HPLC Analysis of Iridoid Glycosides from the Stem of Paederia scandens*
WANG Yong-bing, LI Quan, JIANG Yi, LIU Guang-yao
Suzhou Yihua Biomedical Technology Co.,Ltd,Suzhou,Jiangsu 215123,China
1 Introduction
Paederia scandens(Lour.)Merri.,a climbing plant,belongingtothefamily Rubiaceae,ispopularly known as “Ji Shi Teng”in Chinese and widely grows in India,Vietnam,China,Japan,Philippines and USA[1].It has been traditionally used as folk medicine and food in Southeast of Asia for thousands of years.The leaves of the plant are used as an ingredient in various foods in Vietnam.
Recently,it has been reported that the iridoid glycosides paederoside,asperuloside,paederosidic acid,methyl paederosidate,deacetylasperuloside and scandoside were isolated from the MeOH extract from the stems and roots of P.scandens[2].These chemical constituents of P.scandens have biological activities such as anti-virus,anti-tumor,anti-inflammation and anti-microbialactivities.In folklore medicine,the roots,stems,leaves,barks and fruits of P.scandens have been used to treat toothache,chest pain,piles,inflammation ofthe spleen,emesis,rheumatic arthritis and bacillary dysentery in China,Japan,Vietnam and other countries in the south east Asia for thousands of years.
2 Experiments
2.1 Chemical reagents and samples
Acetonitrile was of HPLC grade from Merck(Darmstadt,Germany);distilled water was further purified by a Mili-Q system (Milipore,MA,USA);the other chemicals were of analytical grade.All solvents and samples were filtered through a 0.45μm micropore filters before they were injected for HPLC.
The threereference compoundspaederosidic acid(1),paederoside(2)and methyl paederosidate(3)were isolated previously from Paederia scandens(Lour.)Merri.in our laboratory,and the structures of them were confirmed based on spectroscopic experiments(1HNMR,13CNMR,ESI-MS)and by comparison with literature data[1].The purity of each compound was determined to be higher than 98%by normalization of the peak area detected by HPLC-DAD,and the chemicals in aqueous solution were very stable during our experimental period.
Eight batches of Paederia scandens(Lour.)Merri.samples were collected from different provinces in China and the voucher specimens of these collections were deposited at our company.
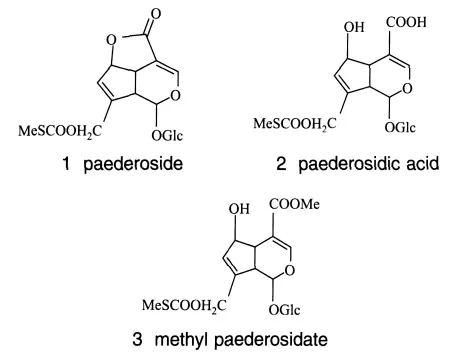
2.2 Preparation of Paederia scandens extracts
The stems ofP.scandens collected from differentareas were powdered by an electrical blender and sieved through a 40-mesh sieve.The powderwasquantitatively extracted by methanol(1g to 100mL)through refluxing for 2hrs twice.The combined extractswere concentrated on a rotary evaporator. The residues were then transferred into a 10 mL volumetric flask,and brought to volume with water.The sample solutions were filtered through a 0.45 μm micropore filter before HPLC analysis.
2.3 Preparation of standard solutions
The stock mixed solution of the three standardswhich were separated from the crude extract samples was prepared by dissolving accurately weighted portions of the standards in water.The concentrations of the three reference compounds paederosidic acid(1),paederoside(2)and methyl paederosidate(3)were 1.047,0.556 and 0.494 mg·mL-1,respectively.The solution was further diluted to a series of concentrations with water for gain ofcalibration curve,limits of detection(LOD)and quantification(LOQ).
2.4 Instrumentation and chromatographic conditions
An Agilent 1200 series HPLC system(Agilent Technologies,USA)and AgilentChem Stations software were used for the chromatographic analysis.The separation wascarried outon a Shim-pack VP-ODS C18column(250 mm×4.6 mm,5 μm).The mobile phase was composed of solvent A(0.1% formic acid aqueous,V/V)and solvent B(acetonitrile).A linear gradient program at a flow rate of 1.0 mL·min-1was performed as follows:0~5 min,15.0%B;5~30 min,linear gradient 15.0%B~20.0%B;30~45 min,linear gradient 20.0%B~45.0%B.The injection volume,column temperature,and UV wave length were set at 20 μL,25°C and 240 nm, respectively. The typical HPLC -DAD chromatograms of the three reference compounds and samples were shown in Figure 1.
