Prevalence of Anti-endothelial Cell Antibodies in Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Associated with Connective Tissue Diseases△
Meng-tao Li,Jun Ai,Zhuang Tian,Quan Fang,Wen-jie Zheng,Xue-jun Zeng,and Xiao-feng Zeng*
1Department of Rheumatology,2Department of Cardiology,Peking Union Medical College Hospital,Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences &Peking Union Medical College,Beijing 100730,China
PULMONARY arterial hypertension (PAH) is a chronic disease of pulmonary circulation with latent severe damage,and it has puzzled the clinicians for many years.Since World Health Organization(WHO) reclassified PAH in 2003,connective tissue diseases(CTD) have been paid more attention as the important correlated diseases of PAH.Systemic sclerosis (SSc),systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE),and mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD) are major associated ones,of which,the morbidity can reach 5%-32%.The prognosis of CTD with PAH is relatively poor,so early diagnosis and interventions are thought to be important to improve the prognosis.Some specific biological markers might be helpful for early diagnosis.Researches on SSc,SLE,and MCTD with cyto-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay(cyto-ELISA) showed that anti-endothelial cell antibodies(AECAs) were more frequently found in patients with PAH than those without PAH.1,2Advanced research with Western blotting revealed that AECAs from patients with SSc were bound to two major bands (75 kD and 85 kD),but the relationship with PAH was still uncertain.3In this study,we investigated the prevalence of AECAs in the sera of CTD patients with PAH by Western blotting and its correlation with clinical manifestations,trying to find out specific AECAs from CTD patients with PAH.
PATIENTS AND METHODS
Patient enrollment
CTD patients admitted to Rheumatology Department of Peking Union Medical College Hospital between January 1999 and May 2006 were enrolled.All of them were screened by Doppler echocardiography for PAH,and PAH was defined as systolic pulmonary artery pressure(sPAP)>40 mm Hg.According to whether they had PAH,the CTD patients were classified as study group (PAH group)and disease control group (non-PAH group).All the enrolled patients had no other systemic involvement except PAH.Meanwhile,healthy blood donors were included as normal control group.
Serum samples
Serum samples from all patients and healthy controls were aliquoted and stored at -80°C until being tested.
EA.hy926 cell culture
Frozen EA.hy926 cells were taken from nitrogen canister and swinged in aqueous bath at 37-40°C for 1-3 minutes to be melt.We then added suitable medium (high glucose DMEM cataining 10% fetal calf serum) and rotated it at the rate of 1 000/min (centrifuge radius:15 cm) for 5-10 minutes.After the supernatant was removed,the medium was added again.Then cells were inoculated in the culture flask with a density of 1×109cells/L and cultured in an incubator at 37°C in 5% CO2.
Detecting AECAs with Western blotting
Extraction of membrane and cytoplasmic proteins from endothelial cells
When confluent,EA.hy926 cells were detached with 0.05% trypsin and 0.02% ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA).Then they were centrifuged at the rate of 1 000/min (centrifuge radius:15 cm) for 10 minutes.After the supernatant was removed,they were washed with PBS twice and centrifuged at the rate of 3 000/min (centrifuge radius:15 cm) for 10 minutes.We then added suitable lysate (containing 1% Triton X-100,2 mmol/L EDTA,40 mmol/L Tris),dithiothreitol (DDT),phenylmethyl sulfonylfluorid (PMSF),and protease inhibitors before we kept them in ice aqueous bath for 1 hour and broke the cells with ultrasound for 6 times,5 seconds in each time.They were centrifuged at the rate of 13 000/min (centrifuge radius:15 cm) for 30 minutes at 4°C and the resulting upper stratum contained the protein needed.The protein density was then detected with Braford test by ultraviolet spectrophotometer.
Detection of AECAs by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
Separation gel (10% acrylamide) and spacer gel were prepared.Equal amounts of solvable proteins (500 μg)were subjected to preparative SDS-PAGE through 10%polyacrylamide gels.The proteins were then transferred onto nitrocellulose membrane for 1 hour at 0.8 mA/cm2with a semi-dry electroblotter model A (Ancos,Hojby,Denmark).After blocking with PBS-0.2% Tween for 90 minutes,the membranes were incubated with serum samples for 12 hours at 4°C.They were then extensively washed before being incubated with the secondary caprine anti-human IgG for 1 hour at room temperature.Then we added the substrate A (0.05% diaminobenzidine,0.5 mL)and B (0.02% H2O2,0.5 mL) for staining.The dark bands represented positive results.Finally,stop buffer (2 mol/L H2SO4,0.5 mL) was added.
Statistical analysis
Statistical software of SPSS for Windows 13.0 was used for statistical analysis.The prevalence of AECA was measured with Chi-square test,and it was considered statistical significance if thePvalue less than 0.05.
