Reliability Sensitivity Analysis for Location Scale Family
HONG Dong-pao(洪东跑),ZHANG Hai-rui(张海瑞)
(China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology,Beijing 100076,China)
Due to the variety of mission profile and the complexity of operating environment conditions,many products always operate under various environment conditions[1].The product's reliability is influenced by the environment conditions[2-3].Traditional analysis methods always attend to the reliability under a fixed environment condition,and ignore the dynamic influence of environment factors on the reliability.Therefore,a reliability sensitivity analysis method is introduced in this paper to analyze the dynamic influence of environment factors on the reliability[4-5].
A reliability model of environment factors is necessary for the reliability sensitivity analysis[6].It will influence the analysis accuracy greatly.Generally,some physical statistical models are used to relate the life parameters to the environment factors.Many wellknown and commonly-used models belong to the accelerated life test models,including the Arrhenius,inverse power law,Eyring model and their combined models[7].With these models,the influences of environment factors on the failure behavior of the product can be measured quantitatively.However,they can only be used to treat the influences of one or two environment factors.Whereas the environment conditions are complex and their influences on the reliability are interactive.As a result,the life is a function of several variables and is difficult to be evaluated by using the accelerated life test models.
For location scale family,this paper introduces the location scale model to describe the relation between life and environment factors.Rather than using the model directly,the radial basis function(RBF)is used to fit the location parameters of environment variables in the model.Then,a reliability sensitivity analysis method for products under various environment conditions is proposed.
1 Reliability Modeling
1.1 Location Scale Model
The location scale model is one of the well-known and commonly-used models in reliability analysis.Assume that the life isTand the environment covariance vector isX=(x1,x2…,xp),the model can be expressed as
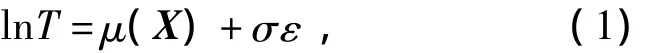
whereμ(·)is an unknown location parameter function,σis an unknown positive scale parameter,andεis a random variable with distribution functionG(t).Moreover,G(·)andμ(·)are all independent fromσ.
Given the environment covariate vectorX,according to Eq.(1),the reliability under the environment conditionXis

In a certain condition,the well-known and commonly-used distributions,including Weibull distribution and log-normal distribution,belong to the location scale model.IfTfollows Weibull distribution and its scope parameter is independent of environment covariates,it belongs to the location scale model.G(·)in Eq.(2)is the cumulative distribution function of standard extreme-value distributionG(t)=1-exp(-et),thus,the reliability under the environment conditionXis
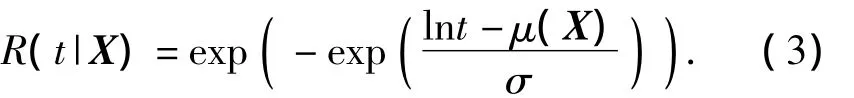
1.2 Fitting of Location Parameters
The location parameterμ(X)is an unknown function of environment covariateX.Rather than a usual linear model,a non-linear model is necessary to describe the influence of complex covariate on the location parameter.Hence,RBF is introduced to establishμ(X)due to its good adaptability[8].RBF is one kind of weighted interpolation based on distance.It takes the advantage of fitting the non-linear model.
The basic idea of the radial basis function method is to weight and interpolate Euclidean distance basis function[9].Generally,RBF takes the low rank linear function as a regression function and Gaussian function as a radial basis function.Then,the location parameter function can be written as
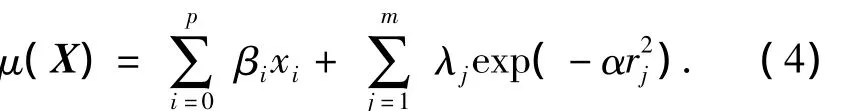
2 Model Parameter Estimation
2.1 Maximum Likelihood Function
Denote the test data under varied environment conditions as
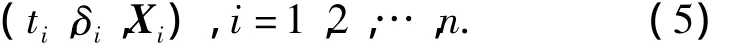
whereXi=(xi1,xi2,…,xip)is the environment covariate ofi-th sample,andδiis the test indicator,δi=1 fortibeing failure time andδi=0 fortibeing censored time.

