Research on the Elements of Firm’s IS Absorptive Capacity
CAO Yong NING Dong-ling
Biography: Ning Dong-ling(1975-), Female, Masters Degree in management science and engineering, Lecturer in Yunnan University of Finance and Economics, currently responsible for research in the following fields: knowledge management, organization learning.
Abstract: In this paper, we explore the capacity during the process of a firms information system adoption and implementation from knowledge management perspective, based on a firms level construct. According to the dimensions of absorptive capacity proposed by Zahra and George, we point out that the concept of IS absorptive capacity, analyze and summarize the elements of potential absorptive capacity and realized absorptive capacity. We use data from two manufacturing organizations, analyze two firms realities of IS absorptive capacity. The study indicates differing antecedents may have differing effects on potential absorptive capacity and realized absorptive capacity.
Key words: Absorptive Capacity;Information Adoption;Information Technology
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-0194.2009.15.025
CLC number: F270.7;C931.6Article character:AArticle ID:1673-0194(2009)15-0081-04
1 Introduction
On the study of technology adoption, researcher have used TRA, TAM, TPB to explain IS adoption.But these models are individual level construct and they are useful in predicting an individual propensity to successfully adopt a technology, they fall short of predicting a firms propensity to successfully adopt a technology.The effectiveness of a firm to implement IS will depend on their ability to quickly acquire, renew and exploit IS knowledge and skill.That capacity is absorptive capacity (AC).The construct of absorptive capacity, introduced by Cohen and Levinthal, has received increased attention in the IS literature for the past decade. IS absorptive capacity is a set of processes by which firms adopt and implement IS to produce a dynamic capability. It has two dimensions, which are potential absorptive capacity (PAC) and realized absorptive capacity (RAC). Both subsets of AC coexist at all times and fulfil a necessary but insufficient condition to improve firm performance.
2 Elements of Absorptive Capacity
Elements affecting PAC include prior knowledge, learning intensity, external linkage, organization structure,management support,diversity in background of employees, knowledge comparability.Elements of RAC include knowledge communication, information integration,empowerment of employee,strategic programming,training competence,level of exploitation.
2.1 Elements of PAC
(1) Prior knowledge
A firms prior knowledge is the basic of absorbing new knowledge,and includes basic skills,experience,a shared language,but also includes knowledge of the most recent scientific or technological developments in a given field.Prior knowledge reflects the level of IS knowledge held by a firm,so it effects the attitude of absorbing new knowledge and the decision made to future knowledge.A Learner who already has a basic understanding of the new technology has greater potential to learn the new technology.
(2) Learning intensity
Learning intensity is the efforts on absorbing knowledge spent by a firm,includes compensation policies and technology learning.The more intensity is the new knowledge invested,the more efficiency is learning.The firm need acquire the new knowledge actively and inspire a desire for learning.
(3) External linkage
External linkage is the link with external knowledge source.External knowledge source has many sources, including R&D organizations,universities,consultation organization scompetitors, strategic alliances.Social capital is used to describe a resource derived from social interaction,relationship quality and network ties.The more close the linkages is,the more the opportunity to learn,the more intensity acquire capacity is.
(4) Organization structure
Organization structure affects dissemination,which involves transferring the acquired knowledge to all units of organization in product innovation.A functional organizational structure permits a high efficiency of absorption,but a limited scope and flexibility of absorption.Functional structure increases the effect of specialization,which creates communication barriers between the different departments.Matrix Structure facilitates the flexibility of knowledge absorption,which is detrimental to efficiency.
(5) Management support
Managers participate in the process of making decision,and facilitate the cooperation of different departments and persons.IS adoption must result in the change of technology and organizational structure,which need managers support from resources,administrative and emotional support.Managers have the dominated capability to initiate a reform through authority,so involvement will facilitate different units communication and reorganization.
(6) Diversity in background of employees
Diversity in background of employees can be defined by gender, age,education and area of expertise.Diversity in background can strengthen assimilative powers and facilitate the innovative process by enabling the individual to make novel associations and linkages.In addition,Diversity in background can provides a variety of perspectives from which to process the acquired knowledge,leading to new associations,linkages and innovation.