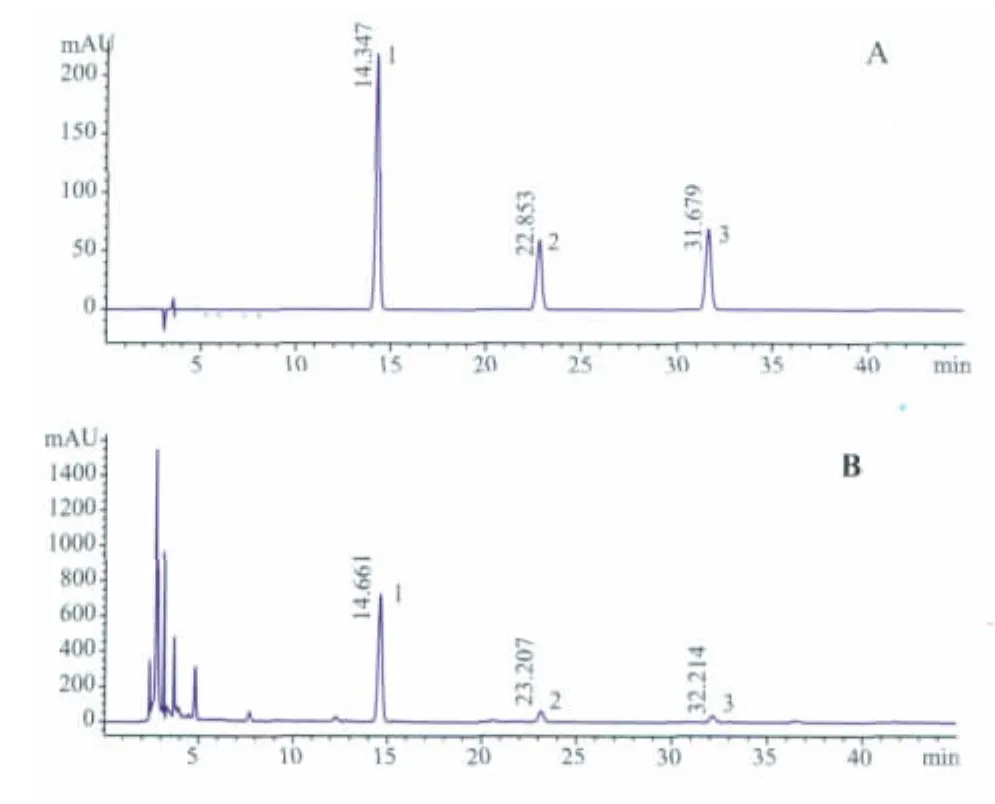
Fig.1 Typical HPLC-DAD chromatograms
2.5 Calibration curve,limits of detection and quantification
The standard stock solution containing three iridoid glucosides was prepared and diluted to ap-propriate concentrations for the plotting of calibration curves.Each analyte solution of five concentrations covering the concentration range according to the level expected in the plant samples was analyzed in triplicate,and then the calibration curves were constructed by plotting the peak areas versus the concentration(μg·mL-1)of each analyte.
Dilutions and injections of the stock standards were made until an HPLC chromatogram showed that the iridoid glycosides peak height reached an S/N of approximately 10︰1 and 3︰1 for LOQ and LOD respectively.
2..6 Precision,stability,repeatability,and accuracy
The precisions were determined by analyzing standard solutions of three iridoid glycosides in six replicates during a single day.The relative standard deviation(RSD)of peak area of each compound were calculated.Stability ofsample was tested separately at 0,2,4,8,24,and 48hrs,within 2days.The sample solution was kept at 4℃before analysis.To confirm the repeatability,six replicates of sample solutions describes as above were prepared and analyzed,the RSD values of the peak areas were calculated.
Method accuracy was calculated by spiking six samples of the extract of P.scandens with standard stock solution of standard compounds of 1~3.The theoretical amount of analyte in the sample preparations and the average percentage analyte recovered in the spiked solutions were calculated.
