic fingerprinting using nuclear magnetic resonance and multivariate data analysis[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2005,53(4):1 237-1 245.
[29] Kim H K,Saifullah,Khan S,et al.Metabolic classification of South American Ilex species by NMR-based metabolomics[J].Phytochemistry,2010,71(7):773 -784.
[30] Johson H E,Broadhurst D,Goodacre R,et al.Metabolic fingerprinting of salt- stressed tomatoes[J].Phytochemistry,2003,62(6):919-928.
[31] Shuib N H,Shaari K,Khatib A,et al.Discrimination of young and mature leaves of Melicope ptelefolia using1H NMR and multivariate date analysis[J].Food Chemistry,2011,126(2):640-645.
[32] Pongsuwan W,Bamba T,Yonetani T,et al.Quality prediction of japanese green tea using pyrolyzer coupled GC/MS based metabolic fingerprinting[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2008,56(3):744-750.
[33] Boudonck K J,Mitchell M W,Wulff J,et al.Characterization of the biochemical variability of bovine milk using metabolomics[J].Metabolomics,2009,5(4):375 -386.
[34] Choi H K,Kim K H,Kim K H,et al.Metabolomic differentiation of deer antlers of various origins by H1NMR spectrometry and principal components analysis[J].Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis,2006,41(3):1 047-1 050.
[35] Rochfort S,Ezernieks V,Bastian S E P,et al.Sensory attributes of wine influenced by variety and berry shading discriminated by NMR metabolomics[J].Food Chemistry,2010,121(4):1 296-1 304.
[36] Cajka T,Riddellova K,Tomaniova M,et al.Ambient mass spectrometry employing a DART ion source for metabolomic fingerprinting/profiling:a powerful tool for beer origin recognition[J].Metabolomics,2011(doi:10.1007/s11306-010-0266-z).
[37] Chen Huanwen,Wortmann A,Zenobi R.Neutral desorption sampling coupled to extractive electrospray ionization mass spectrometry for rapid differentiation of bilosamples by metabolomic fingerprinting[J].Journal of Mass Spectrometry,2007,42(9):1 123-1 135.
[38] Lee J E,Lee B J,Chung J O,et al.1H NMR-based metabolomic characterization during green tea(Camellia sinensis)fermentation[J].Food Research International,2011,44(2):597-604.
[39] Del Bove M,Lattanzi M,Rellini P,et al.Comparison of molecular and metabolomic methods as characterization tools of Debaryomyces hansenii cheese isolates[J].Food Microbiology,2009,26(5):453-459.
Metabolic Fingerprinting Analysis and the Application in Food Science
Liang Qiang1,Guo Xiao-hui1,Zhou Bei-li1,Zhao Guo - hua1,2
1(College of Food Science,Southwest University,Chongqing 400715,China)
2(Chongqing Special Food Programme and Technology Research Center,Chongqing 400715,China)
Metabolic fingerprinting analysis is one of the important research strategies of metabolomics.It is fast,high - throughput,and overall analysis.With the summarizes of relevant metabolites from home and abroad in recent years,the paper describes its concept and classification,processing and application in metabolic markers in nutrition study,metabolism study,investigation and evaluation of diet,differences identification in raw materials,and food quality evaluation and food trace back.Meanwhile,the problems of the technology applied in food science and future development of the technology were discussed.
metabolic fingerprinting analysis,food science,traceability
硕士研究生(赵国华教授为通迅作者,E-mail:zhaoguohua1971@163.com)
2011-07-06,改回日期:2011-09-03