7) Knowledge comparability
Research on cognitive structures indicates that an individuals learning is greatest when the new knowledge is related to the individuals knowledge base.As a result,learning is more difficult in novel domains.Similar knowledge can drive different departments and members to make linkages and associations, encourage frequent dialogue and create a common cognitive ground facilitating the transfer of tacit knowledge.
2.2 Elements of RAC
(1) Knowledge communication
Knowledge communication refers to transfer knowledge within a firm.Knowledge communication makes members of the firm aware of the existence of this knowledge,which process can promote mutual understanding and comprehension according to direction,policies,procedures and manuals.Information systems facilitate the need of communication and coordination among subunits.Structural, cognitive,behavioural,and political barriers may stifle the effective sharing of knowledge.
(2) Information integration
In essence,information integration is data integration, including data quality and data flexibility.Data quality means that acquired data from IS will be identical with reality data.Flexibility data is the extent to which a firm can access additional, explicit and tacit knowledge within an organization. Just as a firm is an organization of people who have a common goal,an information system is an organization of data used to provide timely and accurate information for the decision being made by people with a common goal.
(3) Empowerment of employee
When employees are empowered,a knowledge-sharing culture is encouraged.When power is applied through authority,employees may ignore their critical sense and blindly accept instructions from their superiors.This makes them unable to adopt complex learning,that is,the creation of new ideas and new “mental models”.
(4) Strategic programming
Porter indicated that the fundamental choices in business strategy available to firms in established market economies can be categorized as cost leadership or differentiation.Lane indicated that IJVs can potentially access both knowledge of the domestic market and foreign expertise about marketing,service,and product development.This knowledge can be used to avoid direct competition with large and state-owned enterprises,develop distinct competitive advantages.
(5) Training competence
Lane found that training by the foreign parent not only can provide a vehicle for transferring explicit or codified knowledge,but also can be a vehicle for learning and knowledge transfer of tacit knowledge via socialization by the foreign parent management.Boyacigiller and Adler suggest that differences in global environments mean that knowledge transferred by foreign firms may not directly fit the local context.Managerial training can help managers overcome behavioural patterns.
(6)Level of exploitation
Venkatraman identified five levels of IT enabled transformation, including localized exploitation,inner integration,business process redesign,business network redesign,business scope redefinition.The first and second level of enabled transformation is low level of exploitation,the third,fourth and fifth level of enabled transformation is high level of exploitation,which touch the change of firms business process.Venkatraman argues that performance will improve as a firm is categorized into higher levels of transformation.
3 Method
3.1 Data and measure
The empirical data is this study was drawn from two manufacturing firms using a questionnaire. In 2007,we send 110 questionnaires to respondents,who had implement and use IS.To ensure confidentiality,we agreed not to reveal the managers names and asked them to return the questionnaire directly to me.A total of 82 responses were received,yielding a satisfactory effective response rate of 74.5 percent.
We used multiple items to measure the construct.The items were assessed on a five-point Likert scale from “very disagree” to “very agree”.The construct of PAC was measured with 27 items and the construct of RAC was measured with 21 items.The pilot study used an adapted version of Lanes measure.For each element,the items responses were averaged to create composite measure.
For easily,we used “Pk, Li, El, Os, Ms, Db, Kc” and “Kn, Di, Ee, Sp,Tc, Le”to substitute for the elements of PAC and RAC.
3.2 Discussion
Figure 1 shows the mean scores of two organizations IS PAC and RAC.The mean score of PAC (3.05) is larger than the mean of RAC (2.98) for organization 1.The mean score of PAC (2.94) is less than the mean of RAC (3.15) for organization 2.To further understand the difference between PAC and RAC,we analyze each element of PAC and RAC in the following study.