RESULTS
General information
The PAH group included 39 CTD patients with PAH.Among them,there were 17 SLE,7 MCTD,3 SSc,3 primary Sjögren’s syndrome (pSS),and 9 undifferentiated connective tissue disease (uCTD) patients.The non-PAH group included 22 CTD patients (13 SLE,6 pSS,3 uCTD) without PAH.The normal control group included 10 healthy donors(Table 1).Patients in PAH and non-PAH groups as well as healthy controls were all female.There was no difference in age distribution among the three groups.
AECAs detected by Western blotting
The prevalence of serum AECAs in PAH group,non-PAH group,and normal control group was 82.1% (32/39),72.7% (16/22),and 20.0% (2/10),respectively.It was significantly higher in CTD patients with PAH than that in healthy donors (P<0.05).But in CTD patients,there was no significant difference between the PAH and non-PAH groups.Figure 1 shows results of AECAs detected by Western blotting.
Major recognized antigens by AECAs
The recognized antigens were bands of 22 kD,38 kD,53 kD,68 kD,75 kD,and 102 kD in PAH group.The bands of 38 kD,53 kD,68 kD,and 75 kD were found in non-PAH group.While 68 kD and 90 kD bands were detected in healthy donors.Anti-22 kD AECA was only detected in CTD patients with PAH (15.4%).Anti-75 kD AECA was more frequently detected in CTD patients with PAH than in those without PAH (51.3%vs.22.7%,P<0.05) (Table 2).
Relationship between AECAs and clinical manifestations
AECA and Raynaud's phenomenon (RP)
All AECAs were found in 84.2% (16/19) patients with RP and 80.0% (16/20) patients without RP.Among them,anti-75 kD AECA was found in 63.2% (12/19) patients with RP and 40.0% (8/20) patients without RP,and it seemed to be more frequently found in patients with RP than without RP,but the difference was not significant (P=0.15).
AECA and anti-RNP antibody
All AECAs were found in 90.5% (19/21) patients with positive anti-RNP antibody and 72.2% (13/18) patients with negative anti-RNP antibody.Among them,anti-75 kD AECA was more frequently detected in patients with positive anti-RNP antibody (71.4%,15/21) than those with negative anti-RNP antibody (27.8%,5/18) (P<0.05).
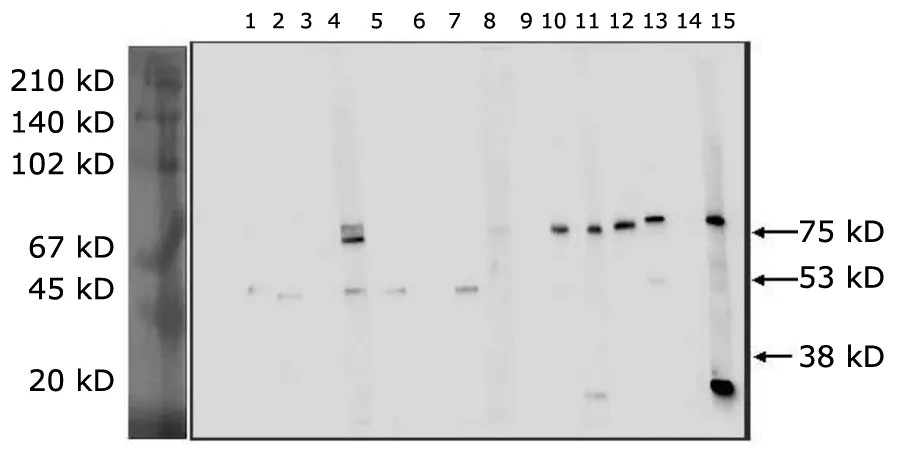
Figure 1.Result of AECAs detected by Western blotting.