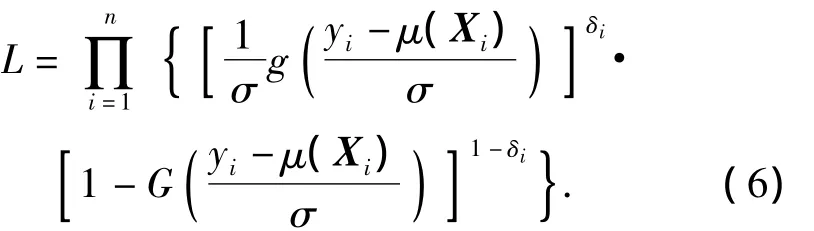
2.2 Generalized Linear Estimations
Suppose thatTfollows Weibull distribution,thus,Yfollows extreme-value distribution.SubstitutingG(t)=1-exp(-et)andg(t)=exp(-et)etinto Eq.(6),the log likelihood function can be written as
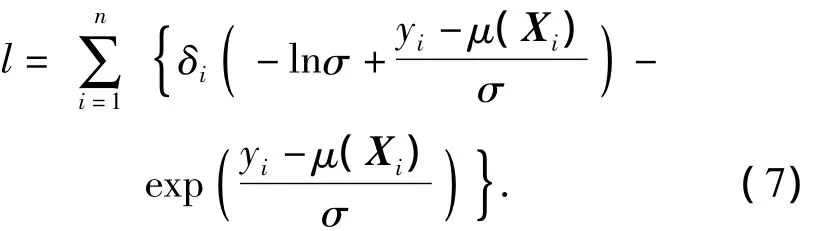
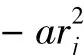


The log ofwiis
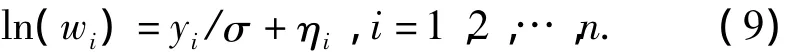
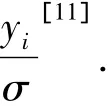
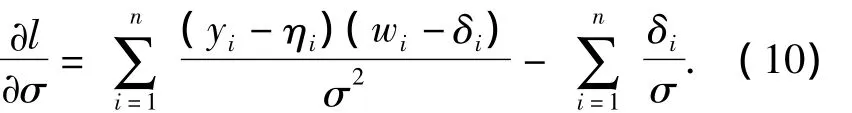
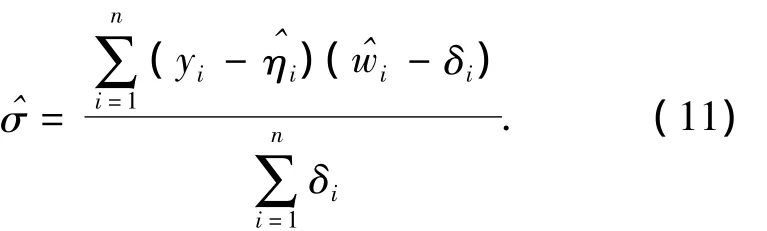
The estimation begins withσ=1,uses the loglinear model algorithm to fit the parametersβ,then obtainsσfrom Eq.(11).This iteration continues till the parameter estimation converges.Then,we can obtain the estimationsand
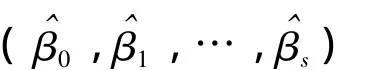
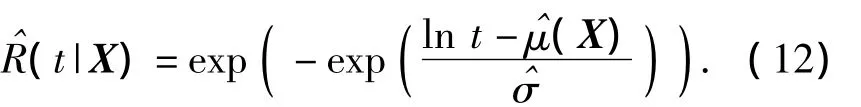
3 Reliability Sensitivity Analysis Method
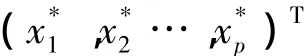
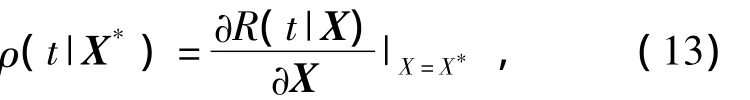

Taking the Weibull distribution as example,for givenX*,the reliability sensitivity can be expressed as
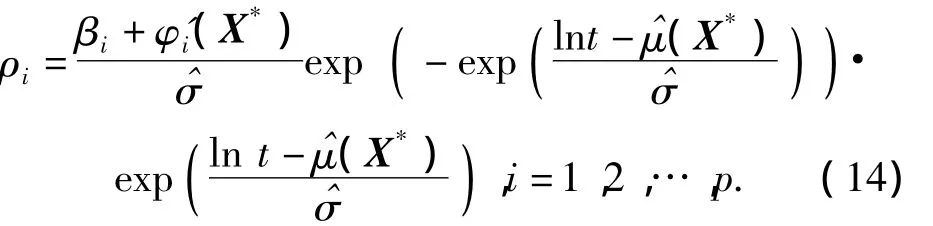
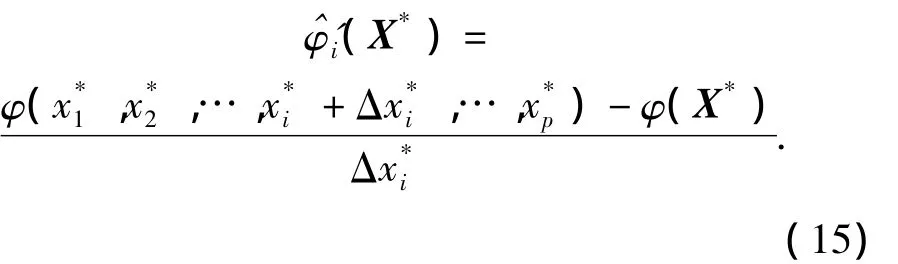
4 Example
Tab.1 shows the results of reliability test on a kind of DC motors,in on/off cycling or continuous operation under 7 different environment conditions[1].The environment covariates are
x1:voltage(Volts);
x2:load(Amperes).