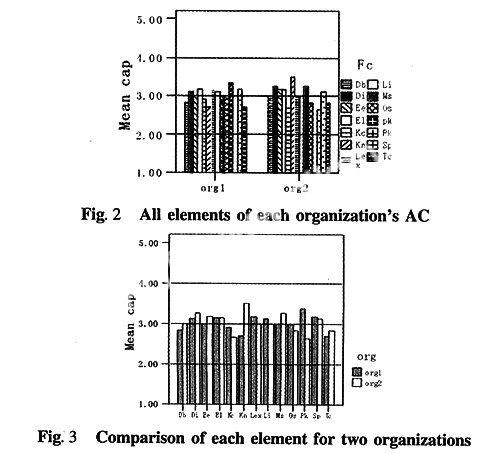
Figure 2 shows all elements of each organizations AC.For organization1s PAC,the mean score of prior knowledge for organization1 is the greatest score,3.36 and the mean score of diversity in background of employees is the least score,2.83,which is little low compared to the average score (3).For organization1s RAC,the mean score of strategic programming and level of exploitation is the greatest score,3.17 and the mean score of knowledge communication is the least score,2.7.According these analyse,we found that the mean score of organization1s AC shows a relatively wide range as well,from a low of 2.7 to a high of 3.36,with a mean score of 3.02.For organization2s PAC,the mean score of management support is the greatest score,3.25 and the mean score of prior knowledge is the least score,2.64.For organization2s RAC,the mean score of knowledge communication is the greatest score,3.5 and the mean score of strategic programming is the least score,2.83.The mean score of organization2s AC shows a relatively wide range as well,from a low of 2.64 to a high of 3.5,with a mean score of 3.03.The mean score of AC of two organizations is about the same.Prior knowledge is the key element of PAC,which secures the newness and diversity of knowledge,whereas communication and strategic programming is the key elements of RAC,which can transform and exploit the acquired knowledge.Also,the results are very interesting.Both of organization1 and organization2,the mean score of diversity in background of employees and training competence is less than the average score. In this result,our firms focus on improving training competence, which is difference with foreign firms.
Figure 3 shows the comparison of each element for two organizations.Organization 1 has a long history and flexible structure,accumulates very much knowledge related to IS,and focuses on the linkage with other firms,which factors make organization 1 have higher potential absorptive capacity.But organization 1 can not share and exploit new knowledge through training.Organization 1 will lay emphasis on improving the level of realized absorptive capacity.Organization 2 has about 800 employees,and has not enough IS experiences.But organization 2 can communicates new knowledge within units,so has high realized absorptive capacity.Organization 2 should improve potential absorptive capacity by accumulating experience and enhancing the level of knowledge of employees.
4 Conclusion
The study of absorptive capacity is contribute to the literature that explains the success of IS projects.A high PAC reflects the potential to increase performance,but does not necessarily guarantee the successful exploitation of the new knowledge.Therefore,PAC is an antecedent to RAC that mediates the relationship between PAC and performance.The research related to IS absorptive capacity needs to identify the elements of PAC and RAC,and clarify measures of PAC and RAC to reflect the richness of the construct,which helps firms to understand the realities of IS absorption and improve IS absorptive capacity through focusing on the elements of absorptive capacity.
References
[1] W Cohen, D Levinthal. Absorptive Capacity: A New Perspective on Learning and Innovation [J] . Administrative Science Quarterly, 1990,35(1):128-152.
[2] P J Lane J E Salk, and M A Lyles. Absorptive Capacity, Learning and Performance in International Joint Ventures[J]. Strategic Management Journal,2001, 22( 12):1239-1161.
[3] Nonaka. A Dynamic Theory of Organizational Knowledge Creation[J]. Organization Science , 1990,5(1): 14-37.
[4] G Stasser, W Titus.Effects of Information Load and Percentage of Shared Information on the Dissemination of Unshared Information During Group Discussion[J]. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 1987, 53(1): 81-93.
[5] F A J Van Den Bosch, H W Volberda, M De Boer.Coevolution of Firm Absorptive Capacity and Knowledge Environment: Organizational Forms and Combinative Capabilities, Organizational Science, 1999,10(5): 551-568.
[6] N Venkatraman, V Ramanujam Measuring of Business Strategy Research: A Comparison Approach[J]. Academy of Management, 1986, 11(4): 801-814.
[7] S A Zahra, G George Absorptive Capability: A Review, Reconceptulization and Extension[J]. Academy of Management Review,2002 ,27( 2):185-203.

