大气中强致癌物3-硝基苯并蒽酮GC/MS检测方法的建立
李怀建,吴 梅,张宏伟,王帮进,占 洁,王杨君,汪 午,
(1.上海大学环境污染与健康研究所,上海 200444;2.青岛大学医学院,山东青岛 266071; 3.南方医科大学,广东广州 510515)
大气中强致癌物3-硝基苯并蒽酮GC/MS检测方法的建立
李怀建1,吴 梅2,张宏伟3,王帮进1,占 洁1,王杨君1,汪 午1,3
(1.上海大学环境污染与健康研究所,上海 200444;2.青岛大学医学院,山东青岛 266071; 3.南方医科大学,广东广州 510515)
持久性有机污染物 (POPs)3-硝基苯并蒽酮(3-NBA)是一种极强的直接致突变和致癌物,多种动物试验以及人体细胞试验证明其具有极强的致突变能力。环境中的3-NBA主要来源于机动车尾气和大气光氧化反应,其在大气中浓度远低于多环芳烃。利用高效液相色谱(HPLC)法,分离、富集目标组分,再结合气相色谱-质谱(GC/MS)技术,可建立大气中3-硝基苯并蒽酮的检测方法,仪器检测限为13.7 pg,方法检测限为1.9 pg·m-3。方法回收率为88.52%,目标化合物回收率为78.2%。该方法重现性好、测定精度高,可用于实验室常规分析。
持久性有机污染物(POPs);3-硝基苯并蒽酮;气相色谱-质谱(GC/MS)
硝基多环芳烃 (nitro polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon,NPAH)是一类极强的直接致突变和致癌物,主要来源于化石燃料的燃烧过程,例如柴油机或汽油机机车燃料燃烧[1];也可以由大气中多环芳烃 (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon,PAH)与 OH或者 NO3自由基反应生成[2-9]。由于NPAH被证明其致突变或致癌能力要比相应的PAH高出很多倍[10],所以分析排放源和大气环境中的NPAH极为重要。
3-硝基苯并蒽酮(3-nitrobenzanthrone,3-NBA)于1997年在柴油机尾气和大气颗粒物中首次被发现,与1,8-二硝基芘的致突变能力相当,后者是文献报道致突变性最强的多环芳烃[11]。由于特殊而稳定的环状结构,3-NBA难以被生物降解。3-NBA的主要代谢物——3-氨基苯并蒽酮(3-aminobenzanthrone,3-ABA)曾在受柴油机尾气职业暴露的盐矿工人的尿液中被检出,说明暴露于柴油机尾气中极有可能给大多数人带来健康风险[12]。各种生物试验研究表明,3-NBA及其代谢产物是突变和癌变过程中DNA加合物形成的一个关键环节[13-14],这些加合物不仅具有致细胞损伤突变,可参与病变的诱变过程,而且是机体内致癌作用的关键因素。
3-硝基苯并蒽酮在大气环境中的浓度极低,存在于基质复杂的颗粒物中,对大气中3-硝基苯并蒽酮的测定,由于存在着分析手段和技术方面的挑战,目前报道的并不多[15-17],国内这方面的研究还是空白。本工作利用正相 HPLC法分离、富集目标组分,结合GC/MS技术,建立大气中3-硝基苯并蒽酮的检测方法。
1 试验部分
1.1 主要仪器与装置
Waters 2695高效液相色谱仪:美国Waters公司产品,配有2996型二级管阵列检测器;气相色谱-质谱联用仪:美国 Hewlett-Packard公司产品,配有6890气相色谱仪/5975四极杆质谱检测器和ChemStation工作站。
1.2 主要材料与试剂
3-硝基苯并蒽酮(纯度99%):德国环境致癌物生物化学研究所产品;1-硝基芘-d9:美国Chiron公司产品;二氯甲烷(色谱纯):德国CNW公司产品;正己烷(色谱纯):德国Merck公司产品;N,N-二甲基甲酰胺:美国 Tedia公司产品。
1.3 试验条件