x3:1(on/off cycling),or 0(continuous operation);
The motor's common environment covariates arex1=3 V,x2=0.08 A andx3=0.It is required to assess the reliability under the common conditions in operating time of 100 h.
The curves of reliability estimations under 4 different environment conditions are shown in Fig.1.
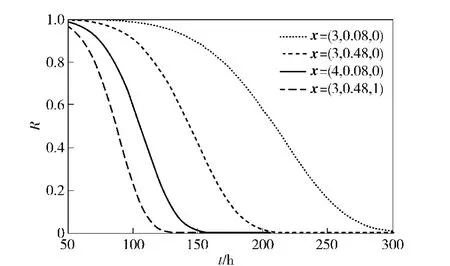
Fig.1 Reliability of four different environments
From Fig.1,it can be known that the influences of environment factors on reliability are great.And the influences of any two environment factors are observably different.For given voltagex1=3 V and operating modex3=0,three curves of reliability sensitivity of loads are shown in Fig.2.
From Fig.2,it can be known that the reliability sensitivity relative to loads depends on the operation timetunder given environment conditions.However,the curve shapes are similar.
For given loadsx2=0.08 A and operating modex3=0,three curves of reliability sensitivity relative to voltage are shown in Fig.3.

Fig.2 Reliability sensitivity curves relative to loads
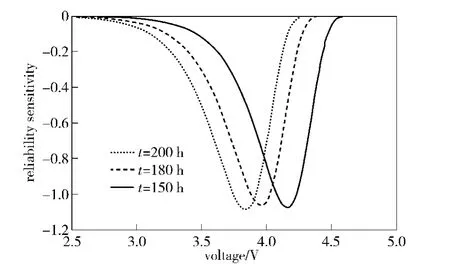
Fig.3 Reliability sensitivity curves relative to voltage
From Fig.3,it can be known that the reliability sensitivity relative to voltage depends on the operation timetunder given environment conditions.However,the curve shapes are similar.
The operation mode is described as an indicator variable.So we only pay attention on the reliability sensitivity relative to load and voltage.Whent>400 h,the reliability tends to 0 under normal operation environment conditions.In this case,it is not significant to analyze the reliability sensitivity.When 0≤t≤400 h,the curves of reliability sensitivity are shown in Fig.4.