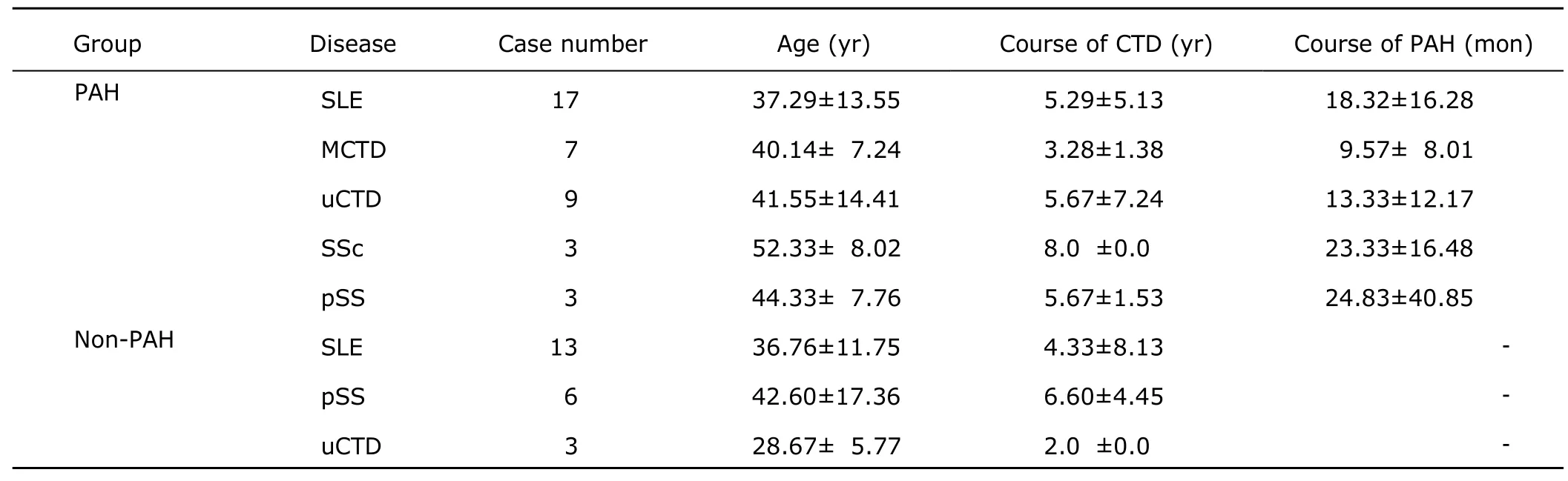
Table 1.General information of CTD patients with PAH and without PAH§
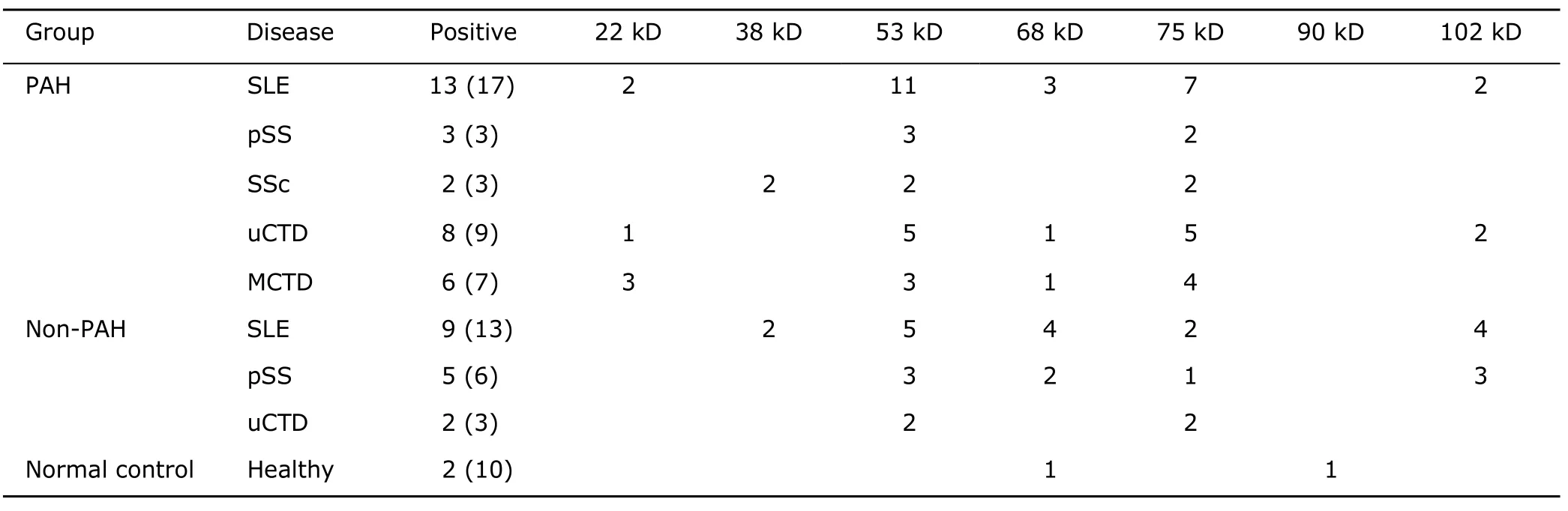
Table 2.Major antigens of AECAs detected in three groups
DISCUSSION
AECA was firstly reported by Lindquist and Osterland in 1971.4Its antigens were a group of heterogeneous proteins with molecular weight between 15 kD and 200 kD located on the surface of the endothelial cells.In recent studies,AECAs were more frequently detected in patients with SLE,SSc,MCTD,and some vasculitis such as Wegner’s granulomatosis (WG).It was also found that AECAs might be closely related to RP and PAH.1,2,5-7But all these studies were based on the results of cyto-ELISA,which could hardly confirm the existence of specific AECAs related to PAH.With Western blotting,Tamby et al3had detected serum AECAs in patients with PAH,and they found that the prevalence of 36 kD band was significant higher in idiopathic PAH patients,while in SSc patients 75 kD and 85 kD bands were more frequently detected,which seemed not definitely related to PAH.