1.3.1 样品采集及前处理 使用PM2.5Anderson大流量采样器(美国),流量1.0 m3·min-1,石英纤维滤膜(Whatman,20.3 cm×25.4 cm),采集时间24 h。取1/2滤膜,先用二氯甲烷提取,再用 N,N-二甲基甲酰胺(DMF)-H2O系统提取其中的芳烃类和极性化合物,最后用环己烷萃取,得到弱极性的芳烃类化合物。
1.3.2 仪器分析 使用正相 HPLC法,分离、富集目标组分前,先采用环己烷-N,N-二甲基甲酰胺-H2O系统萃取PAH类化合物,根据质谱特征离子及保留时间进行定性,外标法定量。
1.3.2.1 HPLC条件 分离柱:Kromasil 60-5SIL(250 mm×4.6 mm×5μm,60 A);流动相:正己烷/二氯甲烷;梯度淋洗程序:100%正己烷保持10 min,5 min内等梯度变换为95%正己烷:5%二氯甲烷,35 min内等梯度变换为100%二氯甲烷,保持10 min。收集40~50 min之间的组分,其中包含3-NBA组分。
1.3.2.2 气相色谱条件 色谱柱:Rtx-5MS石英毛细柱(30 m×0.25 mm×0.25μm);升温程序:70℃保持1 min,以8℃·min-1升至200℃,保持1 min,以5℃·min-1升至260℃,保持4 min,以1℃·min-1升至280℃,保持1 min,以20℃·min-1升至300℃,保持2 min;载气(He):流速1.5 mL·min-1;进样量1μL,不分流进样。
1.3.2.3 质谱条件 电离方式为电子轰击(EI),电子能量70 eV,接口温度275℃,离子源温度230℃,选择离子模式,质量扫描范围 m/z 50~550。
1.4 样品分析全流程的质量控制与质量保证(QA/QC)措施
对每个分析样品(包括样品、方法空白、基质加标、加标空白)都要添加回收率指示物标样,以控制整个分析流程的回收率。
1.5 仪器分析的QA/QC措施
连续分析6个浓度约为5倍噪音的标样,得标准偏差,仪器检测限(IDL)=3.36 S。在空白滤膜上加标,加标浓度为5倍IDL,重复分析6个基质加标样,取得其标准偏差(S),方法检测限(MDL)=3.36 S。方法检测限以实际样品采样体积计算。
取5种浓度为0.5~8 mg·L-1的标样,用外标法建立工作曲线,检测器的响应值与每个浓度的相关系数均大于0.97。使用已建立的工作曲线测定新配制的已知浓度的标准溶液,测定值与标准值之差在20%以内。
2 结果与讨论
化合物的GC/MS谱图示于图1,其中相关的有化合物1和5。

图1 标准溶液中目标化合物和内标的GC/MS图a.色谱图;b.1-硝基芘-d9的EI质谱图;c.3-NBA的EI质谱图Fig.1 G as chromatograms and mass spectra for the target compound and surrogate a.chromatograms;b.electron ionization spectra for 1-nitropyrene-d9;c.spectrum for 3-NBA
2.1 仪器检测限和方法检测限
根据分析结果计算,3-硝基苯并蒽酮的仪器检测限值为13.7 pg,按实际采样体积700 m3计算,方法检测限为1.9 pg·m-3,分别列于表1和表2。
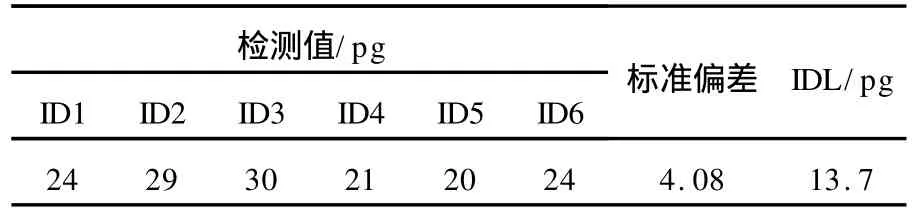
表1 仪器检测限(IDL)Table 1 Instrument detect limit(IDL)

表2 方法检测限(MDL)Table 2 Method detect limit(MDL)
2.2 方法空白
方法空白的数据用来评估和控制整个试验流程可能发生的人为污染,以及操作过程的准确性,在方法空白中未检出目标化合物,可见整个试验流程对目标化合物没有人为的实验室背景因素影响。
2.3 基质加标
基质加标在控制试验流程的基础上还需要考虑基质对试验数据的影响,基质加标回收率列于表3。计算结果表明,3-硝基苯并蒽酮的基质加标平均回收率为78.2%,指示物的平均回收率为76.3%。