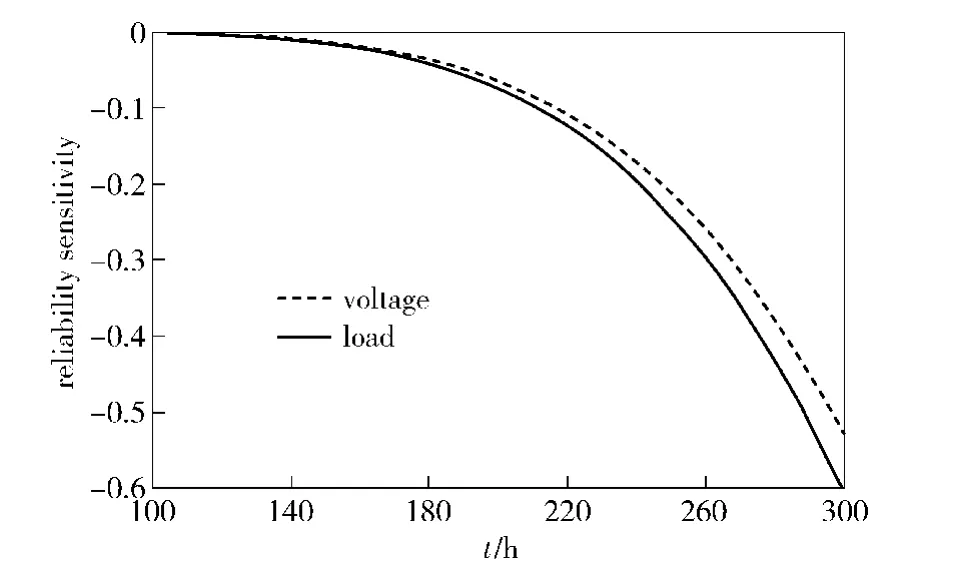
Fig.4 Reliability sensitivity of operation time
From Fig.4,it can be known that the absolute value of the reliability sensitivity relative to load is higher than voltage under common operation conditions.It means that the reliability is more sensitive to the load.Furthermore,the reliability becomes more sensitive to both load and voltage with the increase of operation time.
5 Conclusions
A method of reliability sensitivity analysis using varied environment test data is proposed for location scale family.With an application example,the conclusions can be drawn as follows.
1)RBF method fits the location parameter well,due to its better adaptability.Furthermore,it can be used to describe the interaction of different environment factors on the reliability.
2)Using the generalized linear model to get MLE of parameters is more effective in convergence.
3)The reliability sensitivity is necessary for the reliability design to measure the dynamic influence of environment factors on reliability.
4)The method proposed in this paper combines the test data under different environment conditions to increase the information for reliability analysis.Thus,the analysis precision can be improved.
[1]Wendai W,Dimitri B K.Fitting the Weibull log-linear model to accelerated life-test data[J].IEEE Transactions on Reliability,2000,49(2):217-223.
[2]Wang H Z,Ma B H,Shi J.Estimation of environmental factors for the inverse Gaussian distribution[J].Microelectronics& Reliability,1992,32:931-934.
[3]Elsayed E A,Wang H Z.Bayes& classical estimation of environmental factors for the binomial distribution[J].IEEE Transactions on Reliability,1996,45(4):661-665.
[4]Karamchandani A,Cornell C A.Sensitivity estimation with in first and second order reliability methods[J].Structural Safety,1991,11(2):95-107.
[5]Hohenbicher M,Rackwitz R.Sensitivity and important measures in structural reliability[J].Civil Engineering Systems,1986,3(4):203 -209.
[6]Nelson W.Accelerated testing:statistical model,test plans,and data analyzes[M].US:John Wiley & Sons,1990.
[7]Mettas A.Modeling & analysis for multiple stress-type accelerated life data[J].Proceedings Annual Reliability and Maintainability Symposium,2000:138-143.
[8]Hardy R L.Multi quadratic equations of topography and other irregular surfaces[J]. Journal of Geophysics,1971,76:1905-1915.
[9]Buhmann M D.Radial basis functions[M].UK:Cambridge University Press,2004.
[10]McCullagh P,Nelder J A.Generalized linear models[M].London:Chapman& Hall,1989.
[11]Uusipaikka E.Confidence intervals in generalized regression models[M].US:CRC press,2009.
[12]Ahammed M,Melchers R E.Gradient and parameter sensitivity estimation for systems evaluated using Monte Carlo analysis[J].Reliability Engineering and System Safety,2006,91(5):594-601.
[13]Melchers R E,Ahammed M.A fast approximate method for parameter sensitivity estimation in Monte Carlo structural reliability[J].Computers and Structures,2004,82(1):55-61.
[14]Wu Y T,Monhanty S.Variable screening and ranking using sampling-based sensitivity measures[J].Reliability Engineering and System Safety,2006,91(6):634 -647.
- Defence Technology的其它文章
- Application of Adaptive Backstepping Sliding Mode Control in Alternative Current Servo System of Rocket Launcher
- Optimization Design of Double-parameter Shift Schedule of Tracked Vehicle with Hydrodynamic-mechanical Transmission
- A New Single DIFAR Sonobuoy Target Location Algorithm
- Waveguide Invariant and Passive Ranging Using Double Element
- Research on Estimation of Time Delay Difference in Passive Locating for Impulse Signal
- New Wideband Beam-forming Method Used in Underwater Communication System