3 Result and discussion
3.1 Optimization of extraction procedure
The optimization of extraction was targeted on iridoid glucosides.In order to obtain quantitative extraction of iridoid glycosides from P.scandens,the variables involved in the extraction were optimized,such as solvent and extraction method.Both methanol and ethanol were tested for their efficiency as extraction solvent.Methanol was found to be methanol,which allowed a complete extraction of the iridoid glucosides as tested.In order to find the best extraction better ultrasonic processing for 30 min,refluxing for twice were tested and compared with various other conditions.The results suggested that refluxing for 2hrs twice was simpler and more effective in extracting the iridoid glucosides.
3.2 Optimization ofchromatographic conditions
Studies were carried out in order to validate an efficient method for the analysis of the iridoid glycosides.Parameters,such as detection wavelength,compositions and percentages of the mobile phases,temperatures and flow rates of the chromatographic columns were all studied.
Different settings of mobile phase(organic solvent,acid percentage and gradient programming)were tested.Since acid is known to achieve better separation for paederosidic acid by reducing the tailing of the peaks,various mixtures of water and acetonitrile in combination with formic acid were tried.As a result,a good separation of the iridoid glucoside peaks was achieved with the mobile phase comprising solvent A(0.1%aqueous formic acid,V/V)and solvent B (acetonitrile)with a gradient elution mode.The chromatographic conditions were then validated to be applicable for the analysis of the content of iridoid glucosides of P.scandens.
UV/DAD spectra were recorded within a range of 200~400 nm to select a suitable wavelength and to maximize the detection of the standard compounds.The spectra illustrated that the wavelength of 240 nm was determined to be the most appropriate for the simultaneous analyses of the three iridoid glucosides present in P.scandens.
The flow rate and column temperature were also optimized to obtain suitable resolution.At temperature 25°C and flow rate 1.0 mL·min-1,the method achieved the best separation.
3.3 Method validation
The typical HPLC-DAD chromatograms of the three reference compounds was shown in Figure 1(A). As a result, a baseline separation was achieved within 45min under the optimized conditions,with symmetrical,sharp and well-resolved peaks for all the three analytes.The linear regression analytical data for the calibration plots showed a good linear relationship with r2>0.9999 wit hin the tested ranges.The LOD and LOQ for all the compounds were less than 52 ng·mL-1and 170 ng·mL-1,respectively.These values were described in Table 1.They were sufficient for the analyses of the extracts and met the precision and accuracy criteria.The variations of precision were less than 2.08%for the analytes.The standards in sample extracted from P.scandens remained very stable in aqueous solution(RSD <2.00%)at 4°C over the tested period.The recovery studies were carried out at six samples,and the developed analytical method has an excellentaccuracy with a recovery rates from 98% to 105% for the three iridoid glycosides(Table 2).Therefore,the HPLC–DAD method wasprecise,accurate and sensitive enough for simultaneous quantitative evaluation of the three iridoid glycosides in the stem of P.scandens.
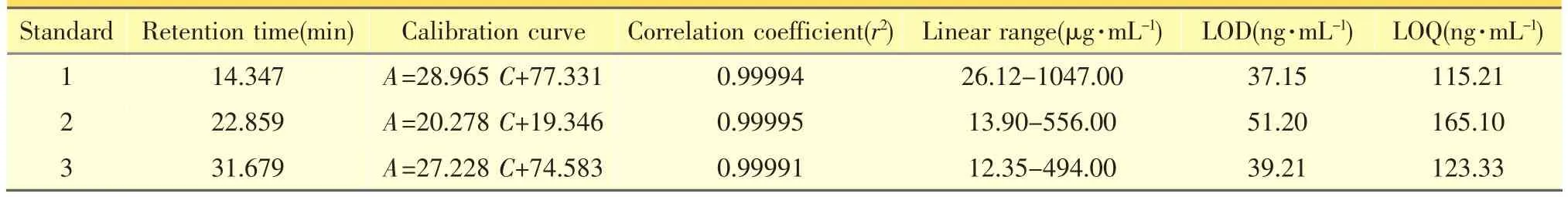
Table1 Calibration curves,LOD and LOQ for the standards
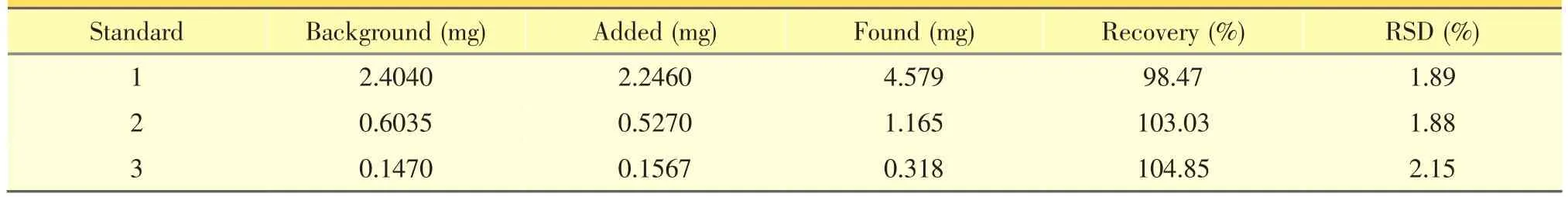
Table2 Recoveries of the three iridoid glycosides inP.scandens(n=6)
3.4 Sample analysis
The suitability of the developed analytical method was demonstrated by analyzing P.scandens extracts from cultivated or wild samples from different place of China and the results were summarized.The concentration ranges of the iridoid glycosides were very wide in samples from different places of China,as shown in Table 3,the contents of the three glycosides were 3~16 mg·g-1(paederosidic acid),0.1~2 mg·g-1(paederoside),and 0.2~7 mg·g-1(methyl paederosidate),respectively.