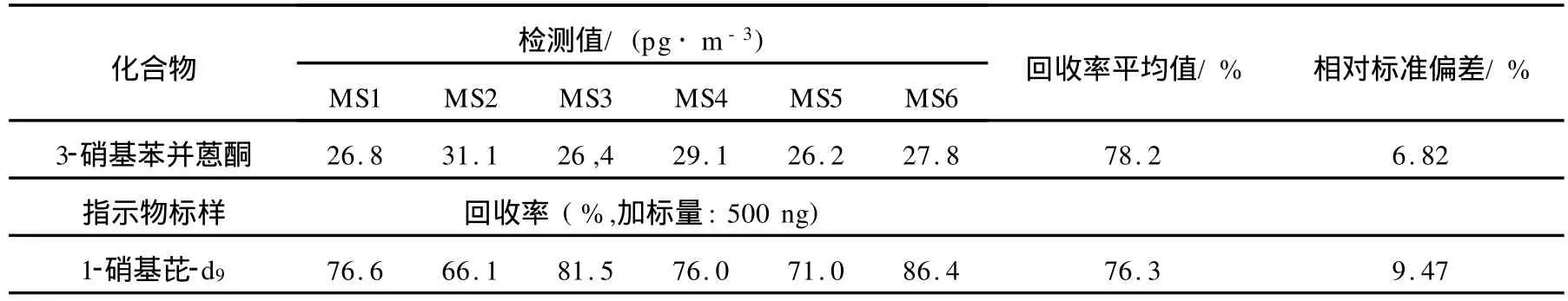
表3 基质加标回收率Table 3 Recovery of matrix spike
2.4 平行样品
对同一真实样品进行重复测试,3次测试得到的指示物回收率平均值为88.5%,相对标准偏差均小于15%,列于表4。
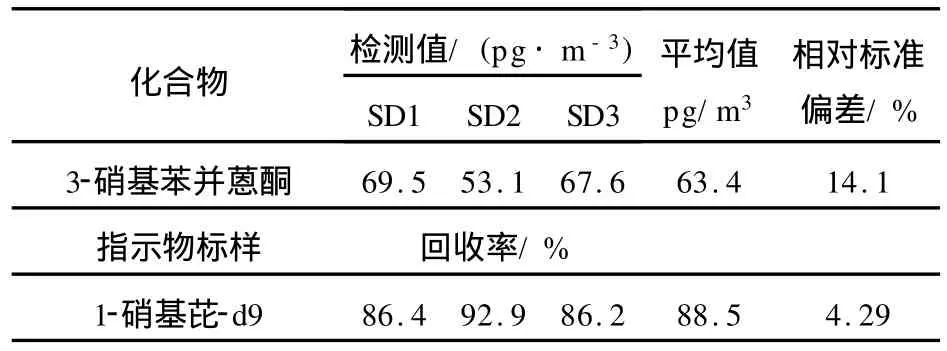
表4 平行样品测试结果Table 4 Results of sample duplicate
3 结 论
本工作建立了大气中3-硝基苯并蒽酮的检测方法,利用 HPLC对含3-硝基苯并蒽酮组分进行分离、富集,再用 GC/MS法对其进行定量分析。该法具有较好的选择性、重现性和灵敏度,可用于大气中3-硝基苯并蒽酮的常规检测。
[1]PAPUTA-PECK M,MARANO R,SCHUETZLE D,et al.Determination of nitrated polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons in particulate extracts by capillary column gas chromatography with nitrogen selectivedetection[J]. AnalyticalChemistry, 1983,55:1 946-1 954.
[2]AREYJ,ZIELINSKA B,ATKINSON R,et al. The formation of nitro-PAH from the gas-phase reactions of fluoranthene and pyrene with the OH radical in the presence of NOx[J].Atmospheric Environment,1986,20(12):2 39-2 345.
[3]AREYJ,ZIELINSKA B,ATKINSON R,et al. Nitroarene products from the gas-phase reactions of volatile polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with the OH radical and N2O5[J].International Journal of Chemical Kinetics,1989,21(9):775-799.
[4]ATKINSON R,AREYJ,ZIELINSKA B,et al. Kinetics and nitro-products of the gas-phase OH and NO3radical-initiated reactions for naphthalene-d8,fuoranthene-d10,and pyrene[J].International Journal of Chemical Kinetics,1990,22 (9):999-1 014.
[5]ATKINSON R,AREYJ.Atmospheric chemistry ofgas-phase polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: formation of atmospheric mutagens[J].Environmental Health Perspectives,1994,102(Suppl4): 117-126.
[6]AREYJ.The handbook of environmental chemistry[M].Berlin:Springer,1998:347-385.
