Surgical Treatment of Intralobar Pulmonary Sequestration
Hong-sheng Liu,Shan-qing Li*,Ying-zhi Qin,Zhi-yong Zhang,and Hua Ren
Department of Thoracic Surgery,Peking Union Medical College Hospital,Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences &Peking Union Medical College,Beijing 100730,China
PULMONARY sequestration is a rare congenital forgut malformation.It is characterized by a mass of non-functioning pulmonary tissue and lack of a normal communication with the tracheobronchial tree.It is usually supplied by systemic artery.It can be divided into two subtypes,intralobar and extralobar.The intralobar pulmonary sequestration (ILS) is in the normal pulmonary parenchyma without own pleural covering.Because of infection,hemoptysis and even malignancy can occur in the ILS patients,surgery is recommended.In this present study,we evaluated the clinical characteristics,diagnosis,treatment,and outcome of ILS.
PATIENTS AND METHODS
Patients who were diagnosed with ILS between January 1988 and January 2009 in Peking Union Medical College Hospital were retrospectively reviewed.We recorded and analyzed the clinical symptoms,diagnostic methods,imaging presentations,operative technique,complications,and outcome of these patients.
RESULTS
General characteristics
Forty-seven ILS patients were reviewed.Among them,25 were male and 22 were female.Their ages ranged from 12 to 58 years,with an average age of 32.3 years.
Clinical presentations
Of the 47 patients,5 were asymptomatic,others presented with symptoms as follows.Thirty-seven patients had fever,cough,and sputum,12 had hemoptysis,6 had chest pain,4 had dyspnea,and 23 patients had more than one symptom.The disease course ranged from 1 week to 40 years (mean 67 months).
Imaging findings
All patients underwent examinations of chest X-ray and computed tomography (CT),13 had contrast enhanced CT,among which 5 had three-dimensional (3-D) reconstruction;1 had magnetic resonance imaging (MRI),and 3 had angiography.CT revealed mass in 19 patients,cyst in 15 (4 had air-fluid level),hydrothorax in 1,and bronchiectasis in the other 12 patients (Fig.1).In the patients with enhanced scan,the aberrant supplying artery can be seen in all the patients,while in the patients with 3-D reconstruction,more details can be revealed (Figs.2,3),MRI and angiography are helpful in confirming the diagnosis (Fig.4).Based on radiological examination,35 patients were diagnosed as pulmonary sequestration,7 patients as pulmonary cyst,3 patients as bronchietasis,1 as hydrothorax,and 1 as pulmonary carcinoma.
Surgical treatment
Thoracotomy was performed in 45 patients and thoracoscopy was performed in 2.The aberrant supplying artery originated from diaphragmatic artery was found in 5 patients,from abdominal aorta was found in 3 patients,and from descending thoracic aorta was found in the other patients.The number of supplying artery ranged from 1 to 3 branches (mean 1.25).Seven patients had more than one supplying artery.The diameter of the supplying artery ranged from 3 mm to 25 mm (mean 8 mm).Lobectomy was performed in all patients.The sequestered lung was located in right lower lobe in 12 patients,right upper lobe in 2 patients,and left lower lobe in 33 patients,respectively.
Outcome
Only two patients developed intraoperative massive bleeding,the other patients were operated smoothly.After operation,1 patient had venous thrombosis of upper extremity,1 had atrial fibrillation,and both recovered uneventfully.The drainage time ranged from 2 to 8 days(mean 3.7 days).All the patients were proved to be sequestration pathologically,4 accompanied with bronchogenic cyst,15 with bronchiectasis,8 with infection,2 with aspergilloma,and 1 with carcinoid.Five patients were lost to follow-up and the other 42 patients were followed up from 2 months to 15 years (mean 8 years).All patients recovered,with no late recurrence.

Figure 1.Computed tomography (CT) shows a mass in the left lower lobe.
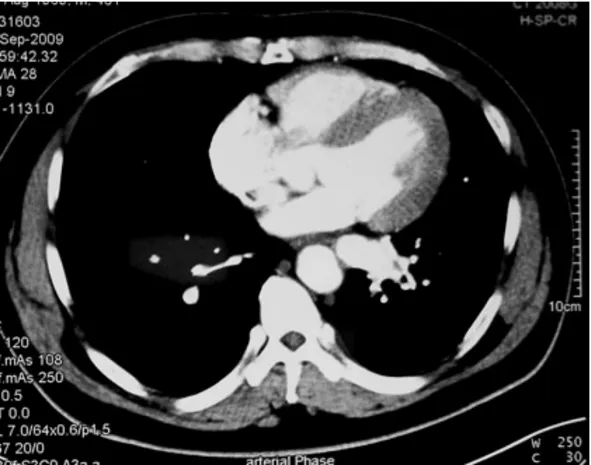
Figure 2.Contrast enhanced CT shows the aberrant artery.

Figure 3.Three-dimensional reconstruction shows detail of the aberrant artery.