PAH was chronic obstruction of small pulmonary arteries caused by endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cell dysfunction and proliferation,which might be AECA-mediated inflammation in CTD patients.In our study,we detected AECAs in sera of CTD patients with or without PAH and healthy donors with Western blotting.Results showed that the prevalence of AECAs was significantly higher in CTD patients than healthy controls,but there was no difference between CTD patients with PAH and those without PAH.Other study also showed that AECAs were more frequently detected in patients with SLE (87.5%) and WG(84.6%),8which was in accordance with our study.It could be explained that endothelial damage might be correlated with CTD.
In the further analysis,we had found that major antigens of AECAs were bands of 22 kD,38 kD,53 kD,68 kD,75 kD,and 102 kD in CTD patients with PAH,while 38 kD,53 kD,68 kD,and 75 kD bands in CTD patients without PAH.Only 68 kD and 90 kD bands were detected in healthy donors.Morever,anti-22 kD AECA was uniquely found in CTD patients with PAH (6/39).The prevalence of anti-75 kD AECA was significantly higher in CTD patients with PAH than those without PAH.By reviewing literatures,we found that anti-22 kD AECA was rarely reported,while Tamby et al3did report the existence of anti-75 kD AECA in SSc patients.Based on our results,we proposed that anti-22 kD and anti-75 kD AECAs might be related to PAH with CTD and play some roles in pathogenesis of PAH.
Because RP and anti-RNP antibodies were considered risk factors of PAH associated with CTD,we thus investigated their relationship with AECA.Statistical results showed that the prevalence of anti-75 kD AECA was higher in CTD groups with RP or with positive anti-RNP antibody than control groups,although its correlations with RP and PAH had not reached statistical significance,probably owning to the small sample size of the present study.Such results somehow suggest that anti-75 kD AECA might be closely related to PAH associated with CTD.
In conclusion,our study detected AECAs with Western blotting in sera of CTD patients with PAH,and revealed that anti-22 kD and anti-75 kD AECAs might be specific biomarkers of PAH associated with CTD.Further studies on specific AECAs should be expected to approach the pathogenesis of CTD with PAH.
1.Bodolay E,Csipo I,Sipka S,et al.Anti-endothelial cell antibodies in mixed connective tissue disease:frequency and association with clinical symptoms.Clin Exp Rheumatol 2004;22:409-15.
2.Taku Y,Masuyama J,Sumiya M,et al.Anti-endothelial cell antibodies and their relation to pulmonary hypertension in systemic lupus erythematosus.J Rheumatol 1994;21:2058-63.
3.Tamby MC,Chanseaud Y,Humbert M,et al.Anti-endothelial cell antibodies in idiopathic and systemic sclerosis associated pulmonary arterial hypertension.Thorax 2005;60:765-72.
4.Lindquist KJ,Osterland CK.Human antibodies to vascular endothelium.Clin Exp Immunol 1971;9:753-60.
5.Zheng WJ,Tang FL,Zhao Y,et al.Prevalence of antiepithelial cell antibody in systemic vasculitis and identification of the target antigen thereof.Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2005;85:3272-6.
6.Goberl U,Eichhorn BG,Kettritz R,et al.Disease activity and autoantibodies to endothelial cell in patients with Wegener’s granulormatosis.Am J Kidney Dis 1996;28:4946-51.
7.Cruz D,Keser G,Khamashta MA,et al.Antiendothelial cell antibodies in inflammatory myopathies:distribution among clinical and serologic groups and association with interstitial lung disease.J Rheumatol 2000;27:161-4.
8.Fattorossi A,Aurbach GD,Sakaguchi K,et al.Anti-endothelial cell antibodies:detection and characterization in sera from patients with autoimmune hypoparathyroidism.Proc Natl Acad Sci 1988;85:4015-9.
 Chinese Medical Sciences Journal2010年1期
Chinese Medical Sciences Journal2010年1期
- Chinese Medical Sciences Journal的其它文章
- Sex Hormones and Androgen Receptor:Risk Factors of Coronary Heart Disease in Elderly Men△
- Comparison between Ophthalmologists and Community Health Workers in Screening of Shallow Anterior Chamber with Oblique Flashlight Test△
- Factors Influencing Pleural Effusion after Fontan Operation:an Analysis with 95 Patients
- Relationship between Carotid Atherosclerosis and Cerebral Infarction
- Expression of FLICE-inhibitory Protein in Synovial Tissue and Its Association with Synovial Inflammation in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis△
- A Case of Large“Silent”Extra-adrenal Retroperitoneal Paraganglioma Resected Laparoscopically