[7]ZIELINSKA B,AREYJ,A TKINSON R.et al. Reaction of dinitrogen pentoxide with fluoranthene [J].Journal of American Chemical Society,1986, 108:4 126-4 132.
[8]ZIELINSKA B,AREYJ,A TKINSON R.et al. Formation ofmethylnitronaphthalenes from the gas-phase reactions of 1-and 2-methylnaphthalene with OH radicals and N2O5and their occurrence in ambient air[J].Environmental Science and Technology,1989,23(6):723-729.
[9]ZIELINSKA B,AREY J,ATKINSON R.Nitroarenes-occurrence,metabolism,and biologicalimpact[M].New York:Plenum,1990:73.
[10]DURANT J L,BUSBY W F,LAflEUR A L,et al.Human cell mutagenicity of oxygenated,nitrated and unsubstituted polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons associated with urban aerosols[J]. Mutation Research-Genetic Toxicology,1996, 371(3/4):123-157.
[11]ENYA T,SUZU KI H,WATANABE T,et al. 3-Nitrobenzanthrone,a powerful bacterial mutagen and suspected human carcinogen found in diesel exhaust and airborne particulates[J].Environmental Science and Technology,1997,31 (10):2 772-2 776.
[12]SEIDEL A,DAHMANN D,KREKEL ER H,et al.Biomonitoring of polycyclic aromatic compounds in the urine of mining workers occupationally exposed to diesel exhaust[J].International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health,2002,204(5/6),333-338.
[13]POIRIER M C,SANTELLA R M,WESTON A,et al.Carcinogen macromolecular adducts and theirmeasurement[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2000,21(3),353-359.
[14]ARL T V M,ZHAN L,SCHMEISER H H,et al.DNA adducts and mutagenic specificity of the ubiquitous environmental pollutant 3-nitrobenzanthrone in Muta Mouse[J].Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis,2004,43(3):186-195.
[15]李怀建,李 强,汪 午,等.环境中3-硝基苯并蒽酮的研究[J].化学进展,2010,22(1): 220-224.
[16]郭 丽,惠亚梅,郑明辉,等.气相色谱-质谱联用测定土壤及底泥样品中的多环芳烃和硝基多环芳烃[J].环境化学,2007,26(2),192-196.
[17]林 刚,孙贵范,田村宪治,等.抚顺大气悬浮颗粒物、PAHs和NPAH污染调查[J].中国公共卫生,2005,21(5):604-606.
Development of Analytical Method for 3-Nitrobenzanthrone, A Potential Carcinogen in Atmosphere by GC/MS
LI Huai-jian1,WU Mei2,ZHAN G Hong-wei3,WANGBang-jin1, ZHAN Jie1,WANG Yang-jun1,WANG Wu1,3
(1.Institute ofEnvironmental Pollution and Health,Shanghai University,S hanghai200444,China; 2.Qingdao University Medical College,Qingdao266071,China; 3.Southern Medical University,Guangzhou510515,China)
3-Nitrobenzanthrone,a persistent organic pollutants(POPs),is an extremely potential mutagen and susceptible carcinogen as proved by the tests using both animal and human cells.The major sources of 3-nitrobenzanthrone are believed to be vehicle exhaust from diesel engines,as well as photooxidation reaction in the atmosphere.Its atmospheric concentration is far below polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.This paper reported an analytical method that was established by using high pressure liquid chromatography(HPLC)to separate and enrich the target fraction and consequently measured with gas chromatographymass spectrometry(GC/MS).The instrument detection limit(IDL)is 13.7 pg,and themethod detection limit(MDL)is 1.86 pg·m-3.The method recoveries for the deuterated surrogate,1-nitropyrene-d9,and 3-nitrobenzanthrone are 88.5%and 78.2%,respectively. The method features good accuracy,precision and reproducibility,and could be used for regular measurements of 3-nitrobenzanthrone.
persistent organic pollutants(POPs);3-nitrobenzanthrone;gas chromatography-mass spectrometry(GC/MS)
O 657.63
A
1004-2997(2010)03-0187-05
2009-12-30;
2010-03-18
国家自然科学基金(20677036,20877051),上海市教育委员会科研创新项目(10YZ08),上海市重点学科(S30109)资助
李怀建(1985~),男(汉族),贵州人,硕士研究生,环境科学专业。E-mail:lihuaijian@shu.edu.cn
汪 午(1968~),女(汉族),安徽人,博士,从事大气化学研究。E-mail:wangwu@shu.edu.cn