Figure 4.Aortography shows an aberrant artery arising from the descending thoracic aorta.
DISCUSSION
Pulmonary sequestration is a rare congenital malformation,and its prevalence is 0.15%-6.4%.1Extralobar pulmonary sequestration (ELS) has its own visceral pleura which is isolated from the normal lung tissue,while ILS is in the normal lung parenchyma.The prevalence of ILS is six times more than that of ELS.2
The ILS patients usually develop recurrent bronchitis,pneumonia,hemoptysis,while 10%-15% patients are asymptomatic.More than 50% patients develop symptoms in their two decades of life.3In our series,5 (10.6%) patients are asymptomatic,52.4% (22/42) patients develop symptoms in their two decades of life,and all patients develop symptoms before 60 years old.Infection is the most common symptom (88%),hemoptysis is the second(28%).Hofman et al4reported a case of hemoptysis and massive hemothorax underwent emergency thoracotomy.
Chest X-ray and CT are most commonly used,which usually reveal pulmonary mass,cyst,or/and air-fluid level,though they are not specific.Angiography remains a gold standard for diagnosis,but it is rather complicated and more traumatic.Contrast enhanced CT and 3-D reconstruction is more commonly used and accepted recently.5In our series,34 patients underwent CT plain scan,12 patients were misdiagnosed as other diseases,while the patients who underwent contrast enhanced CT and 3-D reconstruction confirmed the diagnosis.Thus contrast enhanced CT with 3-D reconstruction is a convenient and accurate diagnostic method,wihch is the first choice in patients who are suspected as sequestration,while MRI and angiography are helpful in confirming the diagnosis.6
The most common site of the sequestered lung is in the posterior basal segment,about 2/3 is in the left,and it is rarely seen in the middle and upper lobe.In our series,33(70%) patients were in the left lower lobe,12 (25%) in the right lower lobe,and 2 (5%) in the left upper lobe.
Hemoptysis or malignancy can occur in ILS patients due to recurrent infection,therefore surgery is recommended.If the lesion is limited,segmentectomy can be performed,otherwise lobectomy is the best choice.In our series,lobectomy was performed on all patients.We think it is safer,because sequestration usually accompanied with bronchiectasis,fungi infection,even malignancy.If sequestration is suspected preoperatively,the inferior pulmonary ligament should be managed cautiously,because the aberrant supplying artery is usually hidden in it.Thoracoscopy is used more widely in thoracic surgery.Wan et al7first reported treatment of sequestration by thoracoscopy,which can relieve the pain and shorten the recovery time.We performed thoracoscopy in 2 patients,and both recovered uneventfully.The diagnosis was confirmed pathologically in all patients.
Most aberrant supplying arteries are from descending thoracic aorta and abdominal aorta.Savic et al3retrospectively reviewed 547 patients,74% are from descending thoracic aorta,18.7% are from abdominal aorta.In our series,83% are from descending thoracic aorta.Some studies reported the supplying arteries from rare origin,such as coronary artery,subclavian artery,etc.8The aberrant artery is usually rather thick,and has more than one branch,it should be managed carefully,otherwise disastrous consequences can occur.In our series,massive bleeding from aberrant artery developed in 2 patients.We think identification of the supplying artery is very important.
In conclusion,ILS is rare,surgery is recommended because of its potential severe complications.Contrast enhanced CT and 3-D reconstruction is the best diagnostic method.Both thoracotomy and thoracoscopy are appropriate for the selected candidates.
1.Halkie N,Cuenoud PF,Corthesy ME,et al.Pulmonary sequestration:a review of 26 cases.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 1998;14:127-33.
2.Sugio K,Kaneko S,Yokoyama H,et al.Pulmonary sequestration in older child and in adults.Int Surg 1992;77:102-7.
3.Savic B,Birtel FJ,Tholen W,et al.Lung sequestration:report of seven cases and review of 540 published cases.Thorax 1979;34:96-101.
4.Hofman FN,Pasker HG,Speekenbrink RG.Hemoptysis and massive hemothorax as presentation of intralobar sequestration.Ann Thorac Surg 2005;80:2343-4.
5.Toya SP,Douskou M,Tomos P,et al.Pulmonary sequestration diagnosed by multidetector computed tomographic angiography.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2007;32:535.
6.Ko SF,Wan YL,Ng SH,et al.MRI of thoracic vascular lesions with emphasis on two-dimensional time-of-flight MR angiography.Br J Radiol 1999;72:613-20.
7.Wan IY,Lee TW,Sihoe AD,et al.Video-assisted thoracicsurgery lobectomy for pulmonary sequestration.Ann Thorac Surg 2002;73:639-40.
8.Temes RT,Talbot WA,Carrillo YM,et al.Sequestration of the lung arising from the circumflex coronary artery.Ann Thorac Surg 1998;65:257.
 Chinese Medical Sciences Journal2010年1期
Chinese Medical Sciences Journal2010年1期
- Chinese Medical Sciences Journal的其它文章
- Sex Hormones and Androgen Receptor:Risk Factors of Coronary Heart Disease in Elderly Men△
- Comparison between Ophthalmologists and Community Health Workers in Screening of Shallow Anterior Chamber with Oblique Flashlight Test△
- Factors Influencing Pleural Effusion after Fontan Operation:an Analysis with 95 Patients
- Relationship between Carotid Atherosclerosis and Cerebral Infarction
- Expression of FLICE-inhibitory Protein in Synovial Tissue and Its Association with Synovial Inflammation in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis△
- A Case of Large“Silent”Extra-adrenal Retroperitoneal Paraganglioma Resected Laparoscopically