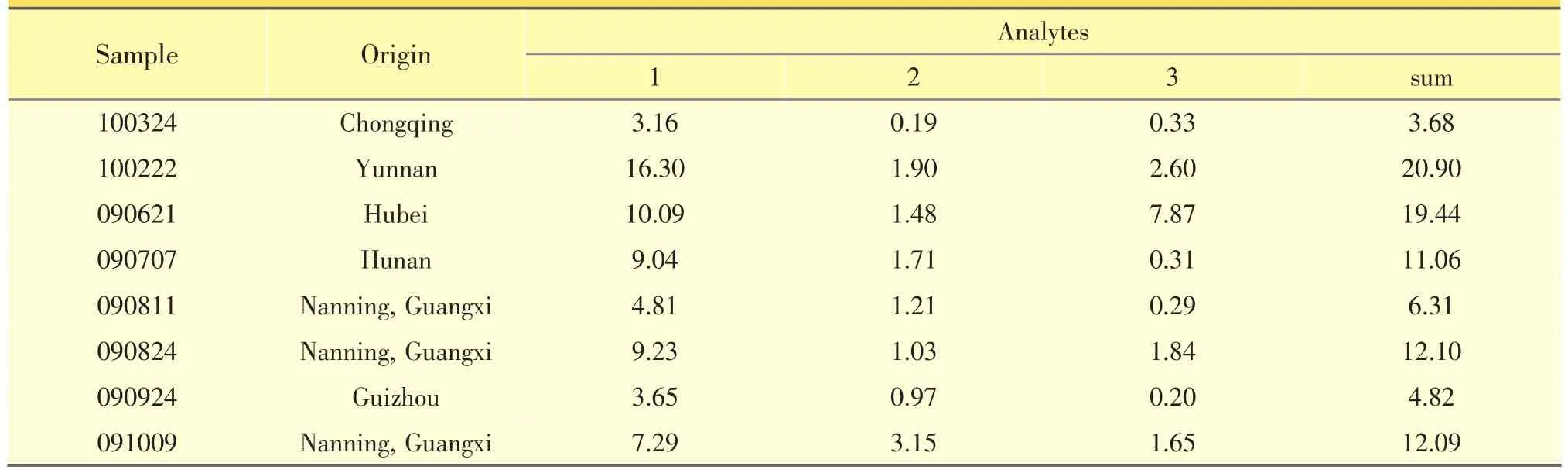
Table3 Contents of the three iridoid glycosides in P.scandens collected from different provinces in China(mg.g-1)
4 Conclusion
It is the first time to establish a quantitative method to investigate the content of iridoid glucosides of in Paederia scandens.Among the three glucosides,paederosidic acid was commonly distributed,and was found to be the most abundant one,which can be applied to the quality control of Paederia scanden.This method can meet the requirements of quantitative analysis of the samples.
Reference
[1] Quang DN,Hashimoto T,Tanaka M,et al.Iridoid glucosides from roots of Vietnamese Paederia scandens[J].Phytochemistry.2002,60(5):505-14.
[2] Zou X,Peng S,Liu X,et al.Sulfur-containing iridoid glucosides from Paederia scandens[J].Fitoterapia,2006,77(5):374-7.

